Android 10(Android Q) 适配心得
参考网站
1. 设备硬件信息读取限制
在Android10中, 系统不允许普通App请求android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE权限, 故新版App需要取消该动态权限的申请。
当前获取设备唯一ID的方式为使用SSAID, 若获取为空的话则使用UUID.randomUUID().toString()获得一个随机ID并存储起来, 该ID保证唯一, 但App卸载重装之后就会改变
SSAID的获取方式为:
String id = android.provider.Settings.Secure.getString(context.getContentResolver(), android.provider.Settings.Secure.ANDROID_ID);
复制代码
2. 后台App启动限制
Android10中, 当App无前台显示的Activity时,其启动Activity会被系统拦截, 导致启动无效。
个人觉得官方这样做的目的是在用户使用的过程中, 不希望被其他App强制打断, 但这样就对闹钟类, 带呼叫功能的App不太友好了。
对此官方给予的折中方案是使用全屏Intent(full-screen intent), 既创建通知栏通知时, 加入full-screen intent 设置, 示例代码如下(基于官方文档修改):
Intent fullScreenIntent = new Intent(this, CallActivity.class);
PendingIntent fullScreenPendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0,
fullScreenIntent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
NotificationCompat.Builder notificationBuilder =
new NotificationCompat.Builder(this, CHANNEL_ID)
.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.notification_icon)
.setContentTitle("Incoming call")
.setContentText("(919) 555-1234")
//以下为关键的3行
.setPriority(NotificationCompat.PRIORITY_HIGH)
.setCategory(NotificationCompat.CATEGORY_CALL)
.setFullScreenIntent(fullScreenPendingIntent, true);
NotificationManager notifyManager = (NotificationManager) context.getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
notifyManager.notify(notifyId, builder.build());
复制代码
注意在Target SDk为29及以上时,需要在AndroidManifest上增加USE_FULL_SCREEN_INTENT申明
//AndroidManifest中
复制代码
测试下来, 当手机处于亮屏状态时, 会显示一个通知栏, 当手机处于锁屏或者灭屏状态时,会亮屏并直接进入到CallActivity中
3. App沙盒化存储
在Android10上, 当App的target sdk为29及以上时或者在AndroidManifest中申明时, App即使有外部存储的写入权限, 也无法直接通过路径访问外部存储
疑惑
网上有些其他的文章有一些说法
新的存储权限取消并替换了READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE 和 WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE权限,如果要访问沙盒外的媒体共享文件,比如照片,音乐,视频等,需要申请新的媒体权限:READ_MEDIA_IMAGES,READ_MEDIA_VIDEO,READ_MEDIA_AUDIO,申请方法同原来的存储权限
我在实际测试中并没有找到这3个权限类型, 对此查看了官方文档
官方文档的原文为:
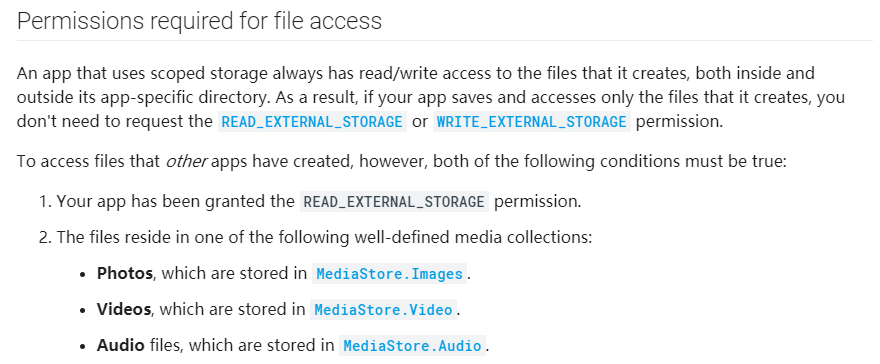
大致意思是当你访问沙盒内部时,是不需要READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE 或 WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE权限的, 若要访问外部存储, 需要拥有READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE 权限并且使用MediaStore来进行访问
所以我觉得在Android 10上, 若要访问外部文件, 还是需要进行READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE 和 WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE 动态权限的申请的
适配方案
对应App的数据, 需要存储到App的沙盒中, 对应的路径为下
文件类型
地址
视频文件
context.getExternalFilesDir(Environment.DIRECTORY_MOVIES)
音频文件
context.getExternalFilesDir(Environment.DIRECTORY_MUSIC)
图片文件
context.getExternalFilesDir(Environment.DIRECTORY_PICTURES)
存储到沙盒中的这些地址的实际路径在/data/user/0/包名/中,所以这些文件在App卸载之后会被清除
在这些目录里的文件受系统保护, 其他App无法直接对其访问
若需要将沙盒中的视频或图片文件保存在外部存储时, 需要使用ContentValues和MediaStore来进行操作,对此我封装了一个工具类:
public static boolean SavePictureFile(Context context, File file) {
if (file == null) {
return false;
}
Uri uri = insertFileIntoMediaStore(context, file, true);
return SaveFile(context, file, uri);
}
public static boolean SaveVideoFile(Context context, File file) {
if (file == null) {
return false;
}
Uri uri = insertFileIntoMediaStore(context, file, false);
return SaveFile(context, file, uri);
}
private static boolean SaveFile(Context context, File file, Uri uri) {
if (uri == null) {
LogUtil.e("url is null");
return false;
}
LogUtil.i("SaveFile: " + file.getName());
ContentResolver contentResolver = context.getContentResolver();
ParcelFileDescriptor parcelFileDescriptor = null;
try {
parcelFileDescriptor = contentResolver.openFileDescriptor(uri, "w");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (parcelFileDescriptor == null) {
LogUtil.e("parcelFileDescriptor is null");
return false;
}
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(parcelFileDescriptor.getFileDescriptor());
FileInputStream inputStream;
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
LogUtil.e(e.toString());
try {
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
LogUtil.e(ex.toString());
}
return false;
}
try {
copy(inputStream, outputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
LogUtil.e(e.toString());
return false;
} finally {
try {
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
LogUtil.e(e.toString());
}
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
LogUtil.e(e.toString());
}
}
return true;
}
//注意当文件比较大时该方法耗时会比较大
private static void copy(InputStream ist, OutputStream ost) throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
int byteCount;
while ((byteCount = ist.read(buffer)) != -1) {
ost.write(buffer, 0, byteCount);
}
ost.flush();
}
//创建视频或图片的URI
private static Uri insertFileIntoMediaStore(Context context, File file, boolean isPicture) {
ContentValues contentValues = new ContentValues();
contentValues.put(MediaStore.Video.Media.DISPLAY_NAME, file.getName());
contentValues.put(MediaStore.Video.Media.MIME_TYPE, isPicture ? "image/jpeg" : "video/mp4");
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 29) {
contentValues.put(MediaStore.Video.Media.DATE_TAKEN, file.lastModified());
}
Uri uri = null;
try {
uri = context.getContentResolver().insert(
(isPicture ? MediaStore.Images.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI : MediaStore.Video.Media.EXTERNAL_CONTENT_URI)
, contentValues
);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return uri;
}
复制代码Android 10 之前, 往系统文件夹写入文件需要文件读写权限, Android10中, 可以无需权限直接往系统文件夹写入文件
默认保存的地址, 视频默认在Movies中, 图片默认在Pictures中, 若想保持到对应的子文件夹中, 则需要以下设置
//注意MediaStore.Images.Media.RELATIVE_PATH需要compileSdkVersion=29,
//故该方法只可在Android10的手机上执行
//图片, 对应存储的地址为 Pictures/test
contentValues.put(MediaStore.Images.Media.RELATIVE_PATH,
Environment.DIRECTORY_PICTURES + File.separator + test);
//视频, 对应存储的地址为 Movies/test
contentValues.put(MediaStore.Video.Media.RELATIVE_PATH,
Environment.DIRECTORY_MOVIES + File.separator + test);
复制代码
结语
以上是我在适配中的总结,希望对大家的适配有所帮助,若有错误,敬请斧正。





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








