在介绍Result之前,先熟悉几个类
Field 用来存储SQL字段信息,主要是关于表字段列属性的判断和获取
classField
{public:
...............................private:
std::string name_; //the field's name
std::string table_; //name of table field comes from
std::string db_; //name of database field comes from
mysql_type_info type_; //info about the field's type
size_t length_; //creation size of column(指数据类型的长度varchar(30) length_=30)
size_t max_length_; //size of largest item in column in result set
unsigned int flags_; //DB engine-specific set of bit flags(就是数据表中列的属性:自增,主键,时间戳,枚举,二进制类型,BLOB类型,默认值等)
}
typedef std::vector Fields;
Row 一个对象表示一行数据
class MYSQLPP_EXPORT Row : publicOptionalExceptions
{
.......................................// 创建一个Row对象
Row::Row(MYSQL_ROW row, const ResultBase*res,const unsigned long* lengths, boolthrow_exceptions) :
OptionalExceptions(throw_exceptions),
initialized_(false)
{if(row) {if(res) {
size_type size= res->num_fields(); //表字段的数量
data_.reserve(size);for (size_type i = 0; i < size; ++i) {bool is_null = row[i] == 0;
//将数据存储到data_中
data_.push_back(value_type(is_null? "NULL": row[i], is_null? 4: lengths[i], res->field_type(int(i)), is_null));
}
field_names_= res->field_names(); //所有字段名称
initialized_ = true;
}else if(throw_exceptions) {throw ObjectNotInitialized("RES is NULL");
}
}else if(throw_exceptions) {throw ObjectNotInitialized("ROW is NULL");
}
}...............................................private:
list_type data_;//用来存储一行的数据,一行5列则data_.size()=5
RefCountedPointer field_names_; //用来存储表列名称,表有3列则field_names_.size()=3
boolinitialized_;
};
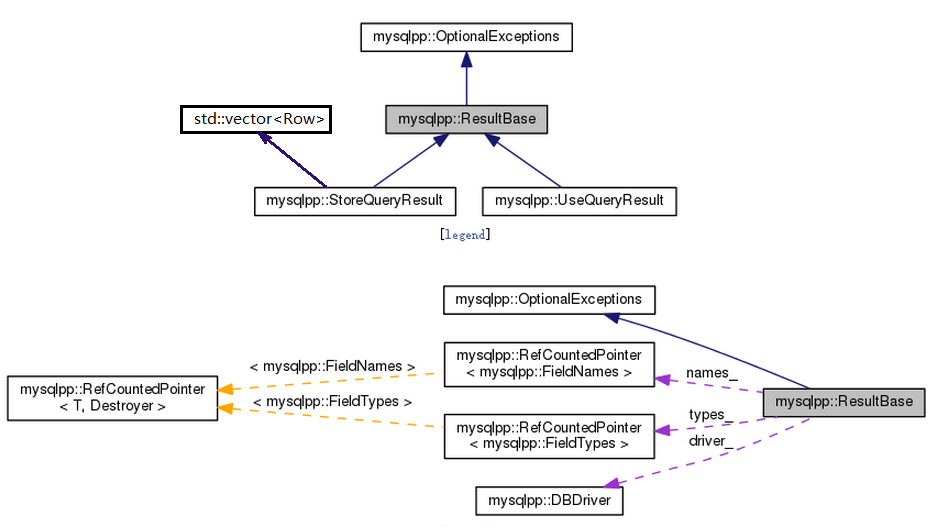
ResultBase
这个类型是StoreQueryResult和UseQueryResult的父类型,该类型其实没有特别的含义,只是作为一个common methods的container而已。但是该类型提供的几乎所有的public methods都是和fields有关的,包括了
根据index查找field;
根据name查找field;
根据index查找到field的名字和属性类型;
获取当前所在的field(ResultBase内部会有一个mutable的index名为current_field_用于指明当前fetch_field的是哪一个field,在fetch_field中该index会自增)
该类型的核心成员有如下几个
Fields(std::vector) 类型的 fields_
FieldNames (继承自std::vector<: string>)类型的 names_
FieldTypes ( 继承自std::vector)类型的types_
其中FieldNames和FieldTypes都是被RefCountedPointer包裹着,估计这样做能够节省空间。关于Field类型在后续进行介绍。至于刚才说的几个找field的操作,看着这几个核心成员的类型还是比较好理解的。不就是在vector中不找。
需要额外关注的是以下这个最主要的构造函数
ResultBase::ResultBase(MYSQL_RES* res, DBDriver* dbd, boolte) :
OptionalExceptions(te),
driver_(res? dbd : 0),
fields_(Fields::size_type(res? dbd->num_fields(res) : 0)),
current_field_(0)
{if(res) {
Fields::size_type i= 0;const MYSQL_FIELD*pf;
//直接通过DBDriver的fetch_field方法进行获取到一个MYSQL_FIELD*,然后直接就仍给了fields_(fields_是一个Fields类型,他是一个typedef std::vector)while ((i < fields_.size()) && (pf = dbd->fetch_field(res))) {
fields_[i++] =pf;
}
dbd->field_seek(res, 0); //semantics break otherwise!
names_= new FieldNames(this);
types_= new FieldTypes(this);
}
}
以下几点需要注意,
names_和types_在new出来之后是不需要显式delete的,因为他们都在智能指针RefCountedPointer包裹着。
成员初始化列表中的 fields_(Fields:: size_type(…)) 这一句其实调用的是
explicit std::vector::vector (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type(), const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
从以上构造函数可以看到,其实关于Field的信息还是从DBDriver中拿到的,然后关于FieldNames和FieldTypes的信息,则是通过这两个类型自身的构造函数给实现的(其实就是收到ResultBase*,然后遍历其中的成员变量 fields_ 再各求所需罢了。
为什么要有重新将指示field_当前index的指针重置的过程(dbd->field_seek(res, 0))?这是因为方便这个DBDriver再次循环访问这些fields。
查看Query源码发现,Query执行操作返回值不外乎就是:bool, SimpleResult, UseQueryResult, StoreQueryResult
1.bool
标识操作执行成功失败,如update, delete,insert,不关心有多少rows被touch的情况
2.SimpleResult
这个类型非常简单,没有父类,主要的成员变量有3个,分别是:
ulonglong insert_id_; //Get the last value used for an AUTO_INCREMENT field
ulonglong rows_; //query操作影响的行数
std::string info_; //获取从server返回的query操作附加信息
3.UseQueryResult
UseQueryResule适用于For these large result sets,a “use” query tells the database server to send the results back one row at a time, to be processed linearly。use的语义类似于使用游标,也就是支持一行一行地拉出内容,所以UseQueryResult 也就自然而然地支持一些关于fetch row的功能。
该类型的方法比StoreQueryResult丰富多了,主要体现在:
可以顺序读取行(mysqlpp::Row fetch_row() const;或者MYSQL_ROW fetch_raw_row() const;)
可以获取当前行的各个field的信息(const Field& fetch_field() const; const Field& fetch_field(Fields::size_type i) const)
可以获取当前行的所有fields的长度(const unsigned long* fetch_lengths() const;)
Row UseQueryResult::fetch_row()const{if (!result_) {if(throw_exceptions()) {throw UseQueryError("Results not fetched");
}else{returnRow();
}
}
MYSQL_ROW row= driver_->fetch_row(result_.raw());if(row) {const unsigned long* lengths =fetch_lengths();if(lengths) {return Row(row, this, lengths, throw_exceptions()); //根据返回的数据构建一个Row对象返回
}else{if(throw_exceptions()) {throw UseQueryError("Failed to get field lengths");
}else{returnRow();
}
}
}else{
returnRow();
}
}
4.StoreQueryResult
StoreQueryResult继承与std::vector,所以它也就是vector,拥有vector的所有操作。用来装载SQL操作返回的结果,所以程序可以直接使用下标的形式来对ROW操作。
StoreQueryResult::StoreQueryResult(MYSQL_RES* res, DBDriver*dbd,boolte) :
ResultBase(res, dbd, te),list_type(list_type::size_type(res&& dbd ? dbd->num_rows(res) : 0)),
copacetic_(res&&dbd)
{if(copacetic_) {
iterator it=begin();while (MYSQL_ROW row = dbd->fetch_row(res)) { //从res中提取一行数据if (const unsigned long* lengths = dbd->fetch_lengths(res)) {*it = Row(row, this, lengths, throw_exceptions()); //StoreQueryResult继承std::vector,在这里将取出的每一行数据存储到自身对象中++it;
}
}
dbd->free_result(res); //数据拷贝完后释放res内存
}
}
Row中如下:
Row::Row(MYSQL_ROW row,const ResultBase*res,const unsigned long* lengths, boolthrow_exceptions) :
OptionalExceptions(throw_exceptions),
initialized_(false)
{if(row) {if(res) {
size_type size= res->num_fields(); //提取当前行的所有列的数量
data_.reserve(size);for (size_type i = 0; i < size; ++i) {data_.push_back(value_type(is_null? "NULL" : row[i], is_null ? 4 : lengths[i], res->field_type(int(i)), is_null)); //
}
field_names = res->field_names(); //将表的列名称赋值给field_names;
initialized = true;
............................
}
通过以上分析:通过DBDriver拿到数据,调用StoreQueryResult构建数据集,首先执行的是父类ResultBase的构造函数(从C结构中获取列字段属性及类型),在通过DBDriver一行一行的获取数据初始化Row(将数据存放到vector data_中),StoreQueryResult继承自Row,自此StoreQueryResult对象对象中包含了数据集合和列名称及属性
//Establish the connection to the database server.
mysqlpp::Connection con(db_name.c_str(), db_ip.c_str(), db_user.c_str(), db_passwd.c_str(), db_port);
mysqlpp::Query query= con.query("select * from student");
mysqlpp::StoreQueryResult res=query.store();if(res)
{//Display header
cout.setf(ios::left);for (size_t i = 0; i < res.fields().size(); i++)
{
cout<< setw(10) <
}
cout<
for (size_t i = 0; i < res.num_rows(); ++i) {
cout<< setw(10) << res[i]["id"] << ' ' <
}
}else{
cerr<< "Failed to get stock table:" << query.error() <
}
通过DBDriver拿到数据,调用UseQueryResult构建数据,首先执行的是父类ResultBase的构造函数(从C结构中获取列字段属性及类型),等到调用fetch_row时在构造一行数据(调用Row的构造函数)
mysqlpp::Connection con(db_name.c_str(), db_ip.c_str(), db_user.c_str(), db_passwd.c_str(), db_port);
mysqlpp::Query query= con.query("select * from student");
mysqlpp::UseQueryResult res=query.use();
cout.setf(ios::left);for (size_t i = 0; i < res.fields().size(); i++)
{
cout<< setw(10) <
}
cout<
{
cout<< setw(10) << row["id"] << ' ' <
}





















 922
922











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








