入数据行业近3年了,这3年的工作时间我绝大多数时间都在写python做分析。但作为合格的一个数据分析师,sql的精通肯定是必不可少的,所以最近疯狂刷sql题,同时也来总结下我以前比较少用的语法。
(工作写的是hive,为方便演示,本文章均使用Mysql8.0.16版本)
一、窗口函数
1、什么是窗口函数
窗口函数,也叫OLAP函数(Online Anallytical Processing,联机分析处理),可以对数据库数据进行实时分析处理。
2、窗口函数基本语法
分析函数 over(partition by 列名 order by 列名 )2.1、分析函数分类
聚合类
avg(列名)、sum(列名)、count(列名)、max(列名)、min(列名)排名类
row_number() 按照值排序时产生一个自增编号,不会重复
rank() 按照值排序时产生一个自增编号,值相等时会重复,会产生空位
dense_rank() 按照值排序时产生一个自增编号,值相等时会重复,不会产生空位注意:排名类分析函数不需要任何参数。
其他类
lag(列名,往前的行数,[行数为null时的默认值,不指定为null])
lead(列名,往后的行数,[行数为null时的默认值,不指定为null])
ntile(n) 用于将分组数据按照顺序切分成n片,返回当前切片值,如果切片不均匀,默认增加第一个切片的分布。
3、窗口函数的功能
1、同时具备分组和排序的功能。
2、不像group by,分组后不减少原表行数
3、不用表连接就能建立辅助分析列。
4、实战理解
#创建学生表格
create table tb_score (id int,class varchar(255),score int);
#插入数据
insert into tb_score (id,class,score)
values
(1,'语文',99),
(1,'数学',90),
(1,'英语',80),
(3,'英语',80),
(3,'语文',80),
(3,'数学',60),
(2,'数学',50),
(2,'语文',40);
#创建用户购买明细表
create table tb_user (name1 varchar(255),orderdate varchar(255),cost int);
#插入数据
insert into tb_user(name1,orderdate,cost)
values
('jack','2017-01-01',10),
('tony','2017-01-02',15),
('jack','2017-02-03',23),
('tony','2017-01-04',29),
('jack','2017-01-05',46),
('jack','2017-04-06',42),
('tony','2017-01-07',50),
('jack','2017-01-08',55),
('mart','2017-04-08',62),
('mart','2017-04-09',68),
('neil','2017-05-10',12),
('mart','2017-04-11',75),
('neil','2017-06-12',80),
('mart','2017-04-13',94);4.1、排名函数row_number() ,rank() ,dense_rank()的区别与用法
row_number() 按照值排序时产生一个自增编号,不会重复。
rank() 按照值排序时产生一个自增编号,值相等时会重复,会产生空位 。
dense_rank() 按照值排序时产生一个自增编号,值相等时会重复,不会产生空位。
select *,
rank() over( order by score desc) ranking ,
dense_rank() over( order by score desc) dense_ranking,
row_number() over( order by score desc) row_num
from tb_score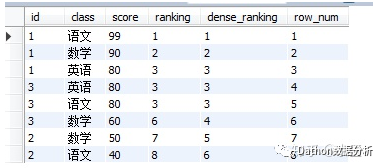
4.2、排名函数经典面试题。
4.2.1、排名问题 :增加成绩排名一列,如果两个分数相同,则排名并列(dense_rank)。
select *, dense_rank() over(order by score desc) ranking from tb_score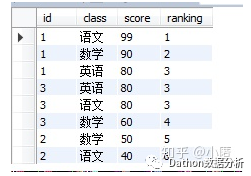
4.2.2、TopN问题:取出各科成绩前两名的记录(TopN问题用row_number)
select * from
(select *,row_number() over(partition by class order by score desc) as ranking from tb_score) t
where ranking <=2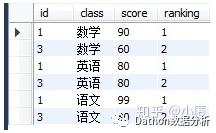
4.3 其他类:lag,lead,ntile的用法
lag(列名,往前的行数,[行数为null时的默认值,不指定为null])
lead(列名,往后的行数,[行数为null时的默认值,不指定为null])
ntile(n) 用于将分组数据按照顺序切分成n片,返回当前切片值,如果切片不均匀,默认增加第一个切片的分布。
4.3.1、lad,lead函数的理解需要想清楚“为什么会出现Null值”
SELECT *,lag(cost,1) over(partition by name1 order by cost desc) as lag_function,
lead(cost,1) over(partition by name1 order by cost desc) as lead_function
FROM test.tb_user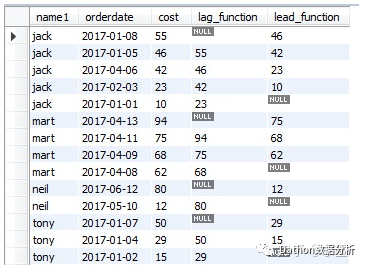
4.4、其他类函数经典面试题
4.4.1、查询顾客上次的购买时间
select *,lag(orderdate,1) over(partition by name1 order by orderdate) as last_buy from tb_user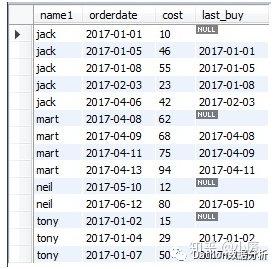
4.4.2、查询前20%时间的订单信息:20%即把数据集切成5分,所以ntile(5)
select * from
(select *,ntile(5) over(order by orderdate) as group_num from tb_user) t
where group_num = 1
4.5、聚合函数用法及经典面试题
语法:sum() over(partition by 列名 order by 列名 )组内对比问题:查询单科成绩高于该科目平均成绩的学生
select * from
(select *,avg(score) over(partition by class) as avg_score from tb_score) t
where score >avg_score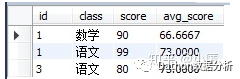
小结:
1、窗口函数原则上只能写在Select句子中。
2、窗口函数做数据处理的核心思想是建立“ 辅助列“去帮助我们做筛选,比较。
3、对我而言,掌握了窗口函数,感觉再也不怕写SQL了(很可能是错觉)
二、变量
1、变量的一些概念:
SQL的变量就是一个参数,和python一样,可以对这个参数进行赋值。
变量分为局部变量和全局变量,局部变量用@标识,全局变量@@标识(全局变量一般已经定义好的)
2、变量的申明与赋值
2.1、变量的申明;sql server中变量要先申明后才能赋值。mysql中变量不用事前申明,在用的时候直接赋值。
语法 :declare @变量名 数据类型;例如:declare @num int;2.2、赋值方法有两种
#第一种方法
set @num = 1; 或 set @num :=1
#第二种方法
select @num:=1; 或 select @num:=字段名 from 表名 where (注意筛选出的结果应为单值)注意:上面两种赋值符号,使用set时可以用“=”或“:=”,但是使用select时必须用“:=赋值”。
3、变量的使用。
#创建订单明细表,字段:订单号,浏览日期,加购物车日期,下订单日期,收货日期
create table tb_order
(order_id int,
view_time varchar(255),
cart_time varchar(255),
buy_time varchar(255),
rec_time varchar(255));
#插入数据
insert into tb_order(order_id,view_time,cart_time,buy_time,rec_time)
values
(1,'2020-05-20','2020-05-21','2020-05-22','2020-05-23'),
(2,'2020-05-20','2020-05-20','2020-05-20','2020-05-20'),
(3,'2020-05-24','2020-05-25','2020-05-26','2020-05-27'),
(4,'2020-05-20','2020-05-21','2020-05-22','2020-05-23'),
(5,'2020-05-28','2020-05-28','2020-05-28','2020-05-28');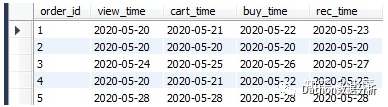
找出浏览日期为'2020-05-20'的订单明细
set @date1 = '2020-05-20';
select * from tb_order where view_time =@date1;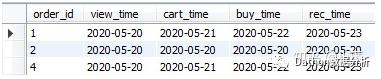
有同学会问,我直接写view_time ='2020-05-20'不就行了嘛,为啥要搞这么复杂?
在上面场景下,确实直接写view_time ='2020-05-20'就足够了,但在某些场景下,写变量会更加简便。比如:
找出浏览日期,浏览日期,加购物车日期,下订单日期,收货日期均为2020年5月20日的订单明细。
set @date1 = '2020-05-20';
select * from tb_order where
view_time =@date1
and cart_time =@date1
and buy_time = @date1
and rec_time =@date1;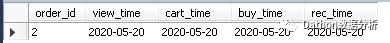
之后,找出各日期均为2020年5月28日的订单明细,这时,你仅仅需要改一个变量即可,无需将所有日期都改。
set @date1 = '2020-05-28';
select * from tb_order where
view_time =@date1
and cart_time =@date1
and buy_time = @date1
and rec_time =@date1;使用变量也可以提高查询效率。
例如:数据库制定两个执行计划,制定执行计划直接是需要消耗资源的。
select * from table where id =1
select * from table where id =2而如果我们改成这样,当我们把id改成2时,数据库还是会执行之前的执行计划,这样就节省了时间。
set @idv = 1
select * from table where id =@idv三、利用case when作数据透视图
1、case when 语法;
select
col0,
(case when col1 = codition2 then 选项值1
when col2 = codition2 then 选项值2
else 默认值 end) as casewhen_col
fron table2、case when的三种最常用的应用场景
(1)、等值替换
(2)、范围替换
(3)、数据透视图(也称列转行)
3、实战
#创建订单价格表
create table tb_order2
(order_id varchar(255),
price int,
time varchar(255),
area varchar(255));
#插入数据
insert into tb_order2(order_id,price,time,area)
values
('S001',10,'2019/1/1','A区'),
('S002',20,'2019/1/1','B区'),
('S003',30,'2019/1/1','C区'),
('S004',40,'2019/1/2','A区'),
('S005',10,'2019/1/2','B区'),
('S006',20,'2019/1/2','C区'),
('S007',30,'2019/1/3','A区'),
('S008',40,'2019/1/3','C区');
select * from tb_order2;
3.1、值替换:将所有A区的订单改成D区的订单
select *,case when area ='A区' then 'D区' end as casewhen_col from tb_order2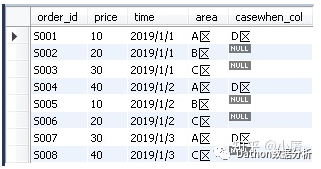
3.2、范围替换:假设有个需求为:价格<=10,劣质订单;>=10&<=20,中等订单;>20,优质订单;
select *,
(case when price <=10 then '劣质订单'
when price <=20 then '中等订单'
else '优质订单' end) label
from tb_order2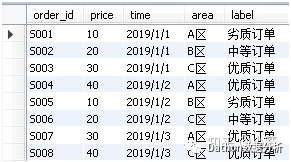
3.3、数据透视图(也称列转行)
需求,想计算各区域各天的销售总价。这种用excel作就很简单直接作数据透视图,如果写sql去实现的话需要用到case when,结果如下表:
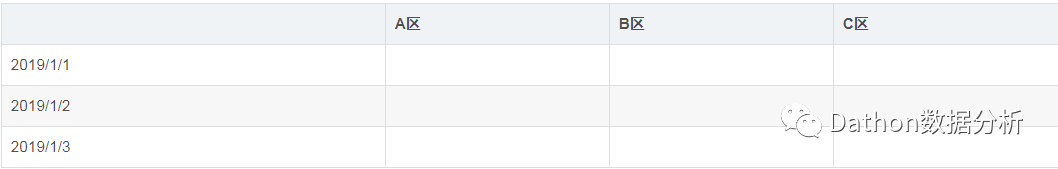
### 实现数据透视。
select time,
sum(case when area ='A区' then price else 0 end) as 'A区总价',
sum(case when area='B区' then price else 0 end) as 'B区总价',
sum(case when area='C区' then price else 0 end) as 'C区总价'
from tb_order2
group by time
四、With as
1、概念:with as也叫做子查询部分,就类似于一个视图或临时表,可以用来存储一部分的SQL语句,它可以提高代码可读性。
2、优点:
(1)、其最大的好处就是提高代码的可读性,如何with子句在后面要多次使用到,这可大大简化SQL。
(2)、可以提高查询性能。
3、使用
3.1、单表with as
with t1 as
(select * from tb_score where class ='语文')
select * from t1;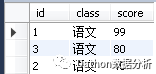
3.2、多表with as
with t1 as
(select * from tb_score where class ='语文'),
t2 as
(select * from tb_score where class ='数学')
#笛卡尔积
select * from t1,t2
注意:这里必须要整体作为一条SQL查询,即with as语句之后不能加分号结束,不然会报错,必须用select结束。
五、group_concat
因为我个人主要用clickhouse数据库 + grafana BI工具,是一款写SQL作数据可视化的BI工具,它需要符合这样的固定格式才能出图:[时间,维度,值],所以若我想多维度展示的时候,就必须用groupArray函数去构建维度这列。后来我发现Mysql也有和groupArray函数几乎相同功能的函数就是group_concat,所以就来学习下。
其语法:
group_concat([DISTINCT] 要连接的字段 [Order BY ASC/DESC 排序字段] [Separator '分隔符'])注意:需要和group by联合使用。
其用法:
1、以id分组,查看所有的class有哪些元素
select id,group_concat(distinct class) as groupc_col from tb_score group by id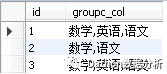
2、改变分隔符为'-'
select id,group_concat(distinct class separator '-') as groupc_col from tb_score group by id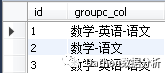
嗯,以上就是我以前比较少用的SQL知识点了。经过这次复习巩固,看别的同事很长的SQL也没这么怕啦。






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








