Java 是一门"繁琐"的语言,使用 Lombok 可以显著地减少样板代码。比如使用 @Getter 注解可以为你的私有属性创建 get 方法。
源代码
@Getter private int age = 10;
生成后代码
private int age = 10;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
Lombok 自身已经拥有许多非常实用的注解,例如 @Getter / @Value / @Data / @Builder 等等。但你可能也想定义自己的注解来减少重复代码,本文将讲解如何实现这一目标。
Lombok是如何实现代码注入的?
在使用 javac 编译器时(netbeans,maven,gradle),Lombok 会以 annotation processor 方式运行。 Javac 会以 SPI 方式加载所有 jar 包中 META-INF/services/javax.annotation.processing.Processor 文件所列举的类,并以 annotation processor 的方式运行它。对于 Lombok,这个类是 lombok.launch.AnnotationProcessorHider$AnnotationProcessor ,当它被 javac 加载创建后,会执行 init方法,在这个方法中会启动一个特殊的类加载器 ShadowClassLoader ,加载同 jar 包下所有以 .SCL.lombok 结尾的类(Lombok 为了对 IDE 隐藏这些类,所以不是通常地以 .class 结尾)。其中就包含各式各样的 handler 。每个 handler 申明并处理一种注解,比如 @Getter 对应 HandleGetter 。
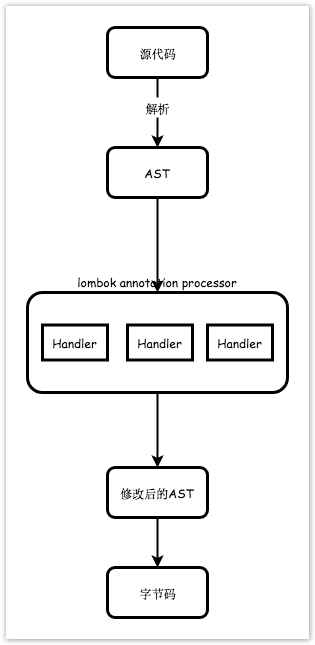
委派给 handler 时,Lombok Annotation Processor 会提供一个被注解节点的Abstract Syntax Tree (AST)节点对象,它可能是一个方法、属性或类。在 handler 中 可以对这个 AST 进行修改,之后编译器将从被修改后的 AST 生成字节码。
下面我们以 @KLog 为例,说明如何编写 Handler 。假设我们希望实现这样的效果:
源代码
@KLog public class Foo { }
生成后代码
public class Foo {
private static final com.example.log.KLogger log = com.example.log.KLoggerFactory.getLogger(Foo.class);
}
KLog 可能是我们的日志类,在通用日志类的基础上做了一些扩展。 使用 @KLog 可以避免因复制粘贴代码导致入参错误,也有利于统一命名。为了实现这个注解,我们需要实现:
创建 Javac Handler
创建 Eclipse Handler
创建 lombok-intellij-plugin Handler
前期准备:Fork Lombok 工程
我们需要先 fork Lombok 工程,项目中添加 Handler。前面谈到因为 shadow loader类加载的原因,在另外的工程中创建 Handler 将变得非常困难, lombok作者推荐直接fork lombok工程定制自己的 lombok.jar。
~ git clone https://github.com/rzwitserloot/lombok.git
需要注意的是,lombok 需要使用 JDK9 以上版本进行编译,确保系统路径配置了正确的 JAVA_HOME 路径,然后执行 ant maven 将构建可以用于安装本地仓库的 jar 包。 可以运行以下命令将构建的 jar 包安装到本地仓库进行工程间共享:
~ mvn install:install-file -Dfile=dist/lombok-{lombok-version}.jar -DpomFile=build/mavenPublish/pom.xml
创建@KLog
package lombok.extern.klog;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) // 1
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface KLog {
String topic() default "";
}
这个注解只用编译阶段,所以使用 RetentionPolicy.SOURCE 就可以
创建 Javac Handler
创建注解后,我们需要再实现一个 Handler 来处理被注解标注了的对象( Foo )。 我们将创建一个属性的 AST 节点,然后插入到 Foo 类对应的节点。
/**
* Handles the {@link lombok.extern.klog.KLog} annotation for javac.
*/
@ProviderFor(JavacAnnotationHandler.class) // 1
public class HandleKLog extends JavacAnnotationHandler {
private static final String LOG_FIELD_NAME = "log";
@Override
public void handle(final AnnotationValues annotation, final JCTree.JCAnnotation ast, final JavacNode annotationNode) {
JavacNode typeNode = annotationNode.up(); // 2
if (!checkFieldInject(annotationNode, typeNode)) {
return;
}
JCTree.JCVariableDecl fieldDecl = createField(annotation, annotationNode, typeNode);
injectFieldAndMarkGenerated(typeNode, fieldDecl); // 3
}
}
lombok 使用 SPI 方式发现 Handler,这里 mangosdk 的注解 @ProviderFor(JavacAnnotationHandler.class) 会为我们生成对应 services 文件;
Foo 是 @KLog 的上层节点;
将属性插入到注解所应用的节点,即 Foo 。
上述代码先检查是否可以插入属性,然后创建属性并插入到 Foo 节点。为什么需要检查? 因为如果已经存在同名的属性或者注解所应用的类不是一个 class 就无法插入。
private boolean checkFieldInject(final JavacNode annotationNode, final JavacNode typeNode) {
if (typeNode.getKind() != AST.Kind.TYPE) {
annotationNode.addError("@KLog is legal only on types.");
return false;
}
if ((((JCTree.JCClassDecl)typeNode.get()).mods.flags & Flags.INTERFACE) != 0) {
annotationNode.addError("@KLog is legal only on classes and enums.");
return false;
}
if (fieldExists(LOG_FIELD_NAME, typeNode) != JavacHandlerUtil.MemberExistsResult.NOT_EXISTS) {
annotationNode.addWarning("Field '" + LOG_FIELD_NAME + "' already exists.");
return false;
}
return true;
}
接着我们实现属性的创建(createField)。我们需要创建属性的 AST 节点,AST 树的结构像下面这样:
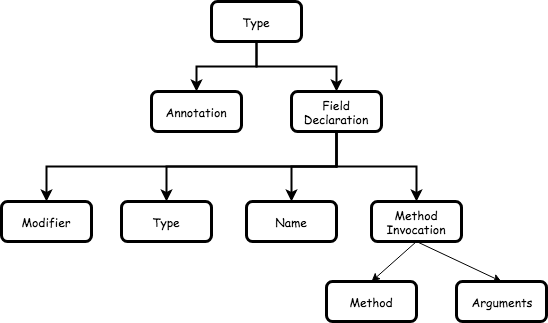
具体到我们需要生成的实际代码则是这样:
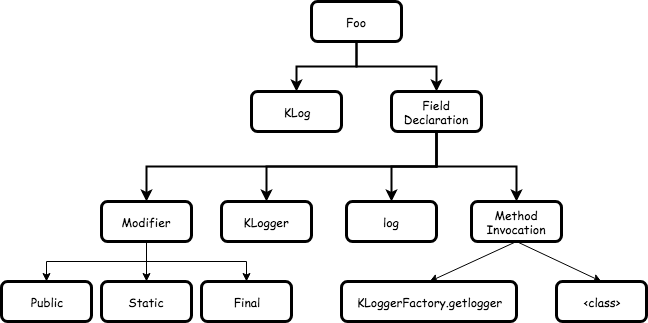
创建属性的代码较为复杂,涉及到许多 AST 包相关的操作,需要熟悉相关 API 的含义。创建 log 属性的代码如下:
private JCTree.JCVariableDecl createField(final AnnotationValues annotation, final JavacNode annotationNode, final JavacNode typeNode) {
JavacTreeMaker maker = typeNode.getTreeMaker();
Name name = ((JCTree.JCClassDecl) typeNode.get()).name;
JCTree.JCFieldAccess loggingType = maker.Select(maker.Ident(name), typeNode.toName("class"));
JCTree.JCExpression loggerType = chainDotsString(typeNode, "com.example.log.KLogger");
JCTree.JCExpression factoryMethod = chainDotsString(typeNode, "com.example.log.KLoggerFactory.getLogger");
JCTree.JCExpression loggerName;
String topic = annotation.getInstance().topic();
if (topic == null || topic.trim().length() == 0) { // 1
loggerName = loggingType;
} else {
loggerName = maker.Literal(topic);
}
JCTree.JCMethodInvocation factoryMethodCall = maker.Apply(List.nil(), factoryMethod, loggerName != null ? List.of(loggerName) : List.nil());
return recursiveSetGeneratedBy(maker.VarDef(
maker.Modifiers(Flags.PRIVATE | Flags.FINAL | Flags.STATIC ),
typeNode.toName(LOG_FIELD_NAME), loggerType, factoryMethodCall), annotationNode.get(), typeNode.getContext());
}
如果指定了 KLog(topic) 就使用 KLoggerFactory.getLogger(topic) ,否则使用 KLoggerFactory.getLogger(topic) 。
添加了 Javac Handler 之后我们就可以在 maven 中使用 @KLog 了,但还无法用于Eclipse/ejc,我们需要继续添加 Eclipse Handler。
创建Eclipse Handler
package lombok.eclipse.handlers;
import lombok.core.AST;
import lombok.core.AnnotationValues;
import lombok.eclipse.EclipseAnnotationHandler;
import lombok.eclipse.EclipseNode;
import lombok.extern.klog.KLog;
import org.eclipse.jdt.internal.compiler.ast.*;
import org.eclipse.jdt.internal.compiler.classfmt.ClassFileConstants;
import org.mangosdk.spi.ProviderFor;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.util.Arrays;
import static lombok.eclipse.Eclipse.fromQualifiedName;
import static lombok.eclipse.handlers.EclipseHandlerUtil.*;
/**
* Handles the {@link KLog} annotation for Eclipse.
*/
@ProviderFor(EclipseAnnotationHandler.class)
public class HandleKLog extends EclipseAnnotationHandler {
private static final String LOG_FIELD_NAME = "log";
@Override
public void handle(final AnnotationValues annotation, final Annotation source, final EclipseNode annotationNode) {
EclipseNode owner = annotationNode.up();
if (owner.getKind() != AST.Kind.TYPE) {
return;
}
TypeDeclaration typeDecl = null;
if (owner.get() instanceof TypeDeclaration) typeDecl = (TypeDeclaration) owner.get();
int modifiers = typeDecl == null ? 0 : typeDecl.modifiers;
boolean notAClass = (modifiers &
(ClassFileConstants.AccInterface | ClassFileConstants.AccAnnotation)) != 0;
if (typeDecl == null || notAClass) {
annotationNode.addError("@KLog is legal only on classes and enums.");
return;
}
if (fieldExists(LOG_FIELD_NAME, owner) != EclipseHandlerUtil.MemberExistsResult.NOT_EXISTS) {
annotationNode.addWarning("Field '" + LOG_FIELD_NAME + "' already exists.");
return;
}
ClassLiteralAccess loggingType = selfType(owner, source);
FieldDeclaration fieldDeclaration = createField(source, loggingType, annotation.getInstance().topic());
fieldDeclaration.traverse(new SetGeneratedByVisitor(source), typeDecl.staticInitializerScope);
injectField(owner, fieldDeclaration);
owner.rebuild();
}
private static ClassLiteralAccess selfType(EclipseNode type, Annotation source) {
int pS = source.sourceStart, pE = source.sourceEnd;
long p = (long) pS << 32 | pE;
TypeDeclaration typeDeclaration = (TypeDeclaration) type.get();
TypeReference typeReference = new SingleTypeReference(typeDeclaration.name, p);
setGeneratedBy(typeReference, source);
ClassLiteralAccess result = new ClassLiteralAccess(source.sourceEnd, typeReference);
setGeneratedBy(result, source);
return result;
}
private static FieldDeclaration createField(Annotation source, ClassLiteralAccess loggingType, String loggerTopic) {
int pS = source.sourceStart, pE = source.sourceEnd;
long p = (long) pS << 32 | pE;
// private static final com.example.log.KLogger log = com.example.log.KLoggerFactory.getLogger(Foo.class);
FieldDeclaration fieldDecl = new FieldDeclaration(LOG_FIELD_NAME.toCharArray(), 0, -1);
setGeneratedBy(fieldDecl, source);
fieldDecl.declarationSourceEnd = -1;
fieldDecl.modifiers = Modifier.PRIVATE | Modifier.STATIC | Modifier.FINAL;
fieldDecl.type = createTypeReference("com.example.log.KLog", source);
MessageSend factoryMethodCall = new MessageSend();
setGeneratedBy(factoryMethodCall, source);
factoryMethodCall.receiver = createNameReference("com.example.log.KLoggerFactory", source);
factoryMethodCall.selector = "getLogger".toCharArray();
Expression parameter = null;
if (loggerTopic == null || loggerTopic.trim().length() == 0) {
TypeReference copy = copyType(loggingType.type, source);
parameter = new ClassLiteralAccess(source.sourceEnd, copy);
setGeneratedBy(parameter, source);
} else {
parameter = new StringLiteral(loggerTopic.toCharArray(), pS, pE, 0);
}
factoryMethodCall.arguments = new Expression[]{parameter};
factoryMethodCall.nameSourcePosition = p;
factoryMethodCall.sourceStart = pS;
factoryMethodCall.sourceEnd = factoryMethodCall.statementEnd = pE;
fieldDecl.initialization = factoryMethodCall;
return fieldDecl;
}
public static TypeReference createTypeReference(String typeName, Annotation source) {
int pS = source.sourceStart, pE = source.sourceEnd;
long p = (long) pS << 32 | pE;
TypeReference typeReference;
if (typeName.contains(".")) {
char[][] typeNameTokens = fromQualifiedName(typeName);
long[] pos = new long[typeNameTokens.length];
Arrays.fill(pos, p);
typeReference = new QualifiedTypeReference(typeNameTokens, pos);
} else {
typeReference = null;
}
setGeneratedBy(typeReference, source);
return typeReference;
}
}
Eclipse Handler 的代码比 Javac Handler 复杂不少,因为 Eclipse 的 AST 不如 Javac 简洁。 代码中创建的节点都需要关联上源码的行数,如果生成的代码出错,Eclipse 可以正确定位到 @KLog 。
在 Lombok 工程目录下执行 ant maven 会生成 dist/lombok.jar 文件,双击运行这个 jar 打开 eclipse installer 窗口。 选择你所使用的 Eclipse,重启 Eclipse 并重新构建工程就可以使用新添加的注解了。

创建lombok-intellij-plugin Handler
对于 Intellij IDEA 的用户,还需要在 lombok-intellij-plugin 插件中添加额外的实现。插件的实现和 lombok 实现相互独立,无法复用。
package de.plushnikov.intellij.plugin.processor.clazz.log;
import lombok.extern.klog.KLog;
public class KLogProcessor extends AbstractLogProcessor {
private static final String LOGGER_TYPE = "com.example.log.KLog";
private static final String LOGGER_CATEGORY = "%s.class";
private static final String LOGGER_INITIALIZER = "com.example.log.KLoggerFactory(%s)";
public KLogProcessor() {
super(KLog.class, LOGGER_TYPE, LOGGER_INITIALIZER, LOGGER_CATEGORY);
}
}
public class LombokLoggerHandler extends BaseLombokHandler {
protected void processClass(@NotNull PsiClass psiClass) {
final Collection logProcessors = Arrays.asList(
new CommonsLogProcessor(), new JBossLogProcessor(),
new Log4jProcessor(), new Log4j2Processor(), new LogProcessor(),
new Slf4jProcessor(), new XSlf4jProcessor(), new FloggerProcessor(), new KLogProcessor());
// ...
}
}
插件编译执行 ./gradlew build ,在 build/distributions 目录下会生成 lombok-plugin-{version}.zip 文件。 在 IntelliJ 中选择 Preferences > Plugins > Install Plugin from disk 安装之前构建得到的文件,重启 IntelliJ。
总结
本文以 @KLog 注解为例,讲述了如何实现 Javac/Eclipse/Intellij 的 Lombok Handler,不同编译器的语法树结构不同,所以需要分别实现。 Eclipse Handler 的实现较为繁琐,如果团队成员没有使用 Eclipse 的也可以略去不实现。
通过上面的例子,你可以定义自己的注解及 Handler。复杂的代码生成会涉及更多的 AST 操作,你可以参考 Lombok 已有的例子了解这些 API 的用法。为了清楚地展示 AST 的构造,log 属性的创建没有使用 Lombok 通用的日志处理类 HandleLog, Lombok 的 @Slf4j/@Log4j/@Log 等都是通过它实现,使用它实现 @KLog 会更为简单。
Lombok 的本质是通过修改 AST 语法树从而影响到最后的字节码生成,普通的 Java Annotation Processor 只能创建新的类而不能修改既有类,这使得 Lombok 尤为强大、无可替代。但同样的,这种方式依赖于特定编译器的语法树结构,需要对编译器语法树相关类较为熟悉才能实现。这些结构也不属于 Java 标准,随时可能发生变化。
Happy coding!





















 208
208











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








