继承是面向对象最显著的一个特性。继承是从已有的类中派生出新的类,新的类能吸收已有类的数据属性和行为,并能扩展新的能力。
编写一个Father类作为父类:
抽象类:
1、父类里必须有一个abstract修饰符
2、方法上也必须有修饰符
3、抽象方法没有具体的实现方法体
4、所有的子类必须都要实现抽象方法
public abstract class Father {
static int money = 1000;
//定义一个抽象方法
public abstract void donation(int money);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//此时main方法什么都不执行
}
}编写子类Child继承父类Father:
继承:
子类可以继承父类的属性、方法,但必须重写父类的抽象方法,
并且可以使用super调用父类的属性、方法。
public class Child extends Father{
//子类可以定义自己的属性
int money = 100;
//使用super单独调用父类的属性
public int getMoneyFromFather(){
return super.money;
}
//重写父类的方法,方法体有具体的实现细节。
@Override
public void donation(int money) {
System.out.println("donation(): Child捐赠所有从Father继承而来的"+money+"万资金建设基础设施");
}
//扩展Child的能力
public void makeMoney(){
System.out.println("makeMoney(): Child利用金融知识赚得人生第一个"+money+"万");
}
}
public class OtherChild extends Father {
@Override
public void donation(int money) {
System.out.println("donation(): OtherChild继承Father的" + money + "万开了一家IT公司");
}
}
最后在父类的main方法中实例化2个子类Child、OtherChild:
public abstract class Father {
...
...
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child child = new Child();
child.donation(money);
child.makeMoney();
System.out.println();
OtherChild otherChild = new OtherChild();
otherChild.donation(money);
}
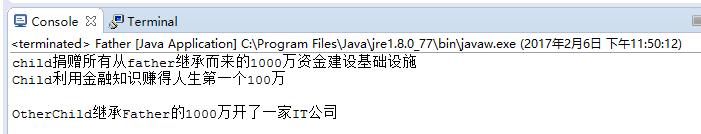
}运行结果:
Child子类继承了父类的money属性,重写了父类的donation方法,并拓展了自己的新方法makeMoney()。
OtherChild只继承了父类的money属性。






















 176
176

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








