作者:田杰,阿里云数据库高级运维专家
查询执行时间长引发应用感知 “卡顿” 的场景在数据库的日常支持和使用中并不少见,但由于时区设置引发的 SQL 执行“卡顿”仍然是一个有趣的现象,之前没有具体关注过。这次客户的细致与坚持让我们找到了问题的源头。
1. 名词解释
序列号名词说明:
1、CPU 使用率非空闲的 CPU 时间占比。
2、User CPU 使用率用户空间(user-space)应用代码消耗的 CPU 时间占比。
3、Sys CPU 使用率系统空间(sys-space)内核代码消耗 CPU 时间占比。
4、FutexLinux 内核提供的快速用户态锁/信号量;在无竞争场景完全在用户空间中运行,但在存在竞争场景会引发系统调用。
2.问题现象
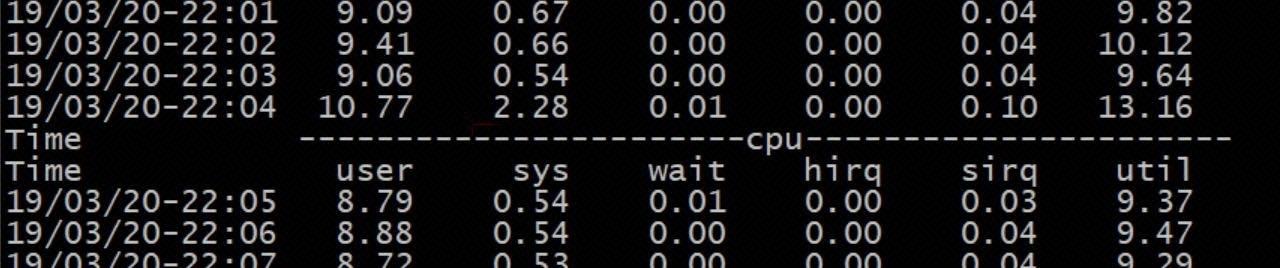
客户 MySQL 8.0 实例在 2020-03-19 22:03 ~ 22:04 出现大量活跃连接堆积,慢日志中出现大量低成本查询,并且 CPU 使用率不高但系统 SYS CPU 使用率出现异常波动。

3. 问题排查
3.1 OS 层面
我们来考虑一下有哪些因素可能会导致卡顿:• 物理机 OS 层面波动(通过 IO_WAIT 指标排除)。• MySQL 自身机制。
3.2 MySQL 层面
排除掉 OS 层面异常类因素,我们开始聚焦在 mysqld 进程调用栈的分析。为了更好的分析 MySQL 的行为,阿里数据库提供了扁鹊系统来跟踪、统计和展示确定时间内的进程内部方法调用情况。
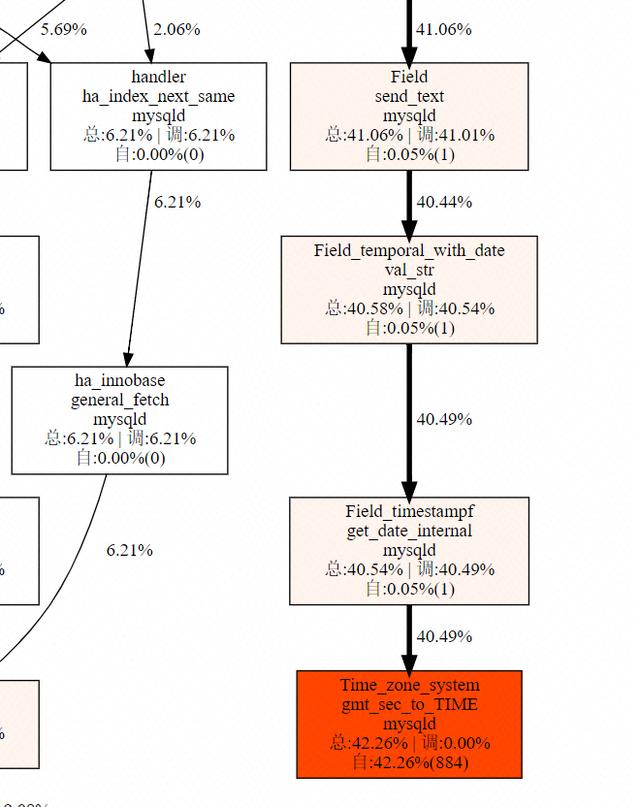
我们分析上图可以看到 40.5% 的 CPU 时间消耗在 Time_zone_system::gmt_sec_to_TIME() 方法的调用上,就是以下这一段的代码。
void Time_zone_system::gmt_sec_to_TIME(MYSQL_TIME *tmp, my_time_t t) const { struct tm tmp_tm; time_t tmp_t = (time_t)t; localtime_r(&tmp_t, &tmp_tm); localtime_to_TIME(tmp, &tmp_tm); tmp->time_type = MYSQL_TIMESTAMP_DATETIME; adjust_leap_second(tmp);}仔细阅读这段代码会发现 localtime_to_TIME() 和 adjust_leap_second() 都是简单的格式转换和计算,并不涉及系统调用。而 localtime_r() 会涉及到 glibc 中的 __localtime_r() 方法,代码如下
/* Return the `struct tm' representation of *T in local time, using *TP to store the result. */struct tm *__localtime_r (t, tp) const time_t *t; struct tm *tp;{ return __tz_convert (t, 1, tp);}weak_alias (__localtime_r, localtime_r)我们继续下钻来看一下 __tz_convert() 的实现,代码如下
/* Return the `struct tm' representation of *TIMER in the local timezone. Use local time if USE_LOCALTIME is nonzero, UTC otherwise. */struct tm *__tz_convert (const time_t *timer, int use_localtime, struct tm *tp){long int leap_correction;int leap_extra_secs;if (timer == NULL) { __set_errno (EINVAL); return NULL; }__libc_lock_lock (tzset_lock);/* Update internal database according to current TZ setting. POSIX.1 8.3.7.2 says that localtime_r is not required to set tzname. This is a good idea since this allows at least a bit more parallelism. */tzset_internal (tp == &_tmbuf && use_localtime, 1);if (__use_tzfile) __tzfile_compute (*timer, use_localtime, &leap_correction, &leap_extra_secs, tp);else { if (! __offtime (timer, 0, tp))tp = NULL; else__tz_compute (*timer, tp, use_localtime); leap_correction = 0L; leap_extra_secs = 0; }if (tp) { if (! use_localtime){ tp->tm_isdst = 0; tp->tm_zone = "GMT"; tp->tm_gmtoff = 0L;} if (__offtime (timer, tp->tm_gmtoff - leap_correction, tp)) tp->tm_sec += leap_extra_secs; elsetp = NULL; }__libc_lock_unlock (tzset_lock);return tp;}注意到 代码中有 加锁 和 解锁 的操作出现,那么现在我们来看一下 __libc_lock_lock() 的定义,代码如下
#if IS_IN (libc) || IS_IN (libpthread)# ifndef __libc_lock_lock# define __libc_lock_lock(NAME) ({ lll_lock (NAME, LLL_PRIVATE); 0; })# endif#else# undef __libc_lock_lock# define __libc_lock_lock(NAME) __libc_maybe_call (__pthread_mutex_lock, (&(NAME)), 0)#endif继续追溯 lll_lock() 的实现,代码如下
static inline void__attribute__ ((always_inline))__lll_lock (int *futex, int private){ int val = atomic_compare_and_exchange_val_24_acq (futex, 1, 0); if (__glibc_unlikely (val != 0)) { if (__builtin_constant_p (private) && private == LLL_PRIVATE) __lll_lock_wait_private (futex); else __lll_lock_wait (futex, private); }}#define lll_lock(futex, private) __lll_lock (&(futex), private)可以看到代码中使用 atomic_compare_and_exchange_val_24_acq() 尝试对 futex 加锁。而 futex 作为多个 thread 间共享的一块内存区域在多个 client thread(多个会话/查询)竞争的场景下会引发系统调用而进入系统态,导致 SYS 系统态 CPU 使用率上升。并且该临界区保护的锁机制限制了时区转换方法 __tz_convert() 的并发度,进而出现多个会话/查询 等待获取锁进入临界区的情况,当冲突争抢激烈的场景下引发卡顿那么是什么引发的Time_zone_system::gmt_sec_to_TIME() 调用呢,追溯下 Field_timestampf::get_date_internal() 方法,代码如下
bool Field_timestampf::get_date_internal(MYSQL_TIME *ltime) { THD *thd = table ? table->in_use : current_thd; struct timeval tm; my_timestamp_from_binary(&tm, ptr, dec); if (tm.tv_sec == 0) return true; thd->time_zone()->gmt_sec_to_TIME(ltime, tm); return false;}该方法中调用了基类 Time_zone 的虚函数 gmt_sec_to_TIME() 来进行带时区的秒到时间格式的转换,结合 Field_timestampf::get_date_internal() 的名称能够推断出查询中应该涉及了 timestamp 数据类型的访问。基于上面的推测我们验证下卡顿的查询和其数据类型
# 慢查询SELECT id, ...... create_time, update_time, ...... FROM mytab WHERE duid IN (?,?,?,?,? ) and (state in (2, 3) or ptype !=0)# 查询涉及的表CREATE TABLE `mytab` ( `id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `duid` char(32) NOT NULL, ...... `state` tinyint(2) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `ptype` tinyint(4) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, `update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, ......, PRIMARY KEY (`id`),) ENGINE=InnoDB从上面的信息能够看到 create_time 和 update_time 字段都是 timestamp 数据类型,验证了之前的猜测。
4. 问题解决
在上面分析的基础上可以看到调用 Time_zone_system::gmt_sec_to_TIME() 引入的 OS 层面 futex 锁竞争导致了低成本查询执行卡顿。为了规避调用该方法,可以在实例控制台将 time_zone 参数值由 system 调整为当地时区,比如中国东 8 区时区 '+8:00'。修改后,会调用 Time_zone_offset::gmt_sec_to_TIME() 来直接在 MySQL 层面进行计算,避免访问 glibc 的函数引发 OS 层面的加解锁。修改效果对比(对比执行同样次数的 timestamp 数据类型查询完成时间)time_zone='system',需要约 15 分钟 完成

time_zone='+8:00',需要约 5 分钟 完成
5. 最佳实践
高并发应用如果涉及到高频次的 timestamp 类型数据访问:• 如果确实要使用 timestamp 类型,建议控制台设置 time_zone 参数为 UTC/GMT 偏移量格式,比如 东8区 '+8:00',可以有效降低高并发查询执行开销,降低响应时间 RT。• 由于 MySQL 5.7 版本后 Datatime 类型支持 Timestamp 类型的默认值并且支持 on update current_timestamp 属性,建议使用 Datetime 类型替换 Timestamp 类型。





















 818
818











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








