数组 + 矩阵 + 串是常见的数据结构,需要深入掌握与学习。
对于数组:根据指定下标定位相关元素的地址是最为关键的操作,玩数组就是玩下标。
矩阵:M * N 的二维数组,是逻辑线性结构。
稀疏矩阵
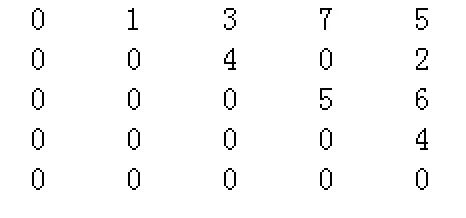 稀疏矩阵:矩阵中绝大多数元素为零,只有少量非零元素;稀疏因子 = 非零元素数量/矩阵总元素数量。
存储空间利用率:有效元素所申请空间/该矩阵所申请的空间。
定位:当给出下标i、j,且i、j在有效下标取值范围内,需要定位其所对应的元素在压缩存储方式中的位置。
2、代码实现
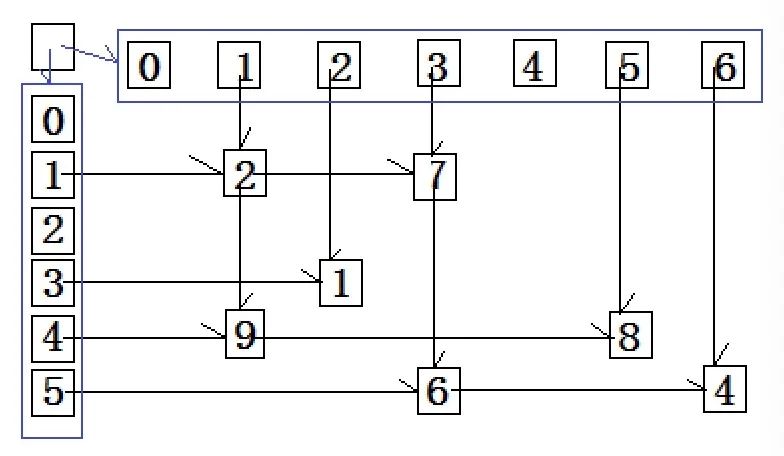
为提升空间利用率(只存储有效元素,避免空间过度浪费),矩阵的存储一般采用三元组法/十字交叉链。
三元组实现:
结构体
稀疏矩阵:矩阵中绝大多数元素为零,只有少量非零元素;稀疏因子 = 非零元素数量/矩阵总元素数量。
存储空间利用率:有效元素所申请空间/该矩阵所申请的空间。
定位:当给出下标i、j,且i、j在有效下标取值范围内,需要定位其所对应的元素在压缩存储方式中的位置。
2、代码实现
为提升空间利用率(只存储有效元素,避免空间过度浪费),矩阵的存储一般采用三元组法/十字交叉链。
三元组实现:
结构体
 结构体
结构体
 结构体
结构体
1、基础概念
模型: 稀疏矩阵:矩阵中绝大多数元素为零,只有少量非零元素;稀疏因子 = 非零元素数量/矩阵总元素数量。
存储空间利用率:有效元素所申请空间/该矩阵所申请的空间。
定位:当给出下标i、j,且i、j在有效下标取值范围内,需要定位其所对应的元素在压缩存储方式中的位置。
2、代码实现
为提升空间利用率(只存储有效元素,避免空间过度浪费),矩阵的存储一般采用三元组法/十字交叉链。
三元组实现:
结构体
稀疏矩阵:矩阵中绝大多数元素为零,只有少量非零元素;稀疏因子 = 非零元素数量/矩阵总元素数量。
存储空间利用率:有效元素所申请空间/该矩阵所申请的空间。
定位:当给出下标i、j,且i、j在有效下标取值范围内,需要定位其所对应的元素在压缩存储方式中的位置。
2、代码实现
为提升空间利用率(只存储有效元素,避免空间过度浪费),矩阵的存储一般采用三元组法/十字交叉链。
三元组实现:
结构体
1typedef struct TRIAD{
2 int value;
3 int row;
4 int col;
5}TRIAD;
6
7typedef struct TRIPLE{
8 TRIAD *element;
9 int rowCount;
10 int colCount;
11 int elementCount;
12}TRIPLE;
1#include
2#include
3
4typedef struct TRIAD{
5 int value;
6 int row;
7 int col;
8}TRIAD;
9
10typedef struct TRIPLE{
11 TRIAD *element;
12 int rowCount;
13 int colCount;
14 int elementCount;
15}TRIPLE;
16
17TRIPLE *inputTriple(void);
18void destoryTriple(TRIPLE *);
19void showMatrix(TRIPLE triple);
20TRIPLE *revangeMatrix(TRIPLE triple);
21TRIPLE *initTriple(int rowCount, int colCount, int elementCount);
22
23TRIPLE *initTriple(int rowCount, int colCount, int elementCount){
24 TRIPLE *triple;
25
26 triple = (TRIPLE *)malloc(sizeof(TRIPLE));
27 triple->rowCount = rowCount;
28 triple->colCount = colCount;
29 triple->elementCount = elementCount;
30
31 triple->element = (TRIAD *)malloc(sizeof(TRIAD) * elementCount);
32
33 return triple;
34}
35
36TRIPLE *revangeMatrix(TRIPLE triple){
37 TRIPLE *revTriple;
38 int *ec;
39 int i;
40 int index;
41
42 revTriple = initTriple(triple.rowCount, triple.colCount, triple.elementCount);
43 revTriple->rowCount = triple.colCount;
44 revTriple->colCount = triple.rowCount;
45 revTriple->elementCount = triple.elementCount;
46
47 ec = (int *)calloc(triple.colCount+1, sizeof(int));
48 for(i = 0; i 49 ec[triple.element[i].col + 1]++;
50 }
51 for(i = 1; i 1; i++){
52 ec[i] += ec[i-1];
53 }
54 for(i = 0; i 55 index = ec[triple.element[i].col];
56 revTriple->element[index].col = triple.element[i].row;
57 revTriple->element[index].row = triple.element[i].col;
58 revTriple->element[index].value = triple.element[i].value;
59 ec[index+1]++;
60 }
61
62 free(ec);
63
64 return revTriple;
65}
66
67void showMatrix(TRIPLE triple){
68 int i;
69 int j;
70 int t = 0;
71
72 for(i = 0; i 73 for(j = 0; j 74 if(i == triple.element[t].row && j == triple.element[t].col)
75 printf("%d\t", triple.element[t++].value);
76 else
77 printf("0\t");
78 }
79 printf("\n");
80 }
81
82}
83
84void destoryTriple(TRIPLE *triple){
85 free(triple->element);
86 free(triple);
87}
88
89TRIPLE *inputTriple(void){
90 TRIPLE *triple;
91 int rowCount;
92 int colCount;
93 int elementCount;
94 int i;
95
96 scanf("%d%d%d", &rowCount, &colCount, &elementCount);
97
98 triple = initTriple(rowCount, colCount, elementCount);
99
100 for(i = 0; i 101 int value;
102 int row;
103 int col;
104
105 scanf("%d%d%d", &row, &col, &value);
106 triple->element[i].row = row;
107 triple->element[i].col = col;
108 triple->element[i].value = value;
109 }
110
111 return triple;
112}
113
114void main(void){
115 TRIPLE *tr;
116 TRIPLE *revTr;
117
118 tr = inputTriple();
119
120 revTr = revangeMatrix(*tr);
121
122 showMatrix(*tr);
123 showMatrix(*revTr);
124
125 destoryTriple(tr);
126 destoryTriple(revTr);
127}
 结构体
结构体
1// 1、稀疏矩阵中的每一个元素的数据类型是 USER_TYPE,用户自定义数据类型
2typedef int USER_TYPE;
3
4// 2、十字交叉链中每一个节点的数据类型
5typedef struct NODE{
6 USER_TYPE data;
7 struct NODE *nextCol;
8 struct NODE *nextRow;
9}NODE;
10
11// 3、无论是行链表、列链表,都应该是多个链表,且用头指针作为起点
12typedef struct CROSS_LINK{
13 int rowCount;
14 int colCount;
15 NODE **rowHead;
16 NODE **colHead;
17}CROSS_LINK;
18
19CROSS_LINK *crossHead = NULL; //通过头结点指针实现逻辑
 结构体
结构体
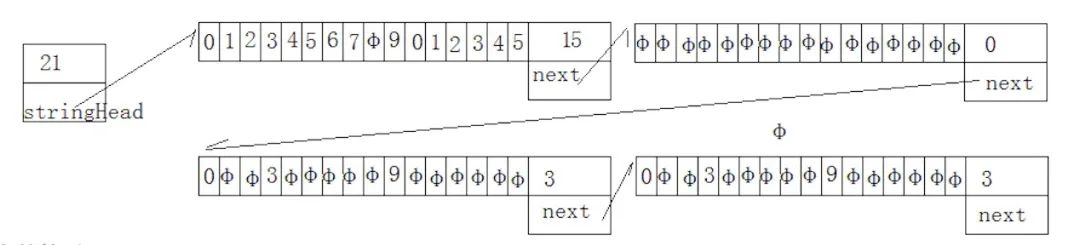
1#define UNIT_LEN 16
2
3// 1、每一个节点的数据类型
4typedef struct STRING_UNIT{
5 char string[UNIT_LEN];
6 struct STRING_UNIT *next;
7 char len;
8}STRING_UNIT;
9
10// 2、头指针进行控制
11typedef struct STRING{
12 STRING_UNIT *stringHead;
13 int length;
14}STRING;
1#ifndef _MEC_STRING_H_
2#define _MEC_STRING_H_
3
4#include
5#include
6#include
7
8#define UNIT_LEN 16
9
10typedef struct STRING_UNIT{
11 char string[UNIT_LEN];
12 struct STRING_UNIT *next;
13 char len;
14}STRING_UNIT;
15
16typedef struct STRING{
17 STRING_UNIT *stringHead;
18 int length;
19}STRING;
20
21boolean initString(STRING **string);
22STRING_UNIT *creatStringUnit();
23void destoryString(STRING **string);
24void removeStringUintAt(STRING_UNIT *curUnit);
25void setStringUnitContent(STRING_UNIT *target, const char *source, int len);
26void stringCopy(STRING *string, const char *source);
27void showString(STRING string);
28
29void showString(STRING string){
30 int count = 0;
31 int index = 0;
32 STRING_UNIT *cur;
33 register char ch;
34
35 cur = string.stringHead;
36 while(cur && count string.length){
37 ch = cur->string[index];
38 if(ch){
39 putchar(ch);
40 count++;
41 if(++index >= UNIT_LEN){
42 index = 0;
43 cur = cur->next;
44 }
45 }
46 }
47}
48
49void stringCopy(STRING *string, const char *source){
50 STRING_UNIT *cur;
51 int sourceLen;
52 int dealedCount = 0;
53
54 sourceLen = strlen(source);
55 string->length = sourceLen;
56 cur = string->stringHead;
57
58 while(sourceLen > 0){
59 setStringUnitContent(cur, source + dealedCount++ * UNIT_LEN,
60 sourceLen > UNIT_LEN ? UNIT_LEN : sourceLen);
61 sourceLen -= UNIT_LEN;
62
63 if(sourceLen > 0){
64 if(cur->next == NULL){
65 cur->next = creatStringUnit();
66 }
67 cur = cur->next;
68 }
69 }
70
71 while(cur->next){
72 removeStringUintAt(cur);
73 }
74
75}
76
77void setStringUnitContent(STRING_UNIT *target, const char *source, int len){
78 int index;
79
80 for(index = 0; index 81 target->string[index] = source[index];
82 }
83
84 while(index 85 target->string[index++] = 0;
86 }
87
88 target->len = len;
89}
90
91void removeStringUintAt(STRING_UNIT *curUnit){
92 STRING_UNIT *p;
93
94 if(curUnit->next){
95 p = curUnit->next;
96 curUnit->next = p->next;
97 free(p);
98 }
99}
100
101void destoryString(STRING **string){
102 STRING_UNIT *head;
103
104 if(!*string){
105 return;
106 }
107
108 head = (*string)->stringHead;
109 while(head){
110 STRING_UNIT *p;
111
112 p = head;
113 head = head->next;
114 free(p);
115 }
116
117 free(*string);
118 *string = NULL;
119}
120
121STRING_UNIT *creatStringUnit(){
122 STRING_UNIT *head;
123
124 head = (STRING_UNIT *)calloc(sizeof(STRING_UNIT), 1);
125
126 head->len = 0;
127 head->next = NULL;
128
129 return head;
130}
131
132boolean initString(STRING **string){
133 if(*string){
134 return FALSE;
135 }
136
137 *string = (STRING *)malloc(sizeof(STRING));
138
139 (*string)->stringHead = creatStringUnit();
140 (*string)->length = 0;
141
142 return TRUE;
143}
144
145#endif






















 140
140











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








