10.Netty之ByteBuf介绍(二)
一、ByteBuf组成
ByteBuf由四部分组成
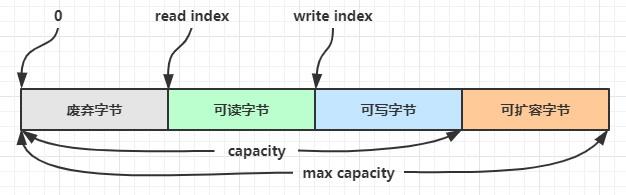
说明
- ByteBuf 是一个字节容器,容器里面的的数据分为四个部分
- 第一个部分是已经丢弃的字节,这部分数据是无效的;(已经读过的内容)
- 第二部分是可读字节,这部分数据是 ByteBuf 的主体数据, 从 ByteBuf 里面读取的数据都来自这一部分;(已经写入但还未读取的内容)
- 第三部分数据是可写字节,所有写到 ByteBuf 的数据都会写到这一段;(剩余可写入数据的空间大小)
- 最后一部分表示的是该 ByteBuf 最多还能扩容多少容量
- 上图中除了可扩容部分,剩下的内容是被两个指针给划分出来的,从左到右,依次是读指针(readerIndex)、写指针(writerIndex),然后还有一个变量 capacity,表示 ByteBuf 底层内存的总容量;
- 从 ByteBuf 中每读取一个字节,readerIndex 自增1,ByteBuf 里面总共有
writerIndex-readerIndex个字节可读, 由此可以推论出当 readerIndex 与 writerIndex 相等的时候,ByteBuf 不可读; - 写数据是从 writerIndex 指向的部分开始写,每写一个字节,writerIndex 自增1,直到增到 capacity,这个时候,表示 ByteBuf 已经不可写了;
- ByteBuf 里面还有一个参数 maxCapacity,当向 ByteBuf 写数据的时候,如果容量不足,那么这个时候可以进行扩容,直到 capacity 扩容到 maxCapacity,超过 maxCapacity 就会报错。
二、读取/写入API
2.1 写入
方法列表,省略一些不重要的方法
| 方法签名 | 含义 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| writeBoolean(boolean value) | 写入 boolean 值 | 用一字节 01/00 代表 true/false |
| writeByte(int value) | 写入 byte 值 | |
| writeShort(int value) | 写入 short 值 | |
| writeInt(int value) | 写入 int 值 | Big Endian,即 0x250,写入后 00 00 02 50 |
| writeIntLE(int value) | 写入 int 值 | Little Endian,即 0x250,写入后 50 02 00 00 |
| writeLong(long value) | 写入 long 值 | |
| writeChar(int value) | 写入 char 值 | |
| writeFloat(float value) | 写入 float 值 | |
| writeDouble(double value) | 写入 double 值 | |
| writeBytes(ByteBuf src) | 写入 netty 的 ByteBuf | |
| writeBytes(byte[] src) | 写入 byte[] | |
| writeBytes(ByteBuffer src) | 写入 nio 的 ByteBuffer | |
| int writeCharSequence(CharSequence sequence, Charset charset) | 写入字符串 |
注意
- 这些方法的未指明返回值的,其返回值都是 ByteBuf,意味着可以链式调用
- 网络传输,默认习惯是 Big Endian
示例
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBufAllocator;
import static io.netty.buffer.ByteBufUtil.appendPrettyHexDump;
import static io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil.NEWLINE;
public class ByteBufWriteTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建ByteBuf
ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(16,20);
log(buffer);
// 向buffer中写入数据
buffer.writeBytes(new byte[]{1, 2, 3, 4});
log(buffer);
buffer.writeInt(5);
log(buffer);
buffer.writeIntLE(6);
log(buffer);
buffer.writeLong(7);
log(buffer);
}
private static void log(ByteBuf buffer) {
int length = buffer.readableBytes();
int rows = length / 16 + (length % 15 == 0 ? 0 : 1) + 4;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(rows * 80 * 2)
.append("read index:").append(buffer.readerIndex())
.append(" write index:").append(buffer.writerIndex())
.append(" capacity:").append(buffer.capacity())
.append(NEWLINE);
appendPrettyHexDump(buf, buffer);
System.out.println(buf.toString());
}
}
运行结果
read index:0 write index:0 capacity:16
read index:0 write index:4 capacity:16
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
read index:0 write index:8 capacity:16
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 00 00 00 05 |........ |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
read index:0 write index:12 capacity:16
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 00 00 00 05 06 00 00 00 |............ |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
read index:0 write index:20 capacity:20
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 00 00 00 05 06 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
|00000010| 00 00 00 07 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
还有一类方法是 set 开头的一系列方法,也可以写入数据,但不会改变写指针位置
2.2 读取
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| buffer.readByte() | 每次读取一个字节 |
| buffer.readInt() | 每次读取一个整数,也就是四个字节 |
| buffer.markReaderIndex() | 为读指针做一个标记,配合下面的方法可以实现重复读取某个数 |
| buffer.resetReaderIndex() | 将读指针跳到上一个标记过的地方实现重复读取某个数 |
除了上面一些了read开头的方法以外,还有一系列get开头的方法也可以读取数据,只不过get开头的方法不会改变读指针位置。相当于是按索引去获取。
示例
如果需要重复读取,需要调用buffer.markReaderIndex()对读指针进行标记,并通过buffer.resetReaderIndex()将读指针恢复到mark标记的位置
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBufAllocator;
import static com.lilinchao.netty.bytebuf.ByteBufWriteTest.log;
public class ByteBufReadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建ByteBuf
ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(16, 20);
// 向buffer中写入数据
buffer.writeBytes(new byte[]{1, 2, 3, 4});
buffer.writeInt(5);
log(buffer);
// 读取4个字节
System.out.println(buffer.readByte());
System.out.println(buffer.readByte());
System.out.println(buffer.readByte());
System.out.println(buffer.readByte());
log(buffer);
// 通过mark与reset实现重复读取
buffer.markReaderIndex();
System.out.println(buffer.readInt());
log(buffer);
// 恢复到mark标记处
buffer.resetReaderIndex();
log(buffer);
}
}
运行结果
read index:0 write index:8 capacity:16
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 00 00 00 05 |........ |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
1
2
3
4
read index:4 write index:8 capacity:16
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 00 00 00 05 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
5
read index:8 write index:8 capacity:16
read index:4 write index:8 capacity:16
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 00 00 00 05 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
三、扩容
从上方写入数据示例根据结果可以看到,在如下的代码中产生了动态扩容操作
buffer.writeLong(7);
log(buffer);
运行结果
//扩容前
read index:0 write index:12 capacity:16
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 00 00 00 05 06 00 00 00 |............ |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
//扩容后
read index:0 write index:20 capacity:20
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 01 02 03 04 00 00 00 05 06 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
|00000010| 00 00 00 07 |.... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
扩容规则
- 如何写入后数据大小未超过 512,则选择下一个 16 的整数倍,例如写入后大小为 12 ,则扩容后 capacity 是 16
- 如果写入后数据大小超过 512,则选择下一个 2^n,例如写入后大小为 513,则扩容后 capacity 是 210=1024(29=512 已经不够了)
- 扩容不能超过 max capacity 会报错






















 643
643











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








