一、DES
1 概述
DES算法全称为Data Encryption Standard,即数据加密算法,它是IBM公司于1975年研究成功并公开发表的。DES算法的入口参数有三个:Key、Data、Mode。其中Key为8个字节共64位,是DES算法的工作密钥;Data也为8个字节64位,是要被加密或被解密的数据;Mode为DES的工作方式,有两种:加密或解密。
2 算法原理
DES算法把64位的明文输入块变为64位的密文输出块,它所使用的密钥也是64位,其算法主要分为两步:
(1)初始置换
其功能是把输入的64位数据块按位重新组合,并把输出分为L0、R0两部分,每部分各长32位,其置换规则为将输入的第58位换到第一位,第50位换到第2位……依此类推,最后一位是原来的第7位。L0、R0则是换位输出后的两部分,L0是输出的左32位,R0是右32位,例:设置换前的输入值为D1D2D3……D64,则经过初始置换后的结果为:L0=D58D50……D8;R0=D57D49……D7。
(2)逆置换
经过16次迭代运算后,得到L16、R16,将此作为输入,进行逆置换,逆置换正好是初始置换的逆运算,由此即得到密文输出。
二、 两个密钥的三重DES
由于DES密钥只有56bit,易于遭受穷举时攻击。作为一种替代加密方案,Tuchman提出使用两个密钥的三重DES加密方法,并在1985年成为美国的一个商用加密标准。该方法使用两个密钥,执行三次DES算法,如图2所示。加密的过程是加密-解密-加密,解密的过程是解密-加密-解密。
采用两个密钥进行三重加密的好处有:①两个密钥合起来有效密钥长度有112bit,可以满足商业应用的需要,若采用总长为168bit的三个密钥,会产生不必要的开销。②加密时采用加密-解密-加密,而不是加密-加密-加密的形式,这样有效的实现了与现有DES系统的向后兼容问题。因为当K1=K2时,三重DES的效果就和原来的DES一样,有助于逐渐推广三重DES。③三重DES具有足够的安全性,目前还没有关于攻破三重DES的报道。
什么是三重DES
三重DES是为了增加DES的强度,将DES重复3次所得到的一种密码算法,通常缩写为3DES。
二 三重DSE加密

明文经过三次DES处理才能变成最后的密文,由于DES密钥长度实质是56位,因此3DES的密钥长度就是56*3=168比特。
注意:三重DES的三次DES加密是(加密->解密->加密),而不是(加密->加密->加密),为什么这样设计呢?看看下面这张图就明白了。
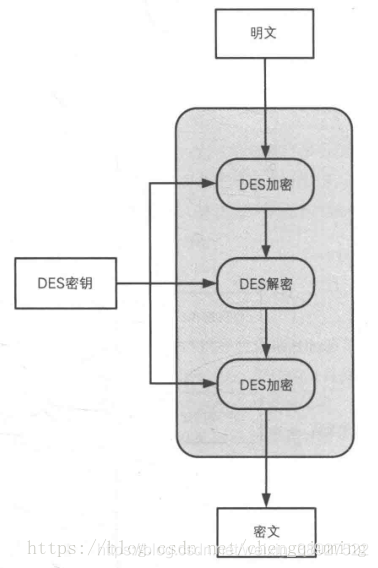
如果三次DES加密的密钥都相同,前两次DES,相当于还原成了密文,这样看来,真正起作用的只是最后一次。这样做的好处是:三重DES对DES具备向下兼容性。
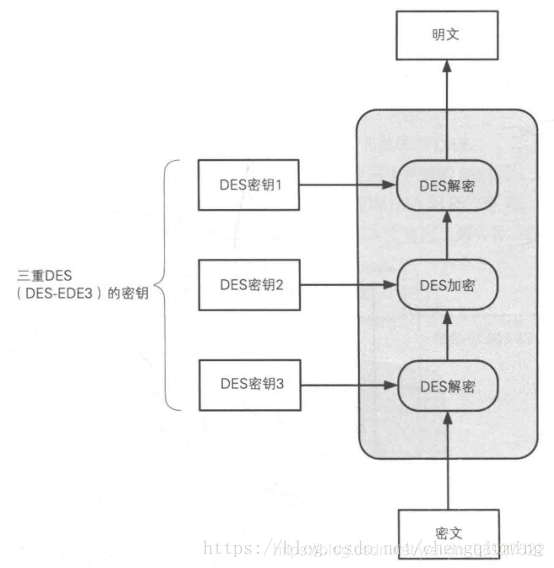
还有一种密码叫DES-EDE2,下面我们用图来描述这一种密码。

当然,只有三个密钥互不相等才是正宗的DES-EDE3。
三 三重DES解密
三重DES的解密过程和加密过程正好相反,是以密钥3、密钥2、密钥1的顺序执行解密->加密->解密的操作。
四 三重DES现状
尽管三重DES目前还被银行等机构使用,但其处理速度不高,除了特别重视向下兼容性的情况外,很少被用于新的用途。
pydes:
#-*- coding: utf8 -*-
#Initial permut matrix for the datas
# IP initial permut
PI = [58, 50, 42, 34, 26, 18, 10, 2,
60, 52, 44, 36, 28, 20, 12, 4,
62, 54, 46, 38, 30, 22, 14, 6,
64, 56, 48, 40, 32, 24, 16, 8,
57, 49, 41, 33, 25, 17, 9, 1,
59, 51, 43, 35, 27, 19, 11, 3,
61, 53, 45, 37, 29, 21, 13, 5,
63, 55, 47, 39, 31, 23, 15, 7]
#Initial permut made on the key
CP_1 = [57, 49, 41, 33, 25, 17, 9,
1, 58, 50, 42, 34, 26, 18,
10, 2, 59, 51, 43, 35, 27,
19, 11, 3, 60, 52, 44, 36,
63, 55, 47, 39, 31, 23, 15,
7, 62, 54, 46, 38, 30, 22,
14, 6, 61, 53, 45, 37, 29,
21, 13, 5, 28, 20, 12, 4]
#Permut applied on shifted key to get Ki+1
CP_2 = [14, 17, 11, 24, 1, 5, 3, 28,
15, 6, 21, 10, 23, 19, 12, 4,
26, 8, 16, 7, 27, 20, 13, 2,
41, 52, 31, 37, 47, 55, 30, 40,
51, 45, 33, 48, 44, 49, 39, 56,
34, 53, 46, 42, 50, 36, 29, 32]
#Expand matrix to get a 48bits matrix of datas to apply the xor with Ki
E = [32, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13,
12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17,
16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21,
20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25,
24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29,
28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 1]
#SBOX
S_BOX = [
[[14, 4, 13, 1, 2, 15, 11, 8, 3, 10, 6, 12, 5, 9, 0, 7],
[0, 15, 7, 4, 14, 2, 13, 1, 10, 6, 12, 11, 9, 5, 3, 8],
[4, 1, 14, 8, 13, 6, 2, 11, 15, 12, 9, 7, 3, 10, 5, 0],
[15, 12, 8, 2, 4, 9, 1, 7, 5, 11, 3, 14, 10, 0, 6, 13],
],
[[15, 1, 8, 14, 6, 11, 3, 4, 9, 7, 2, 13, 12, 0, 5, 10],
[3, 13, 4, 7, 15, 2, 8, 14, 12, 0, 1, 10, 6, 9, 11, 5],
[0, 14, 7, 11, 10, 4, 13, 1, 5, 8, 12, 6, 9, 3, 2, 15],
[13, 8, 10, 1, 3, 15, 4, 2, 11, 6, 7, 12, 0, 5, 14, 9],
],
[[10, 0, 9, 14, 6, 3, 15, 5, 1, 13, 12, 7, 11, 4, 2, 8],
[13, 7, 0, 9, 3, 4, 6, 10, 2, 8, 5, 14, 12, 11, 15, 1],
[13, 6, 4, 9, 8, 15, 3, 0, 11, 1, 2, 12, 5, 10, 14, 7],
[1, 10, 13, 0, 6, 9, 8, 7, 4, 15, 14, 3, 11, 5, 2, 12],
],
[[7, 13, 14, 3, 0, 6, 9, 10, 1, 2, 8, 5, 11, 12, 4, 15],
[13, 8, 11, 5, 6, 15, 0, 3, 4, 7, 2, 12, 1, 10, 14, 9],
[10, 6, 9, 0, 12, 11, 7, 13, 15, 1, 3, 14, 5, 2, 8, 4],
[3, 15, 0, 6, 10, 1, 13, 8, 9, 4, 5, 11, 12, 7, 2, 14],
],
[[2, 12, 4, 1, 7, 10, 11, 6, 8, 5, 3, 15, 13, 0, 14, 9],
[14, 11, 2, 12, 4, 7, 13, 1, 5, 0, 15, 10, 3, 9, 8, 6],
[4, 2, 1, 11, 10, 13, 7, 8, 15, 9, 12, 5, 6, 3, 0, 14],
[11, 8, 12, 7, 1, 14, 2, 13, 6, 15, 0, 9, 10, 4, 5, 3],
],
[[12, 1, 10, 15, 9, 2, 6, 8, 0, 13, 3, 4, 14, 7, 5, 11],
[10, 15, 4, 2, 7, 12, 9, 5, 6, 1, 13, 14, 0, 11, 3, 8],
[9, 14, 15, 5, 2, 8, 12, 3, 7, 0, 4, 10, 1, 13, 11, 6],
[4, 3, 2, 12, 9, 5, 15, 10, 11, 14, 1, 7, 6, 0, 8, 13],
],
[[4, 11, 2, 14, 15, 0, 8, 13, 3, 12, 9, 7, 5, 10, 6, 1],
[13, 0, 11, 7, 4, 9, 1, 10, 14, 3, 5, 12, 2, 15, 8, 6],
[1, 4, 11, 13, 12, 3, 7, 14, 10, 15, 6, 8, 0, 5, 9, 2],
[6, 11, 13, 8, 1, 4, 10, 7, 9, 5, 0, 15, 14, 2, 3, 12],
],
[[13, 2, 8, 4, 6, 15, 11, 1, 10, 9, 3, 14, 5, 0, 12, 7],
[1, 15, 13, 8, 10, 3, 7, 4, 12, 5, 6, 11, 0, 14, 9, 2],
[7, 11, 4, 1, 9, 12, 14, 2, 0, 6, 10, 13, 15, 3, 5, 8],
[2, 1, 14, 7, 4, 10, 8, 13, 15, 12, 9, 0, 3, 5, 6, 11],
]
]
#Permut made after each SBox substitution for each round
P = [16, 7, 20, 21, 29, 12, 28, 17,
1, 15, 23, 26, 5, 18, 31, 10,
2, 8, 24, 14, 32, 27, 3, 9,
19, 13, 30, 6, 22, 11, 4, 25]
#Final permut for datas after the 16 rounds
PI_1 = [40, 8, 48, 16, 56, 24, 64, 32,
39, 7, 47, 15, 55, 23, 63, 31,
38, 6, 46, 14, 54, 22, 62, 30,
37, 5, 45, 13, 53, 21, 61, 29,
36, 4, 44, 12, 52, 20, 60, 28,
35, 3, 43, 11, 51, 19, 59, 27,
34, 2, 42, 10, 50, 18, 58, 26,
33, 1, 41, 9, 49, 17, 57, 25]
#Matrix that determine the shift for each round of keys
SHIFT = [1,1,2,2,2,2,2,2,1,2,2,2,2,2,2,1]
def string_to_bit_array(text):#Convert a string into a list of bits
array = list()
for char in text:
binval = binvalue(char, 8)#Get the char value on one byte
array.extend([int(x) for x in list(binval)]) #Add the bits to the final list
return array
def bit_string_to_array(bitText):
array = list()
for bit in bitText.replace(" ",""):
array.append(int(bit))
return array
def bit_array_to_string(array): #Recreate the string from the bit array
res = ''.join([chr(int(y,2)) for y in [''.join([str(x) for x in _bytes]) for _bytes in nsplit(array,8)]])
return res
# 根据ascil编码把字符转成对应的二进制
def binvalue(val, bitsize): #Return the binary value as a string of the given size
binval = bin(val)[2:] if isinstance(val, int) else bin(ord(val))[2:]
if len(binval) > bitsize:
raise ("binary value larger than the expected size")
while len(binval) < bitsize:
binval = "0"+binval #Add as many 0 as needed to get the wanted size
return binval
def nsplit(s, n):#Split a list into sublists of size "n"
return [s[k:k+n] for k in range(0, len(s), n)]
def showBits(s, n):#Split a list into sublists of size "n"
return " ".join(["".join([str(i) for i in s[k:k+n]]) for k in range(0, len(s), n)])
ENCRYPT=1
DECRYPT=0
class des():
def __init__(self):
self.password = None
self.text = None
self.keys = list()
def run(self, key, text, action=ENCRYPT):
self.password = key
self.text = text
# 产生所有子密钥
self.generatekeys() #Generate all the keys
result = list()
block = self.text
block = self.permut(block,PI)#Apply the initial permutation
g, d = nsplit(block, 32) #g(LEFT), d(RIGHT)
tmp = None
for i in range(16): #Do the 16 rounds
d_e = self.expand(d, E) #Expand d to match Ki size (48bits)
if action == ENCRYPT:
tmp = self.xor(self.keys[i], d_e)#If encrypt use Ki
else:
tmp = self.xor(self.keys[15-i], d_e)#If decrypt start by the last key
tmp = self.substitute(tmp) #Method that will apply the SBOXes
tmp = self.permut(tmp, P)
tmp = self.xor(g, tmp) # tmp = f(Rn-1,Kn)
g = d # Ln = Rn-1
d = tmp # Rn = Ln-1 + f(Rn-1,Kn)
print(f"L{i+1}:{showBits(g, 8)}")
print(f"R{i + 1}:{showBits(d, 8)}")
result += self.permut(d+g, PI_1) #Do the last permut and append the result to result
final_res = "".join([str(i) for i in result])
return final_res
# if padding and action==DECRYPT:
# return self.removePadding(final_res) #Remove the padding if decrypt and padding is true
# else:
# return final_res #Return the final string of data ciphered/deciphered
def substitute(self, d_e):#Substitute bytes using SBOX
subblocks = nsplit(d_e, 6)#Split bit array into sublist of 6 bits
result = list()
for i in range(len(subblocks)): #For all the sublists
block = subblocks[i]
row = int(str(block[0])+str(block[5]),2)#Get the row with the first and last bit
column = int(''.join([str(x) for x in block[1:][:-1]]),2) #Column is the 2,3,4,5th bits
val = S_BOX[i][row][column] #Take the value in the SBOX appropriated for the round (i)
bin = binvalue(val, 4)#Convert the value to binary
result += [int(x) for x in bin]#And append it to the resulting list
return result
# 置换
def permut(self, block, table):#Permut the given block using the given table (so generic method)
return [block[x-1] for x in table]
# 扩展
def expand(self, block, table):#Do the exact same thing than permut but for more clarity has been renamed
return [block[x-1] for x in table]
def xor(self, t1, t2):#Apply a xor and return the resulting list
return [x^y for x,y in zip(t1,t2)]
def generatekeys(self):#Algorithm that generates all the keys
self.keys = []
# 把密钥转成这个形式 00110100 11000010.....
key = self.password
key = self.permut(key, CP_1) #Apply the initial permut on the key
g, d = nsplit(key, 28) #Split it in to (g->LEFT),(d->RIGHT)
for i in range(16):#Apply the 16 rounds
g, d = self.shift(g, d, SHIFT[i]) #Apply the shift associated with the round (not always 1)
tmp = g + d #Merge them
self.keys.append(self.permut(tmp, CP_2)) #Apply the permut to get the Ki
def shift(self, g, d, n): #Shift a list of the given value
return g[n:] + g[:n], d[n:] + d[:n]
def addPadding(self):#Add padding to the datas using PKCS5 spec.
pad_len = 8 - (len(self.text) % 8)
self.text += pad_len * chr(pad_len)
def removePadding(self, data):#Remove the padding of the plain text (it assume there is padding)
pad_len = ord(data[-1])
return data[:-pad_len]
def encrypt(self, key, text):
return self.run(key, text, ENCRYPT)
def decrypt(self, key, text):
return self.run(key, text, DECRYPT)
if __name__ == '__main__':
plain_text = bit_string_to_array("00000001 00100011 01000101 01100111 10001001 10101011 11001101 11101111")
key = bit_string_to_array("00010011 00110100 01010111 01111001 10011011 10111100 11011111 11110001")
d = des()
r = d.encrypt(key,plain_text)
print(r)
# 测试cyberchef
r = bit_string_to_array("01011010 11110101 00010101 10110000 01001011 11101111 01010010 01000001")
r2 = d.decrypt(key,r)
print("Ciphered: %r" % r)
print("Deciphered: ", r2)
# 07040502033636363636363636363636363636363636363636363636363636363636363636363636363636363636363636363636363636363636363636363636
#
# 6d6e6f68695c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c
l = [1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]
def showBits(s, n):#Split a list into sublists of size "n"
return " ".join(["".join([str(i) for i in s[k:k+n]]) for k in range(0, len(s), n)])
print(showBits(l, 8))CBC模式调用:
from pyDes import des, CBC, PAD_PKCS5
import binascii
# 秘钥
KEY = 'Codeoooo'
def des_encrypt(s):
"""
DES 加密
:param s: 原始字符串
:return: 加密后字符串,16进制
"""
secret_key = KEY # 密码
iv = secret_key # 偏移
# secret_key:加密密钥,CBC:加密模式,iv:偏移, padmode:填充
des_obj = des(secret_key, CBC, iv, pad=None, padmode=PAD_PKCS5)
# 返回为字节
secret_bytes = des_obj.encrypt(s, padmode=PAD_PKCS5)
# 返回为16进制
return bytes.decode(binascii.b2a_hex(secret_bytes))
def des_descrypt(s):
"""
DES 解密
:param s: 加密后的字符串,16进制
:return: 解密后的字符串
"""
secret_key = KEY
iv = secret_key
des_obj = des(secret_key, CBC, iv, pad=None, padmode=PAD_PKCS5)
decrypt_str = des_obj.decrypt(binascii.a2b_hex(s), padmode=PAD_PKCS5)
return bytes.decode(decrypt_str)
print(des_encrypt('codeooo'))
print(des_descrypt('4ff67fd9b661f01d'))ECB模式调用:
from pyDes import des, ECB, PAD_PKCS5
import base64
DES_SECRET_KEY = '12345678'
data = 'codeooo'
des_obj = des(DES_SECRET_KEY, ECB, DES_SECRET_KEY, padmode=PAD_PKCS5)
secret_bytes = str(base64.b64encode(des_obj.encrypt(data)), encoding = 'utf-8')
print(secret_bytes)
























 1235
1235

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










