文章目录
- 102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
- 107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
- 199. Binary Tree Right Side View
- 637. Average of Levels in Binary Tree
- 429. N-ary Tree Level Order Traversal
- 515. Find Largest Value in Each Tree Row
- 116/117. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
- 104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
- 111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
- 226. Invert Binary Tree
- 101. Symmetric Tree
层序遍历
- 102.二叉树的层序遍历
- 107.二叉树的层次遍历II
- 199.二叉树的右视图
- 637.二叉树的层平均值
- 429.N叉树的层序遍历
- 515.在每个树行中找最大值
- 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
- 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
- 104.二叉树的最大深度
- 111.二叉树的最小深度
102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
Given the
rootof a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (i.e., from left to right, level by level).Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
-
Layer BFS, 层次遍历
-
Sol and template
class Solution:
def levelOrderBottom(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
queue = deque([root])
res = []
while queue:
level = []
for _ in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.popleft()
level.append(node.val)
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
res.append(level)
return res
107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
Given the
rootof a binary tree, return the bottom-up level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (i.e., from left to right, level by level from leaf to root).Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[15,7],[9,20],[3]]
class Solution:
def levelOrderBottom(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
queue = deque([root])
res = []
while queue:
level = []
for _ in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.popleft()
level.append(node.val)
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
res.append(level)
return res[::-1]
- reverse: res[::-1]
199. Binary Tree Right Side View
Given the
rootof a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.Example 1:

Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5,null,4] Output: [1,3,4]
class Solution:
def rightSideView(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
if not root:
return []
queue = deque([root])
res = []
while queue:
#level = []
size = len(queue)
for _ in range(size):
node = queue.popleft()
level=node.val
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
res.append(level)
return res
637. Average of Levels in Binary Tree
Given the
rootof a binary tree, return the average value of the nodes on each level in the form of an array. Answers within10-5of the actual answer will be accepted.Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000]
class Solution:
def averageOfLevels(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[float]:
if not root:
return []
queue = deque([root])
res = []
while queue:
level = 0
size = len(queue)
for _ in range(size):
node = queue.popleft()
level += node.val
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
res.append(level/size)
return res
429. N-ary Tree Level Order Traversal
Given an n-ary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes’ values.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] Output: [[1],[3,2,4],[5,6]]
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: 'Node') -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
queue = deque([root])
res = []
while queue:
level =[]
size =len(queue)
for _ in range(size):
node = queue.popleft()
level.append(node.val)
for x in node.children:
if x:
queue.append(x)
res.append(level)
return res
515. Find Largest Value in Each Tree Row
Given the
rootof a binary tree, return an array of the largest value in each row of the tree (0-indexed).
class Solution:
def largestValues(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
if not root:
return []
queue = deque([root])
res = []
while queue:
level_max = float('-inf')
size = len(queue)
for _ in range(size):
node = queue.popleft()
if node.val > level_max:
level_max = node.val
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
res.append(level_max)
return res
- float(‘-inf’)
116/117. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
Given the
rootof a binary tree, return an array of the largest value in each row of the tree (0-indexed).
- define “prev”
class Solution:
def connect(self, root: 'Optional[Node]') -> 'Optional[Node]':
if not root:
return root
queue = deque([root])
while queue:
prev = None
size = len(queue)
for _ in range(size):
node = queue.popleft()
if prev:
prev.next = node
prev = node
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return root
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Given the
rootof a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
queue = deque([root])
res = 0
while queue:
size = len(queue)
for _ in range(size):
node = queue.popleft()
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
res+=1
return res
111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
queue = deque([root])
depth = 1
while queue:
size = len(queue)
for _ in range(size):
node = queue.popleft()
if not node.left and not node.right:
return depth
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
depth+=1
return depth
226. Invert Binary Tree
Given the root of a binary tree, invert the tree, and return its root.
Example 1:

Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
Output: [4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
Sol 1: DFS
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if not root:
return None
root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left
self.invertTree(root.left)
self.invertTree(root.right)
return root
Sol 2: BFS
class Solution1:
def invertTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if not root:
return None
queue = deque([root])
while queue:
size = len(queue)
for _ in range(size):
node = queue.popleft()
node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return root
101. Symmetric Tree
- not a easy problem!!
Given the
rootof a binary tree, check whether it is a mirror of itself (i.e., symmetric around its center).Example 1:
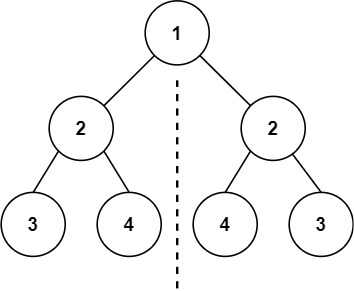
Input: root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] Output: true
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
if not root:
return True
def compare(left,right):
if not left and not right: #左右都不存在
return True
if not left or not right: #左右一个存在一个不存在
return False
if left.val != right.val: #都存在但value不等
return False
#都存在且val相等, 递归
outside = compare(left.left, right.right)
inside = compare(left.right,right.left)
return outside and inside
return compare(root.left,root.right)





















 115
115











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








