课程实验题目:算术编码及其应用 完成时间:2019.6.15 说明:1. 实验成绩占总成绩10%,每人独立完成实验并撰写实验报告。 2. 不限定软件,实验程序应能对1000kb的英文文本编解码。不能使用网络上现成的代码(如:自适应图像算术编码等)。 3. 可以参考 Jyotika Doshi的二次幂总频率算法或 Amir Said的基于树的累积分布更新算法。 4. 实验报告应包含算法原理;关键算法的伪代码;实验结果(压缩比、运行时间和解码错误占比等);算法的主要代码部分。
《信息论课程大作业》
算术编码及其应用
班级: 1601014
姓名: 马秋平
学号:16010140048
一 算法原理
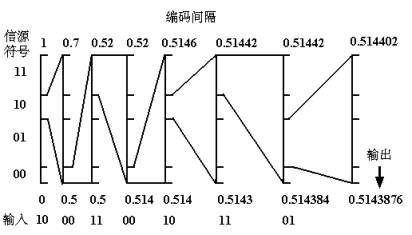
算术编码的主要思想是计算输入信源符号序列所对应的区间,然后在区间中间任取一点,以二进制表示适当截断作为序列的编码结果。
算术编码用到两个基本的参数:符号的概率和它的编码间隔。信源符号的概率决定压缩编码的效率,也决定编码过程中信源符号的间隔,而这些间隔包含在0到1之间。编码过程中的间隔决定了符号压缩后的输出。
算术编码方法是将被编码的一则消息或符号串(序列)表示成0和1之间的一个间隔,即对一串符号直接编码成[0,1]区间上的一个浮点小数。符号序列越长,编码表示它的间隔越小,表示这一段间隔所需的位数也就越多。信源中的符号序列任然需要根据某种模式生成概率的大小来减少间隔。可能出现的符号概率要比不太可能出现的符号减少范围小,因此,只正加较少的比特位。
在传输任何符号串之前,0符号串的完整范围设置为[0,1]。当一个符号被处理时,这一范围就依据分配这一符号的范围变窄。算术编码的过程,实际上就是依据信源符号的发生概率对码区间进行分割的过程。
给定事件序列的算术编码步骤如下:
(1)编码器在开始时将“当前间隔” [ L, H) 设置为[0,1)。
(2)对每一事件,编码器按步骤(a)和(b)进行处理
(a)编码器将“当前间隔”分为子间隔,每一个事件一个。
(b)一个子间隔的大小与下一个将出现的事件的概率成比例,编码器选择子间隔对应于下一个确切发生的事件相对应,并使它成为新的“当前间隔”。
(3)最后输出的“当前间隔”的下边界就是该给定事件序列的算术编码。
算术编码的译码过程就是一系列的比较过程,每一步比较与的大小,为前面已经译出的字符串序列,是的分布函数,即对应区间的下界,是此区间内下一个输入符号所占区间的宽度,对于K元信源,译每一个码元最多需要K-1次比较以确定是信源符号集中的哪一个。
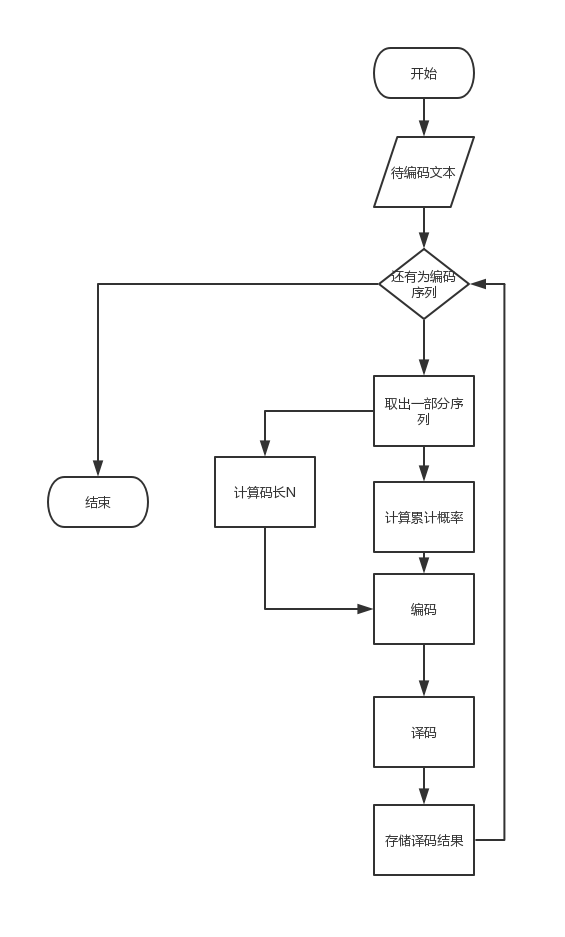
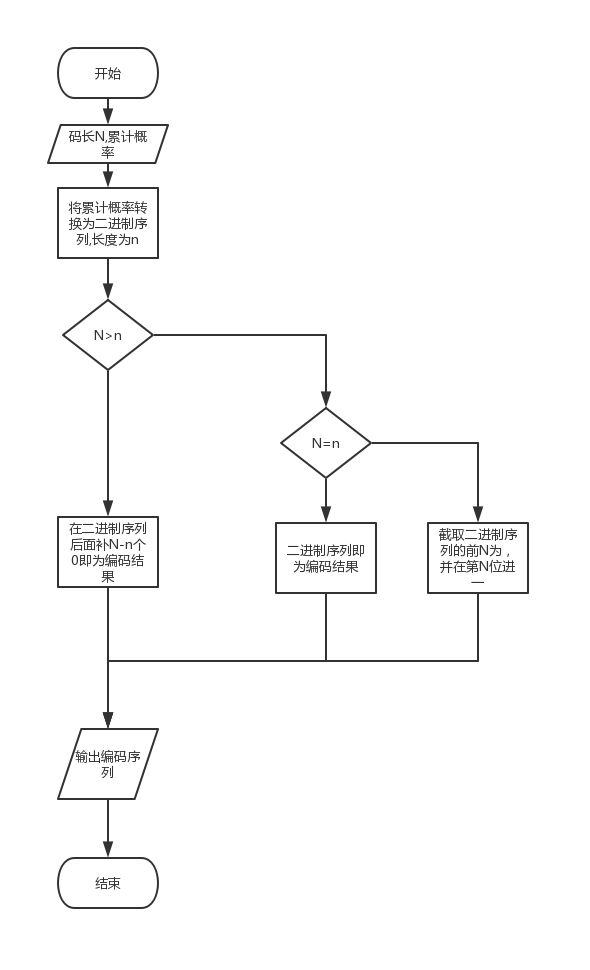
二 算法流程框图
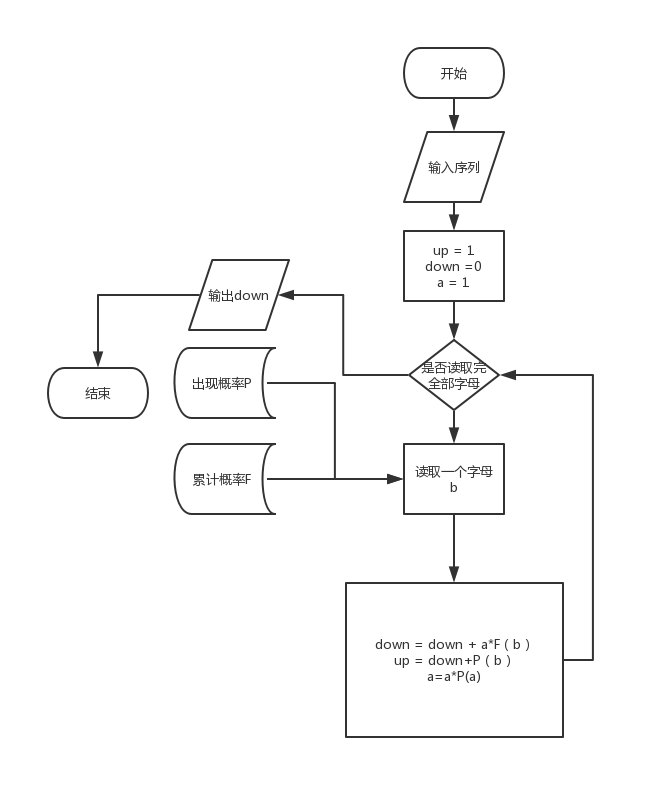
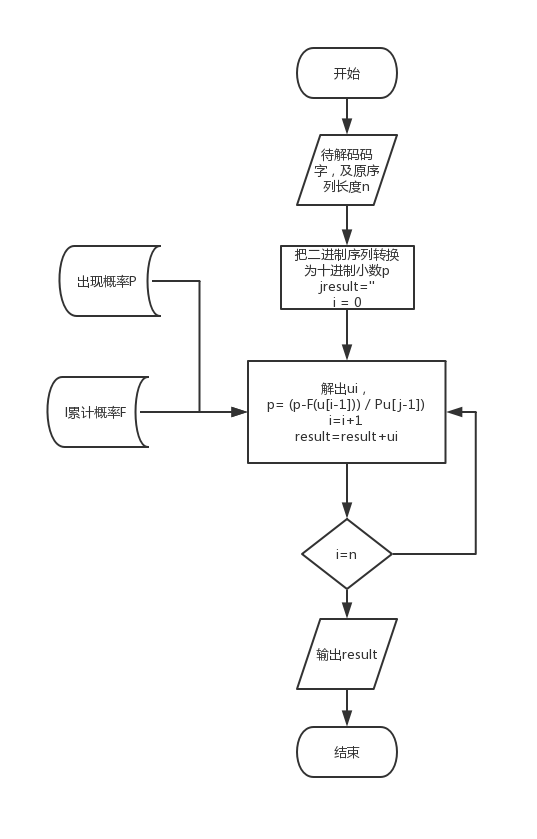
三 实验过程
- 测试文档(test.txt)
Financial regulators in Britain have imposed a rather unusual rule on the bosses of big banks. Starting next year, any guaranteed bonus of top executives could be delayed 10 years if their banks are under investigation for wrongdoing. The main purpose of this “clawback” rule is to hold bankers accountable for harmful risk-taking and to restore public trust in financial institutions. Yet officials also hope for a much larger benefit: more long-term decision making, not only by banks but by all corporations, to build a stronger economy for future generations.
- 实验代码(Python实现)
# -*-coding:utf-8-*-
import time
import numpy as np
import pprint
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
alpha_dict = {
'a': 0.0575,
'b': 0.0128,
'c': 0.0263,
'd': 0.0285,
'e': 0.0913,
'f': 0.0173,
'g': 0.0133,
'h': 0.0313,
'i': 0.0599,
'j': 0.0006,
'k': 0.0084,
'l': 0.0335,
'm': 0.0235,
'n': 0.0596,
'o': 0.0689,
'p': 0.0192,
'q': 0.0008,
'r': 0.0508,
's': 0.0567,
't': 0.0706,
'u': 0.0334,
'v': 0.0069,
'w': 0.0119,
'x': 0.0073,
'y': 0.0164,
'z': 0.0007,
' ': 0.1928,
}
color = ['#dc2624', '#2b4750', '#45a0a2',
'#e87a59', '#7dcaa9', '#649E7D',
'#dc8018', '#C89F91', '#6c6d6c',
'#4f6268', '#c7cccf'
]
# 计算信源熵
def calc_entropy(alpha_dict):
entropy = 0
gailv_jihe = list(alpha_dict.values())
for i in range(len(alpha_dict)):
entropy = entropy+gailv_jihe[i]*np.log(gailv_jihe[i])
return -entropy
# 计算累乘概率
def mul_pos(input_str=''):
pre_possibility = 1
input_list = list(input_str)
for i in input_list:
pre_possibility = pre_possibility*alpha_dict.get(i)
return pre_possibility
# 计算码长
def calc_machang(leic_possibility):
ma_length = np.ceil(-np.log(leic_possibility)/np.log(2))
return ma_length
# 十进制小数转换为二进制小数
def dec2bin(x):
x -= int(x)
bins = []
while x:
x *= 2
bins.append(1 if x >= 1. else 0)
x -= int(x)
return bins
# 二进制小数转换为十进制小数
def bin2dec(b):
d = 0
for i, x in enumerate(b):
d += 2**(-i-1)*x
return d
# 二进制小数进位
def bin_jinwei(input_bin=[]):
for i in range(len(input_bin)):
if input_bin[len(input_bin) - 1 - i] == 0:
input_bin[len(input_bin) - 1 - i] = 1
break
else:
input_bin[len(input_bin) - i - 1] = 0
return input_bin
def accu_pos(para_dict):
accu_pos_dict = {}
# print(len(alpha_dict))
for i in range(len(para_dict)):
pre_pos = 0
pre_alpha = list(para_dict.keys())[i]
if i == 0:
pre_pos = 0
else:
for j in range(i):
pre_pos = list(para_dict.values())[j]+pre_pos
accu_pos_dict[pre_alpha] = pre_pos
return accu_pos_dict
# 计算待编码序列的累计概率
def calc_xulie_pos(xulie, accu_pos_dict={}):
xulie = list(xulie)
alpha_list = list(alpha_dict.keys())
pos_down = 0
pos_up = 0
accu = 1
plt.ion()
xianshi = ''
for i in range(len(xulie)):
xianshi = xianshi+xulie[i]
pos_down = pos_down + accu*accu_dict.get(xulie[i])
pos_up = pos_down + alpha_dict.get(xulie[i])*accu
accu = accu * alpha_dict.get(xulie[i])
# plt.xlim(pos_down, accu_dict[xulie[0]]+alpha_dict[xulie[0]])
# plt.xlim(pos_down, pos_up)
# plt.ylim(0, 10)
# plt.axvspan(pos_down, pos_up, 0, 0.2, alpha=(1-i*0.1), color=random.sample(color, 1)[0])
# plt.axvline((pos_down+pos_up)/2, 0, 0.3,color='black')
# plt.text(pos_down, 5, 'P({})={}'.format(xianshi, (pos_down+pos_up)/2))
# plt.text(pos_down,2,'下界'+str(pos_down))
# plt.text(pos_up, 3.5, '上界' + str(pos_down))
# plt.title('概率区间')
# plt.xlabel(xianshi)
# plt.ylabel('概率')
# plt.show()
# time.sleep(1)
# plt.ioff()
# plt.close()
leiji_pos = (pos_down + pos_up) / 2
leiji_pos = pos_down
return leiji_pos
# # 解码过程
def decode_proceing(rec_pos, accu_pos_dict, machang=0):
pre_pos = rec_pos
alpha_list = list(alpha_dict.keys())
# print(alpha_list)
jiema_result = ''
for i in range(machang):
for j in range(1, len(alpha_list)):
leijigailv = accu_pos_dict.get(alpha_list[j])
if pre_pos > 0.8074:
jiema_result = jiema_result+' '
pre_pos = (pre_pos - accu_dict.get(' ')) / alpha_dict.get(' ')
break
elif pre_pos < leijigailv:
jiema_result = jiema_result+alpha_list[j-1]
pre_pos = (pre_pos-accu_dict.get(alpha_list[j-1])) / alpha_dict.get(alpha_list[j-1])
break
return jiema_result
# 将累计概率由十进制小数转换为二进制小数
def pos_change(leijigailv):
bin_pos = dec2bin(leijigailv)
return bin_pos
# 从小数后截取N位,如果后还有尾数则进位,如果不足则补零
def bianma(bin_pos, pre_length=30):
pre_result = []
if len(bin_pos) == pre_length:
pre_result = bin_pos
elif len(bin_pos) >= pre_length:
'''
如果N小于二进制概率位数,则将二进制小数的第N位进1,然后截取N位
'''
pre_result = bin_pos[:pre_length]
pre_result = bin_jinwei(pre_result)
else:
'''
如果N大于二进制概率位数,则将二进制小数位后面补零至N位,然后截取N位
'''
for i in range(pre_length-len(bin_pos)):
bin_pos.append(0)
pre_result = bin_pos
return pre_result
if __name__ == "__main__":
resouse_entropy = calc_entropy(alpha_dict)
print("信源熵为:{}".format(resouse_entropy))
accu_dict = accu_pos(alpha_dict)
pprint.pprint(accu_dict)
f_test = open('test1.txt', 'r')
text = f_test.read()
a = ''
total = len(text)*8
total_ = 0
count = 0
count_wrong = 0
all_unit = 0
start_time = time.time()
with open('result1.txt', 'a') as f:
for i in range(len(text)):
alp = text[i].lower()
if alp in alpha_dict.keys():
a += alp
if alp == ' ':
all_unit += 1
print(a)
r = calc_xulie_pos(a, accu_pos_dict=accu_dict)
lei_possibility = mul_pos(a)
N = calc_machang(leic_possibility=lei_possibility)
total_ = total_+N
print(N)
print(r)
bin_pos = pos_change(r)
bin_pos = bianma(bin_pos=bin_pos, pre_length=int(N))
print(bin_pos)
back_pos = bin2dec(bin_pos)
print(back_pos)
result = decode_proceing(back_pos, accu_pos_dict=accu_dict, machang=len(a))
print(result)
count += 1
f.write(result)
original_len = len(a)*8
print("压缩比为: {:.2f}%".format(-N/original_len*100))
if a != result:
count_wrong += 1
if count == 12:
f.write('n')
count = 0
a = ''
else:
a += ' '
f_test.close()
print("译码错误占比为: {:.2f}%".format(count_wrong/all_unit*100))
stop_time = time.time()
run_time = stop_time - start_time
print("运行时间为{}".format(run_time))
print("总压缩比为:{:.2f}%".format(total_/total*100))
# 测试序列 baacdaba
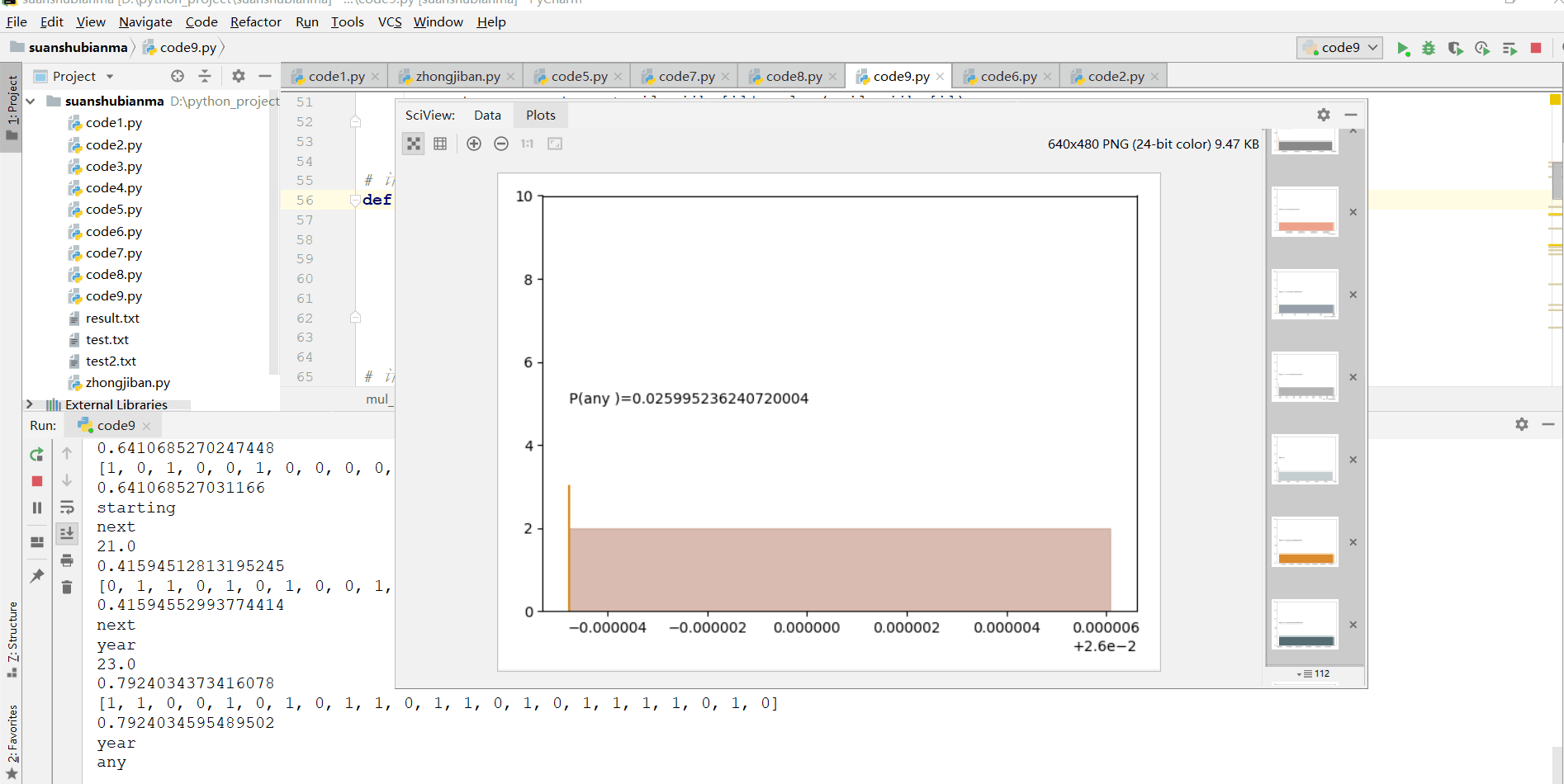
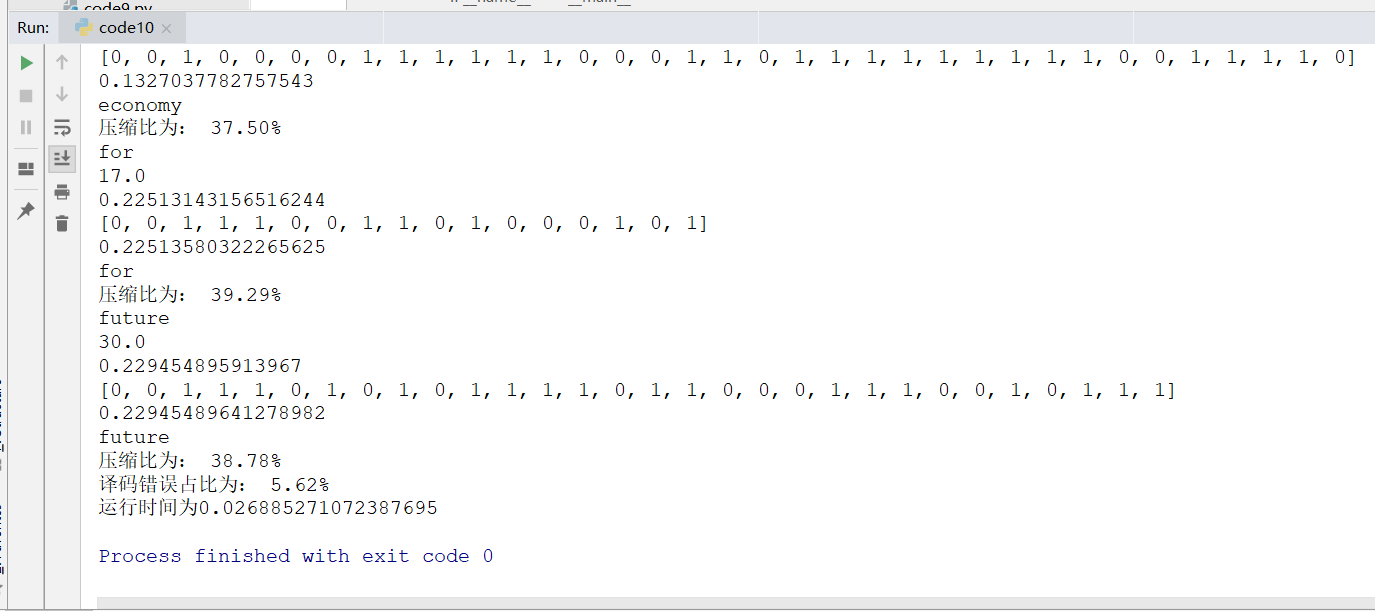
四 实验结果及分析
译码后的文档:(result.txt)
financial regulators in britain have imposed a rather unusual rule on the
bosses of big banks starting next year any guaranteed bonus of top
executives could be delayed years if their banks are under investigatin m
for wrongdoing the main purpose of this clawback yrule is to hold
bankers accountable for harmful risk takingsand to restore public trust in financial
institutiontabyet officials also hope for a much larger benefit more long term
decision making not only by banks but by all corporationtaato build
a stronger economy for future
分析:
- 由于所给信源符号集中只有小写字母及空格,所以在编码过程中我将大写转换为小写,将除空格外的符号全部转换为空格。
- 由于Python 的浮点数精度只有小数点后17位,所以每次编码的序列长度不能过长,当字符串序列长度过长时,序列区间越来越小,计算机不能精确识别,导致译码错误,由于我是以空格来作为字符串的结束标志,所以每次长度不一样,比如原文中的“investigation”错误的译成了“investigatin m”。
- 由于ASCII码在计算机中占7个二进制位,所以我们可以用编码后的二进制码长度和序列长度与7的乘积来计算编码效率。
运行结果如下:
五 心得与体会
略。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。




















 1679
1679

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








