首先是ArrayList的继承体系,代码如下:
Java代码
 publicclassArrayListextendsAbstractList
publicclassArrayListextendsAbstractList
implementsList, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable public class ArrayList extends AbstractList implements List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
可以看到ArrayList是List接口的一个实现类,List接口规定可以存放有序重复的元素,因此ArrayList遵循了这一原则.接着看一下ArrayList的构造方法:
Java代码
 publicArrayList(intinitialCapacity) {
publicArrayList(intinitialCapacity) {
super();
if(initialCapacity <0)//如果参数小于0,则抛出参数不合法异常
thrownewIllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData =newObject[initialCapacity];//初始化ArrayList底层维护的数组
}
publicArrayList() {
this(10);//调用本类的有参构造方法
} public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { super(); if (initialCapacity < 0) //如果参数小于0,则抛出参数不合法异常 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];//初始化ArrayList底层维护的数组 } public ArrayList() { this(10);//调用本类的有参构造方法 }
先看第二个构造方法,虽然构造方法里面没有参数,但是在实现中会默认调用本类的带参构造方法,初始化为10个长度;对于第一个构造方法,传入了一个参数用来初始化ArrayList容量
下面分析部分常用方法:
Java代码
 publicbooleanadd(E e) {
publicbooleanadd(E e) {
ensureCapacity(size +1);//确保底层数组容量可以装入e
elementData[size++] = e;//在第size个索引位置放入e,然后size+1
returntrue;//添加成功,返回true
} public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacity(size + 1); //确保底层数组容量可以装入e elementData[size++] = e; //在第size个索引位置放入e,然后size+1 return true;//添加成功,返回true }
在该方法中,重点是ensureCapacity(size + 1)这个方法,下面看其源码:
Java代码
 publicvoidensureCapacity(intminCapacity) {
publicvoidensureCapacity(intminCapacity) {
modCount++;
intoldCapacity = elementData.length;//得到目前数组的容量大小
if(minCapacity > oldCapacity) {//如果目前数组容量小于传入的参数minCapacity
Object oldData[] = elementData;
intnewCapacity = (oldCapacity *3)/2+1;//则新生成一个容量
if(newCapacity
newCapacity = minCapacity;//则将参数赋予这个新容量
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);//将数组扩大newCapacity 个长度
}
} public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; int oldCapacity = elementData.length;//得到目前数组的容量大小 if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) { //如果目前数组容量小于传入的参数minCapacity Object oldData[] = elementData; int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1;//则新生成一个容量 if (newCapacity < minCapacity) //如果新生成的容量依旧小于传入的参数 newCapacity = minCapacity;//则将参数赋予这个新容量 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);//将数组扩大newCapacity 个长度 } }
因为数组长度一旦定义则不能够变化,所以JDK中使用ensureCapacity方法来确保数组长度能动态变化,这也是ArrayList与数组的不同之处
Java代码
 publicE get(intindex) {
publicE get(intindex) {
RangeCheck(index);//检查一下index是否越界
return(E) elementData[index];//返回第index的元素
} public E get(int index) { RangeCheck(index); //检查一下index是否越界 return (E) elementData[index]; //返回第index的元素 }
get方法用于取出第index的元素,该方法里使用了RangeCheck方法来检查索引是否越界
Java代码
 publicbooleancontains(Object o) {
publicbooleancontains(Object o) {
returnindexOf(o) >=0;
} public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) >= 0; }
contains方法用来判断ArrayList中对象o是否在,调用了indexOf来实现
Java代码
 publicintindexOf(Object o) {
publicintindexOf(Object o) {
if(o ==null) {//如果o为null
for(inti =0; i
if(elementData[i]==null)//如果某个元素为空,则返回该元素的索引
returni;
}else{//如果o不为null
for(inti =0; i
if(o.equals(elementData[i]))//若发现其中某个元素等于o,则返回该元素的索引
returni;
}
return-1;//没有找到返回-1
} public int indexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) {//如果o为null for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)//循环遍历ArrayList底层的数组 if (elementData[i]==null)//如果某个元素为空,则返回该元素的索引 return i; } else { //如果o不为null for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)//循环遍历ArrayList底层的数组 if (o.equals(elementData[i]))//若发现其中某个元素等于o,则返回该元素的索引 return i; } return -1;//没有找到返回-1 }
indexOf方法还是比较简单,注意的是将对象o分为null和非null进行判断
Java代码
 publicE remove(intindex) {
publicE remove(intindex) {
RangeCheck(index);//检查索引边界
modCount++;
E oldValue = (E) elementData[index];//得到index上的元素
intnumMoved = size - index -1;//得到需要移动的元素数量,注意这里要减1,因为不包括将要删除的元素
if(numMoved >0)//需要移动的元素数量大于0,则开始移动ArrayList底层数组
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] =null;// 将最后宇哥元素值为null,便于垃圾回收器回收
returnoldValue;//返回删除的元素值
} public E remove(int index) { RangeCheck(index);//检查索引边界 modCount++; E oldValue = (E) elementData[index];//得到index上的元素 int numMoved = size - index - 1;//得到需要移动的元素数量,注意这里要减1,因为不包括将要删除的元素 if (numMoved > 0)//需要移动的元素数量大于0,则开始移动ArrayList底层数组 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // 将最后宇哥元素值为null,便于垃圾回收器回收 return oldValue;//返回删除的元素值 }
从上面源码可以看到,每删除一个元素且不是最后一个元素则需要移动底层数组,这样会导致效率低下,故ArrayList
不适合删除操作过多的场景
ArrayList还重载了remove方法:
Java代码
 publicbooleanremove(Object o) {
publicbooleanremove(Object o) {
if(o ==null) {
for(intindex =0; index
if(elementData[index] ==null) {
fastRemove(index);
returntrue;
}
}else{
for(intindex =0; index
if(o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
returntrue;
}
}
returnfalse;
} public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; }
其基本思想与remove(int)区别不大
Java代码
 publicvoidadd(intindex, E element) {
publicvoidadd(intindex, E element) {
if(index > size || index <0)
thrownewIndexOutOfBoundsException(
"Index: "+index+", Size: "+size);
ensureCapacity(size+1);
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index +1,
size - index);//移动数组,留出空间给新插入的元素
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
} public void add(int index, E element) { if (index > size || index < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException( "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size); ensureCapacity(size+1); System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); //移动数组,留出空间给新插入的元素 elementData[index] = element; size++; }
上面的add方法用于在指定索引出插入元素,同样需要移动数组,效率低下
二、LinkedList概况:
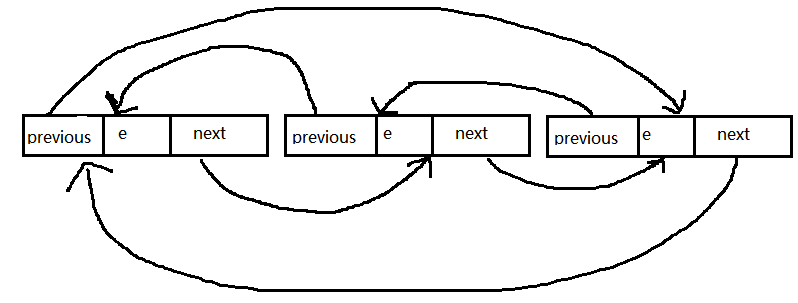
LinkedList属于一个双向循环的链表,其内部是用一个Entry来维护的
Java代码
 privatetransientEntry header =newEntry(null,null,null); private transient Entry header = new Entry(null, null, null);
privatetransientEntry header =newEntry(null,null,null); private transient Entry header = new Entry(null, null, null);
在Entry中就包含链表的三个属性,previous、next、element
Java代码
 privatestaticclassEntry {
privatestaticclassEntry {
E element;
Entry next;
Entry previous;
Entry(E element, Entry next, Entry previous) {
this.element = element;
this.next = next;
this.previous = previous;
}
} private static class Entry { E element; Entry next; Entry previous; Entry(E element, Entry next, Entry previous) { this.element = element; this.next = next; this.previous = previous; } }
element:当前节点的值
previous:指向当前节点的前一个节点
next:指向当前节点的后一个节点
二、接下来重点分析一下方法:
由
Java代码
 publicE removeFirst() {
publicE removeFirst() {
returnremove(header.next);
} public E removeFirst() { return remove(header.next); }
引出
Java代码
 privateE remove(Entry e) {
privateE remove(Entry e) {
if(e == header)
thrownewNoSuchElementException();
E result = e.element;
e.previous.next = e.next;
e.next.previous = e.previous;
e.next = e.previous =null;
e.element =null;
size--;
modCount++;
returnresult;
} private E remove(Entry e) { if (e == header) throw new NoSuchElementException(); E result = e.element; e.previous.next = e.next; e.next.previous = e.previous; e.next = e.previous = null; e.element = null; size--; modCount++; return result; }
可以看出remove(Entry e)是一个私有方法,所有我们是没法直接去调用此方法的,该方法就是为LinkedList本身服务的,因为LinkedList是由Entry维护,Entry即我们所说的节点,删除它的操作很简单,只要把当前节点的前一个节点的next指向当前节点的下一个节点(e.previous.next = e.next;),然后当前节点的下一个节点的previous指向当前节点的前一个节点(e.next.previous = e.previous;),最后把当前节点的next,previous、element置为null,以便GC回收(e.next = e.previous = null; e.element = null;)删除操作就完成了,我们从中可以看出他的时间复杂度仅为O(1),也就是说删除LinkedList中第一个元素和最后一个元素的时间复杂的仅为O(1),所以他的操作是非常快的。
三、但是如果我们是想删除某个具体的对象时,它又是怎么实现的呢?看源码
Java代码
 publicbooleanremove(Object o) {
publicbooleanremove(Object o) {
if(o==null) {
for(Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) {
if(e.element==null) {
remove(e);
returntrue;
}
}
}else{
for(Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) {
if(o.equals(e.element)) {
remove(e);
returntrue;
}
}
}
returnfalse;
} public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o==null) { for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) { if (e.element==null) { remove(e); return true; } } } else { for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) { if (o.equals(e.element)) { remove(e); return true; } } } return false; }
我们发现这方法的内部又调用了一个前面已经分析过的remove(Entry e)方法, 在这个方法中却多了一个for循环,他要从一个节点开始找,直到找到那个值于传入的参数值相等,我们可以看出他的时间复杂度就不是我们普遍认为的O(1) 了,而变成了O(n),之所以这样是LinkedList作为一个通用性的链表结构,由Entry去维护该数据结构,而不是拿我们直接保存在 LinkedList的值,相当于做了一层包装,所以你要删除某个值,你还得去找到那个对应的Entry对象。
四、再来看看下面这个方法:
Java代码
 publicE remove(intindex) {
publicE remove(intindex) {
returnremove(entry(index));
} public E remove(int index) { return remove(entry(index)); }
这是删除某个指定位置元素的方法,跟踪一下entry(index)方法
Java代码 privateEntry entry(intindex) {
if(index <0|| index >= size)
thrownewIndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+
", Size: "+size);
Entry e = header;
if(index >1)) {
for(inti =0; i <= index; i++)
e = e.next;
}else{
for(inti = size; i > index; i--)
e = e.previous;
}
returne;
} private Entry entry(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+ ", Size: "+size); Entry e = header; if (index < (size >> 1)) { for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++) e = e.next; } else { for (int i = size; i > index; i--) e = e.previous; } return e; }
我们很惊奇的发现,哇,原来删除某个位置的元素还是这样实现的,为了找到index位置的 Entry元素,它根据index元素与LinkedList大小的一半(size>>1)做了次比较,如果比size/2小,它就由前往后找,如果比size/2大,它就从后往前找,并不是我们所想的一味的又前往后找,这样一来,除去比较所消耗的时间,他的时间复杂度为O(n/2)
五、相对来说添加的操作就没那么复杂了
Java代码 privateEntry addBefore(E e, Entry entry) {
Entry newEntry =newEntry(e, entry, entry.previous);
newEntry.previous.next = newEntry;
newEntry.next.previous = newEntry;
size++;
modCount++;
returnnewEntry;
} private Entry addBefore(E e, Entry entry) { Entry newEntry = new Entry(e, entry, entry.previous); newEntry.previous.next = newEntry; newEntry.next.previous = newEntry; size++; modCount++; return newEntry; }
这方法的意思是说,把e对应的节点添加到entry的前面,首先构造newEntry对象,即新节点,然后是新节点的前一个节点的next指向当前的新节点,当前新节点的下一个元素的previous也指向新节点.
六、总结:相对于ArrayList来说,普遍认为对数据的修改频繁时最好使用 LinkedList,但是我们发现针对LinkedList要移除某个元素时,发现其效率也并不见得非常的高,因为其中还涉及到一个查询的操作。,所以,在某些特定的领域下特别是对性能很高的情况下,可以自己实现满足要求的LinkedList,而不用jdk提供的通用的 java.util.LinkedList.最后还附上一个很丑的图,以供参考






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








