Map集合为映射类型,映射与集和列表有明显的区别,映射中的每个对象都是成对存在的。映射中存储的每个对象都有一个相应的键(Key)对象,在检索对象时必须通过相应的键对象来获取值(value)对象,类似于在字典中查找单词一样,因此要求键对象必须是惟一的。键对象还决定了存储对象在映射中的存储位置,但并不是键对象本身决定的,需要通过一种散列技术进行处理,从而产生一个被称作散列码的整数值,散列码通常用作一个偏置量,该偏置量是相对于分配给映射的内存区域的起始位置的,由此来确定存储对象在映射中的存储位置。理想情况下,通过散列技术得到的散列码应该是在给定范围内均匀分布的整数值,并且每个键对象都应该得到不同的散列码。 (1)Map集合的用法 Map集合包括Map接口以及Map接口的所有实现类。由Map接口提供用来操作集合的常用方法如下表5所示:
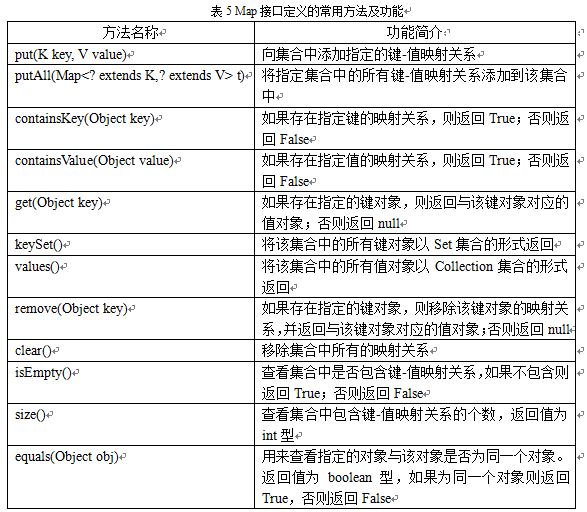
Map接口的常用实现类有HashMap和TreeMap,HashMap类通过哈希码对其内部的映射关系进行快速查找,而TreeMap类中的映射关系存在一定的顺序,如果希望在遍历集合时是有序的,应该使用由TreeMap类实现的Map集合,否则建议使用由HashMap类实现的Map集合,因为由HashMap类实现的Map集合对于添加和删除映射关系更高效。 Map集合允许值对象为null,并且没有个数限制,因此当get()方法的返回值为null时,可能有两种情况,一种是在集合中没有该键对象,另一种是该键对象没有映射任何值对象,即值对象为null。因此,在Map集合中不应该利用get()方法来判断是否存在某个键,而应该利用containsKey()方法来判断。 例如: 源文件:TestMap.java
import java.util.*;
public class TestMap{
public static void main(String args[]){
Map map = new HashMap();
System.out.println("map集合是否为空:"+map.isEmpty());
map.put(22015,null);
System.out.println("map集合是否为空:"+map.isEmpty());
map.put(22016,"马先生");
System.out.println("map集合是否为空:"+map.isEmpty());
System.out.println("get()方法的返回结果:");
System.out.print(map.get(22015));
System.out.print(" "+map.get(22016));
System.out.println(" "+map.get(22017));
System.out.println("containsKey()方法的返回结果:");
System.out.print(map.containsKey(22015));
System.out.print(" "+map.containsKey(22016));
System.out.println(" "+map.containsKey(22017));
System.out.println("map集合中映射的个数:"+map.size());
map.remove(22015);
System.out.println("map集合中映射的个数:"+map.size());
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class TestMap{
public static void main(String args[]){
Map map = new HashMap();
System.out.println("map集合是否为空:"+map.isEmpty());
map.put(22015,null);
System.out.println("map集合是否为空:"+map.isEmpty());
map.put(22016,"马先生");
System.out.println("map集合是否为空:"+map.isEmpty());
System.out.println("get()方法的返回结果:");
System.out.print(map.get(22015));
System.out.print(""+map.get(22016));
System.out.println(""+map.get(22017));
System.out.println("containsKey()方法的返回结果:");
System.out.print(map.containsKey(22015));
System.out.print(""+map.containsKey(22016));
System.out.println(""+map.containsKey(22017));
System.out.println("map集合中映射的个数:"+map.size());
map.remove(22015);
System.out.println("map集合中映射的个数:"+map.size());
}
}
程序的运行结果如下: map集合是否为空:true map集合是否为空:false map集合是否为空:false get()方法的返回结果: null 马先生 null containsKey()方法的返回结果: true true false map集合中映射的个数:2 map集合中映射的个数:1
(2)使用HashMap类 HashMap类实现了Map接口,由HashMap类实现的Map集合允许以null作为键对象,但是因为键对象不可以重复,所以这样的键对象只能有一个。如果经常需要添加、删除和定位映射关系,建议利用HashMap类实现Map集合,不过在遍历集合时得到的映射关系是无序的。 在使用由HashMap类实现的Map集合时,如果想有效地使用,就必须重写作为主键对象类的hashCode()方法,在重写hashCode()方法时,有两条基本原则: ● 不唯一原则:不必为每个对象生成一个惟一的哈希码,只要通过hashCode()方法生成的哈希码,利用get()方法能够得到利用put()方法添加的映射关系即可。 ● 分散原则:生成哈希码的算法应尽量使哈希码的值分散一些,不要将很多哈希码值都集中在一个范围内,这样有利于提高由HashMap类实现的Map集合的性能。 例如: 源文件:PK_person.java
public class PK_person{
private String prefix;
private long number;
public String setPrefix(){
return prefix;
}
public void setPrefix(String prefix){
this.prefix = prefix;
}
public long getNumber(){
return number;
}
public void setNumber(long number){
this.number = number;
}
public String getPK(){
return this.prefix+"_"+this.number;
}
public void setPK(String pk){
int i = pk.indexOf("_");
this.prefix = pk.substring(0,i);
this.number = new Integer(pk.substring(i));
}
}
public class PK_person{
private String prefix;
private long number;
public String setPrefix(){
return prefix;
}
public void setPrefix(String prefix){
this.prefix = prefix;
}
public long getNumber(){
return number;
}
public void setNumber(long number){
this.number = number;
}
public String getPK(){
return this.prefix+"_"+this.number;
}
public void setPK(String pk){
int i = pk.indexOf("_");
this.prefix = pk.substring(0,i);
this.number = new Integer(pk.substring(i));
}
}
源文件:Person.java
public class Person{
private String name;
private PK_person number;
public Person(PK_person number,String name){
this.number = number;
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public PK_person getNumber(){
return number;
}
public void setNumber(PK_person number){
this.number = number;
}
}
public class Person{
private String name;
private PK_person number;
public Person(PK_person number,String name){
this.number = number;
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public PK_person getNumber(){
return number;
}
public void setNumber(PK_person number){
this.number = number;
}
}
源文件:TestMap.java
import java.util.*;
public class TestMap{
public static void main(String args[]){
Map map = new HashMap();
PK_person pk_person1 = new PK_person();
pk_person1.setPrefix("MR");
pk_person1.setNumber(22015);
map.put(pk_person1,new Person(pk_person1,"马先生"));
PK_person pk_person2 = new PK_person();
pk_person2.setPrefix("MR");
pk_person2.setNumber(22015);
Person person = map.get(pk_person2);
if(person == null){
System.out.println("该键对象不存在!");
}
else{
System.out.println(person.getNumber().getNumber()+" "+person.getName());
}
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class TestMap{
public static void main(String args[]){
Map map = new HashMap();
PK_person pk_person1 = new PK_person();
pk_person1.setPrefix("MR");
pk_person1.setNumber(22015);
map.put(pk_person1,new Person(pk_person1,"马先生"));
PK_person pk_person2 = new PK_person();
pk_person2.setPrefix("MR");
pk_person2.setNumber(22015);
Person person = map.get(pk_person2);
if(person == null){
System.out.println("该键对象不存在!");
}
else{
System.out.println(person.getNumber().getNumber()+""+person.getName());
}
}
}
程序的运行结果如下: 该键对象不存在! 无论执行多少次,输出的信息都为“该键对象不存在!”,即在集合中不存在该键对象。这是因为没有重写java.lang.Object()类中的hashCode()和equals()方法,equals()方法默认比较两个对象的地址,因此即使这两个键对象的内容完全相同,也不认为是同一个对象,重写后的hashCode()和equals()方法的完整代码如下:
public int hashCode(){//重写hashCode()方法
return (int)(number + prefix.hashCode());
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){//重写equals()方法
if(obj == null){
return false;
}
if(getClass()!=obj.getClass()){
return false;
}
if(this == obj){
return true;
}
final PK_person other = (PK_person)obj;
if(this.hashCode()!=other.hashCode()){
return false;
}
return true;
}
public int hashCode(){//重写hashCode()方法
return (int)(number + prefix.hashCode());
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){//重写equals()方法
if(obj == null){
return false;
}
if(getClass()!=obj.getClass()){
return false;
}
if(this == obj){
return true;
}
final PK_person other = (PK_person)obj;
if(this.hashCode()!=other.hashCode()){
return false;
}
return true;
}
重写PK_person类中的hashCode()和equals()方法后,再次执行程序,结果如下: 2015 马先生
(3)使用TreeMap类 TreeMap类不仅实现了Map接口,还实现了Map接口的子接口java.util.SortedMap。由TreeMap类实现的Map集合不允许键对象为null,因为集合中的映射关系是根据键对象按照一定顺序排列的,TreeMap类通过实现SortedMap接口得到的方法如下表6所示:
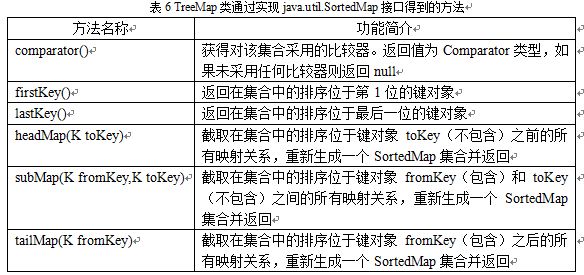
在添加、删除和定位映射关系上,TreeMap类要比HashMap类的性能差一些,但是其中的映射关系具有一定的顺序,如果不需要一个有序的集合,则建议使用HashMap类;如果需要进行有序的遍历输出,则建议使用TreeMap类,在这种情况下,可以先使用由HashMap类实现的Map集合,在需要顺序输出时,在利用现有的HashMap类的实例创建一个具有完全相同映射关系的TreeMap类型的实例。 例如: 源文件:Person.java
public class Person{
private String name;
private long id_card;
public Person(String name,long id_card){
this.id_card = id_card;
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public long getId_card(){
return id_card;
}
public void setId_card(long id_card){
this.id_card = id_card;
}
}
public class Person{
private String name;
private long id_card;
public Person(String name,long id_card){
this.id_card = id_card;
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public long getId_card(){
return id_card;
}
public void setId_card(long id_card){
this.id_card = id_card;
}
}
源文件:TestMap.java
import java.util.*;
public class TestMap{
public static void main(String args[]){
Person p1 = new Person("马先生",22015);
Person p2 = new Person("李小姐",22018);
Person p3 = new Person("马先生",22016);
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(22015,p1);
map.put(22018,p2);
map.put(22016,p3);
System.out.println("由HashMap类实现的Map集合,无序:");
Iterator it1 = map.keySet().iterator();
while(it1.hasNext()){
Person person = map.get(it1.next());
System.out.println(person.getId_card()+" "+person.getName());
}
System.out.println("由TreeMap类实现的Map集合,键对象升序:");
TreeMap treeMap1 = new TreeMap();
treeMap1.putAll(map);
Iterator it2 = treeMap1.keySet().iterator();
while(it2.hasNext()){
Person person = treeMap1.get(it2.next());
System.out.println(person.getId_card()+" "+person.getName());
}
System.out.println("由TreeMap类实现的Map集合,键对象降序:");
TreeMap treeMap2 = new TreeMap(Collections.reverseOrder());
treeMap2.putAll(map);
Iterator it3 = treeMap2.keySet().iterator();
while(it3.hasNext()){
Person person = treeMap2.get(it3.next());
System.out.println(person.getId_card()+" "+person.getName());
}
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class TestMap{
public static void main(String args[]){
Person p1 = new Person("马先生",22015);
Person p2 = new Person("李小姐",22018);
Person p3 = new Person("马先生",22016);
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(22015,p1);
map.put(22018,p2);
map.put(22016,p3);
System.out.println("由HashMap类实现的Map集合,无序:");
Iterator it1 = map.keySet().iterator();
while(it1.hasNext()){
Person person = map.get(it1.next());
System.out.println(person.getId_card()+""+person.getName());
}
System.out.println("由TreeMap类实现的Map集合,键对象升序:");
TreeMap treeMap1 = new TreeMap();
treeMap1.putAll(map);
Iterator it2 = treeMap1.keySet().iterator();
while(it2.hasNext()){
Person person = treeMap1.get(it2.next());
System.out.println(person.getId_card()+""+person.getName());
}
System.out.println("由TreeMap类实现的Map集合,键对象降序:");
TreeMap treeMap2 = new TreeMap(Collections.reverseOrder());
treeMap2.putAll(map);
Iterator it3 = treeMap2.keySet().iterator();
while(it3.hasNext()){
Person person = treeMap2.get(it3.next());
System.out.println(person.getId_card()+""+person.getName());
}
}
}
程序的运行结果如下: 由HashMap类实现的Map集合,无序: 22016 马先生 22018 李小姐 22015 马先生 由TreeMap类实现的Map集合,键对象升序: 22015 马先生 22016 马先生 22018 李小姐 由TreeMap类实现的Map集合,键对象降序: 22018 李小姐 22016 马先生 22015 马先生





















 155
155











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








