数据源有多种:
1、基于集合:有界数据集,更偏向于本地测试用
2、基于文件:适合监听文件修改并读取其内容
3、基于 Socket:监听主机的 host port,从 Socket 中获取数据
4、自定义 addSource:大多数的场景数据都是无界的,会源源不断的过来。比如去消费 Kafka 某个 topic 上的数据,这时候就需要用到这个 addSource,可能因为用的比较多的原因吧,Flink 直接提供了 FlinkKafkaConsumer011 等类可供你直接使用。你可以去看看 FlinkKafkaConsumerBase 这个基础类,它是 Flink Kafka 消费的最根本的类。
我们的例子中的数据属于第三种,通过Socket来获取数据,代码如下:
DataStreamSource<String> text = env.socketTextStream("localhost", port, "\n");通过监听localhost上的port端口,来获取对方发送过来的数据,我们进入到socketTextStream函数中,这个函数是StreamExecutionEnvironment类或其子类中的成员函数,代码如下:
/**
* Creates a new data stream that contains the strings received infinitely from a socket. Received strings are
* decoded by the system's default character set. The reader is terminated immediately when the socket is down.
*
* @param hostname
* The host name which a server socket binds
* @param port
* The port number which a server socket binds. A port number of 0 means that the port number is automatically
* allocated.
* @param delimiter
* A string which splits received strings into records
* @return A data stream containing the strings received from the socket
*/
@PublicEvolving
public DataStreamSource<String> socketTextStream(String hostname, int port, String delimiter) {
return socketTextStream(hostname, port, delimiter, 0);
}socketTextStream函数代码如下:
/**
* Creates a new data stream that contains the strings received infinitely from a socket. Received strings are
* decoded by the system's default character set. On the termination of the socket server connection retries can be
* initiated.
*
* <p>Let us note that the socket itself does not report on abort and as a consequence retries are only initiated when
* the socket was gracefully terminated.
*
* @param hostname
* The host name which a server socket binds
* @param port
* The port number which a server socket binds. A port number of 0 means that the port number is automatically
* allocated.
* @param delimiter
* A string which splits received strings into records
* @param maxRetry
* The maximal retry interval in seconds while the program waits for a socket that is temporarily down.
* Reconnection is initiated every second. A number of 0 means that the reader is immediately terminated,
* while
* a negative value ensures retrying forever.
* @return A data stream containing the strings received from the socket
*/
@PublicEvolving
public DataStreamSource<String> socketTextStream(String hostname, int port, String delimiter, long maxRetry) {
return addSource(new SocketTextStreamFunction(hostname, port, delimiter, maxRetry),
"Socket Stream");
}首先创建了一个SocketTextStreamFunction类对象,这个类实现类接口SouceFunction<T>,该接口的相关继承实现结构图如下:
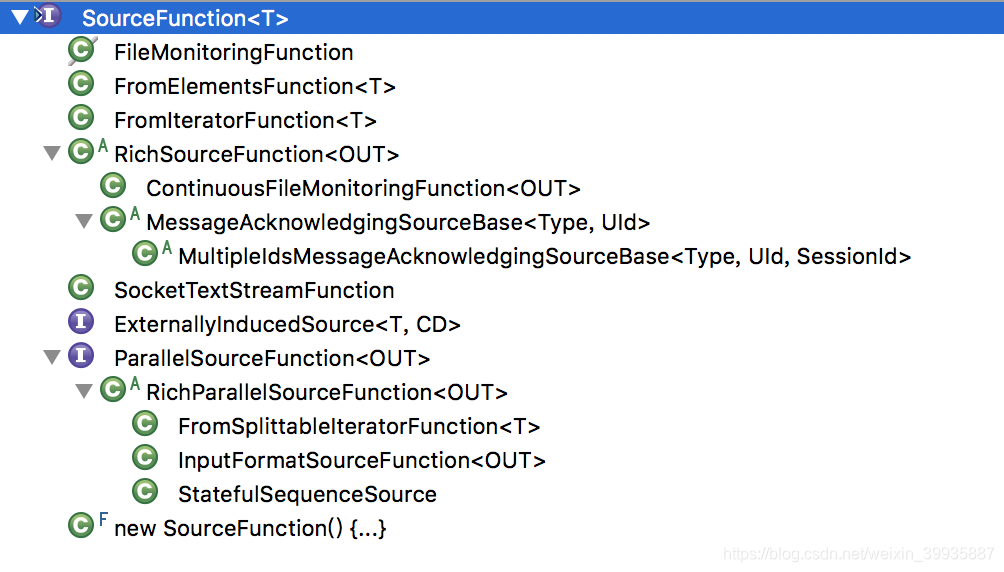
这个类中实现了函数run,用来从网络上获取传输过来的数据,然后根据分词字符来将数据划分成多个,存储到流中,代码如下:
@Override
public void run(SourceContext<String> ctx) throws Exception {
final StringBuilder buffer = new StringBuilder();
long attempt = 0;
while (isRunning) {
try (Socket socket = new Socket()) {
currentSocket = socket;
LOG.info("Connecting to server socket " + hostname + ':' + port);
socket.connect(new InetSocketAddress(hostname, port), CONNECTION_TIMEOUT_TIME);
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()))) {
char[] cbuf = new char[8192];
int bytesRead;
while (isRunning && (bytesRead = reader.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
buffer.append(cbuf, 0, bytesRead);
int delimPos;
while (buffer.length() >= delimiter.length() && (delimPos = buffer.indexOf(delimiter)) != -1) {
String record = buffer.substring(0, delimPos);
// truncate trailing carriage return
if (delimiter.equals("\n") && record.endsWith("\r")) {
record = record.substring(0, record.length() - 1);
}
ctx.collect(record);
buffer.delete(0, delimPos + delimiter.length());
}
}
}
}
// if we dropped out of this loop due to an EOF, sleep and retry
if (isRunning) {
attempt++;
if (maxNumRetries == -1 || attempt < maxNumRetries) {
LOG.warn("Lost connection to server socket. Retrying in " + delayBetweenRetries + " msecs...");
Thread.sleep(delayBetweenRetries);
}
else {
// this should probably be here, but some examples expect simple exists of the stream source
// throw new EOFException("Reached end of stream and reconnects are not enabled.");
break;
}
}
}
// collect trailing data
if (buffer.length() > 0) {
ctx.collect(buffer.toString());
}
}进入到addSource函数中,代码如下:
/**
* Adds a data source with a custom type information thus opening a
* {@link DataStream}. Only in very special cases does the user need to
* support type information. Otherwise use
* {@link #addSource(org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.source.SourceFunction)}
*
* @param function
* the user defined function
* @param sourceName
* Name of the data source
* @param <OUT>
* type of the returned stream
* @return the data stream constructed
*/
public <OUT> DataStreamSource<OUT> addSource(SourceFunction<OUT> function, String sourceName) {
return addSource(function, sourceName, null);
}其中function入参就是上面创建的SocketTextStreamFunction类对象,我们往下到addSource函数中,代码如下:
/**
* Ads a data source with a custom type information thus opening a
* {@link DataStream}. Only in very special cases does the user need to
* support type information. Otherwise use
* {@link #addSource(org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.source.SourceFunction)}
*
* @param function
* the user defined function
* @param sourceName
* Name of the data source
* @param <OUT>
* type of the returned stream
* @param typeInfo
* the user defined type information for the stream
* @return the data stream constructed
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <OUT> DataStreamSource<OUT> addSource(SourceFunction<OUT> function, String sourceName, TypeInformation<OUT> typeInfo) {
//如果传入的function实现了ResultTypeQueryable接口, 则直接通过接口获取
if (function instanceof ResultTypeQueryable) {
typeInfo = ((ResultTypeQueryable<OUT>) function).getProducedType();
}
//如果输出typeInfo为null
if (typeInfo == null) {
try {
//通过反射来获取输出类型
typeInfo = TypeExtractor.createTypeInfo(
SourceFunction.class,
function.getClass(), 0, null, null);
} catch (final InvalidTypesException e) {
typeInfo = (TypeInformation<OUT>) new MissingTypeInfo(sourceName, e);
}
}
boolean isParallel = function instanceof ParallelSourceFunction;
//对function进行清除操作,上篇文章已经讲解过,这里不做过多赘述
clean(function);
final StreamSource<OUT, ?> sourceOperator = new StreamSource<>(function);
//返回一个DataStreamSource类对象
return new DataStreamSource<>(this, typeInfo, sourceOperator, isParallel, sourceName);
}接下来我们分析一下TypeExtractor.createTypeInfo函数,看看里面的实现是什么样的,我们进入到该函数中,代码如下:
/*
baseClass是SourceFunction类的Class类对象
clazz是SocketTextStreamFunction类的Class类对象
*/
@PublicEvolving
public static <IN1, IN2, OUT> TypeInformation<OUT> createTypeInfo(Class<?> baseClass, Class<?> clazz, int returnParamPos,
TypeInformation<IN1> in1Type, TypeInformation<IN2> in2Type) {
TypeInformation<OUT> ti = new TypeExtractor().privateCreateTypeInfo(baseClass, clazz, returnParamPos, in1Type, in2Type);
if (ti == null) {
throw new InvalidTypesException("Could not extract type information.");
}
return ti;
}TypeExtractor是一个类型提取类,我们进入到privateCreateTypeInfo函数中,代码如下:
// for (Rich)Functions
/*
baseClass是SourceFunction类的Class类对象
clazz是SocketTextStreamFunction类的Class类对象
returnParamPos为0
in1Type为null
in2Type为null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <IN1, IN2, OUT> TypeInformation<OUT> privateCreateTypeInfo(Class<?> baseClass, Class<?> clazz, int returnParamPos,
TypeInformation<IN1> in1Type, TypeInformation<IN2> in2Type) {
ArrayList<Type> typeHierarchy = new ArrayList<Type>();
Type returnType = getParameterType(baseClass, typeHierarchy, clazz, returnParamPos);
TypeInformation<OUT> typeInfo;
// return type is a variable -> try to get the type info from the input directly
if (returnType instanceof TypeVariable<?>) {
typeInfo = (TypeInformation<OUT>) createTypeInfoFromInputs((TypeVariable<?>) returnType, typeHierarchy, in1Type, in2Type);
if (typeInfo != null) {
return typeInfo;
}
}
// get info from hierarchy
return (TypeInformation<OUT>) createTypeInfoWithTypeHierarchy(typeHierarchy, returnType, in1Type, in2Type);
}我们进入到getParamterType函数中,代码如下:
private static Type getParameterType(Class<?> baseClass, ArrayList<Type> typeHierarchy, Class<?> clazz, int pos) {
if (typeHierarchy != null) {
typeHierarchy.add(clazz);
}
/*获取实现接口信息的Type数组,包含泛型信息
getInterfaces()函数返回实现接口信息的Class数组,不包含泛型信息
*/
Type[] interfaceTypes = clazz.getGenericInterfaces();
// search in interfaces for base class
for (Type t : interfaceTypes) {
Type parameter = getParameterTypeFromGenericType(baseClass, typeHierarchy, t, pos);
if (parameter != null) {
return parameter;
}
}
// search in superclass for base class
/*
返回直接继承的父类(包含范型)
getSuperclass返回直接继承的父类(不包含范型)
*/
Type t = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();
Type parameter = getParameterTypeFromGenericType(baseClass, typeHierarchy, t, pos);
if (parameter != null) {
return parameter;
}
throw new InvalidTypesException("The types of the interface " + baseClass.getName() + " could not be inferred. " +
"Support for synthetic interfaces, lambdas, and generic or raw types is limited at this point");
}我们进入到函数getParameterTypeFromGenericType中,该函数用来获取参数类型信息,代码如下:
private static Type getParameterTypeFromGenericType(Class<?> baseClass, ArrayList<Type> typeHierarchy, Type t, int pos) {
// base class
if (t instanceof ParameterizedType && baseClass.equals(((ParameterizedType) t).getRawType())) {
if (typeHierarchy != null) {
typeHierarchy.add(t);
}
ParameterizedType baseClassChild = (ParameterizedType) t;
return baseClassChild.getActualTypeArguments()[pos];
}
// interface that extended base class as class or parameterized type
else if (t instanceof ParameterizedType && baseClass.isAssignableFrom((Class<?>) ((ParameterizedType) t).getRawType())) {
if (typeHierarchy != null) {
typeHierarchy.add(t);
}
return getParameterType(baseClass, typeHierarchy, (Class<?>) ((ParameterizedType) t).getRawType(), pos);
}
else if (t instanceof Class<?> && baseClass.isAssignableFrom((Class<?>) t)) {
if (typeHierarchy != null) {
typeHierarchy.add(t);
}
return getParameterType(baseClass, typeHierarchy, (Class<?>) t, pos);
}
return null;
}






















 556
556











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








