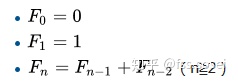
……续上回
fss.sosei:斐波那契数列与Python的尾递归蹦床 连载【3】zhuanlan.zhihu.com
之前那几种算法时间复杂度最好的也只是O(n)
下面是几种高效解法,时间复杂度都是O(log n)
7. 二分递归解法
设n∈R,则有:
F[n]=F[n/2+1]²−F[n/2−1]²=(2F[n/2−1]+F[n/2])F[n/2] 当n为偶数时
F[n]=F[n/2]²+F[n/2+1]² 当n为奇数时下面用递归写出解法,真是很简单
因为这是二元递归函数,所以加上上篇的缓存递归函数装饰器和动态增加栈空间函数
def Fibonacci_sequence_07 (n: int) -> int: #参数n是表示求第n项Fibonacci数
assert isinstance(n, int), 'n is an error of non-integer type.'
@recursive_function_cache
def Calculate_Fibonacci_sequence (n: int) -> int:
'返回单项的二分递归解法'
if n >= 2:
one_half_n = n >> 1
if n & 1 == 0: #当n为偶数项
one_half_fib_n = Calculate_Fibonacci_sequence(one_half_n)
one_half_fib_n_minus_one = Calculate_Fibonacci_sequence(one_half_n - 1)
return (one_half_fib_n_minus_one * 2 + one_half_fib_n) * one_half_fib_n
else: #当n为奇数项
return Calculate_Fibonacci_sequence(one_half_n) ** 2 + Calculate_Fibonacci_sequence(one_half_n + 1) ** 2
elif n == 1:
return 1
elif n == 0:
return 0
if n >= 0:
return Calculate_Fibonacci_sequence(n)
else:
return Nonedynamic_increase_recursion_limit('Fibonacci_sequence_07(1000000)')
用算到第100万项Fibonacci数来测量下用时
Total time: 0.076837秒
算第100万项只用时这么点,按前面最快的for迭代解法速度这点时间也只能算到3万多。看起来是高效多了
具体的时间复杂度是怎样的呢
这二分法的递归形式分析起来有点麻烦
那下面我写成迭代形式再分析时间复杂度吧
8. 二分迭代解法
用迭代形式实现这二分解法,看看用时如何
程序如下:
from collections import deque
def Fibonacci_sequence_08 (n: int) -> int: #参数n是表示求第n项Fibonacci数
assert isinstance(n, int), 'n is an error of non-integer type.'
def Calculate_Fibonacci_sequence (n: int) -> int:
'返回单项的二分迭代解法'
Even = True
Odd = False
if n >= 2:
fib_n_tree = [n, []] #数据存放格式是列表里前后两项,前项是n,后项是对应第n项Fibonacci数或是包含两个子节点的一个列表
fib_n_tier_node_queue = deque()
fib_n_cache = dict()
fib_merge_stack = []
def generating_fib_n_tree(n):
nonlocal fib_n_tier_node_queue, fib_n_cache, current_root
if n >= 2:
if n in fib_n_cache:
child_nodes = dict.get(fib_n_cache, n)
else:
child_nodes = [n, []]
fib_n_tier_node_queue.append(child_nodes)
fib_n_cache.update({n: child_nodes})
elif n == 1:
child_nodes = (n, 1)
elif n == 0:
child_nodes = (n, 0)
current_root[1].append(child_nodes) #将产生的子节点往current_root里装子节点的列表里压入
fib_n_tier_node_queue.append(fib_n_tree)
while len(fib_n_tier_node_queue) > 0: #先从上至下建立二分树
current_root = fib_n_tier_node_queue.popleft()
n_of_current_root = current_root[0]
one_half_n = n_of_current_root >> 1
if n_of_current_root & 1 == 0: #当n_of_current_root为偶数项
generating_fib_n_tree(one_half_n) #往fib_n_tree里先存两者中较大的数字
generating_fib_n_tree(one_half_n - 1)
fib_merge_stack.append((current_root, Even))
else: #当n_of_current_root为奇数项
generating_fib_n_tree(one_half_n + 1) #往fib_n_tree里先存两者中较大的数字
generating_fib_n_tree(one_half_n)
fib_merge_stack.append((current_root, Odd))
while len(fib_merge_stack) > 0: #再二分树从下至上归并算出结果
current_task = fib_merge_stack.pop()
current_root = current_task[0]
odevity = current_task[1]
list_of_current_child_node = current_root[1]
large_value_of_current_child_node = list_of_current_child_node[0][1]
small_value_of_current_child_node = list_of_current_child_node[1][1]
if odevity:
results = (small_value_of_current_child_node * 2 +
large_value_of_current_child_node) * large_value_of_current_child_node
else:
results = small_value_of_current_child_node ** 2 + large_value_of_current_child_node ** 2
current_root[1] = results
return fib_n_tree[1]
elif n == 1:
return 1
elif n == 0:
return 0
if n >= 0:
return Calculate_Fibonacci_sequence(n)
else:
return NoneFibonacci_sequence_08(1000000)
还是算第100万位,Total time: 0.076679秒
用时几乎一样!用时缩短了158us只能算计时误差范畴
现在来分析下这个解法的时间复杂度
主干就是建立二叉树的迭代,对n不断二分,搜索新子节点,迭代次数是2*log2(n),时间复杂度就是O(log n)
未完待续……
fss.sosei:斐波那契数列与Python的尾递归蹦床 连载【5】zhuanlan.zhihu.com




















 5336
5336











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








