在springboot中使用h2数据库
一、h2数据库介绍
h2database为我们提供了十分轻量,十分快捷方便的内嵌式数据库
H2是一个用Java开发的嵌入式数据库,它本身只是一个类库,可以直接嵌入到应用项目中。
可以同应用程序打包在一起发布
它的另一个用途是用于单元测试。启动速度快,而且可以关闭持久化功能,每一个用例执行完随即还原到初始状态
提供JDBC访问接口,提供基于浏览器的控制台,可以执行sql
免费,开源,够快
还方便了程序刚开始dao层单元测试测试,不需要搭建oracle,不需要加载mysql,快速测试写的dao
二、导入过程
1. 在pom.xml中导入相关依赖
com.h2database
h2
runtime
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
2. 修改application.yml文件,加入H2相关配置
server:
port: 8089
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:h2:~/test
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
username: sa
password: 123456
# schema: classpath:db/schema.sql
# data: classpath:db/data.sql
jpa:
database: h2
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
show-sql: true
h2:
console:
path: /h2-console
enabled: true
3. domain层,即Location类(entity):
package com.springboot.demo.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Location {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String type;
private double latitude;
private double longtitude;
}
4. dao层,即LocationRepository接口:
package com.springboot.demo.repository;
import com.springboot.demo.entity.Location;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Repository
public interface LocationRepository extends JpaRepository {
List getLocationsByType(String type);
}
5. controller层,即LocationController:
package com.springboot.demo.controller;
import com.springboot.demo.entity.Location;
import com.springboot.demo.repository.LocationRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class HelloContraller {
@Autowired
private LocationRepository locationRepository;
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public List hello(){
return locationRepository.findAll();
}
}
6. 编写DemoApplication
package com.springboot.demo;
import com.springboot.demo.entity.Location;
import com.springboot.demo.repository.LocationRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
@Bean
InitializingBean saveData(LocationRepository repo){
return ()->{
repo.save(new Location((long) 1,"1",38.998064, 117.317267));
repo.save(new Location((long)2,"2",38.997793, 117.317069));
repo.save(new Location((long)3,"3",38.998006, 117.317101));
repo.save(new Location((long)4,"4",38.997814, 117.317332));
};
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
7. 启动项目,打开浏览器访问http://localhost:8089/hello

8. 下面使用H2控制台查看:
输入用户名sa,密码123456
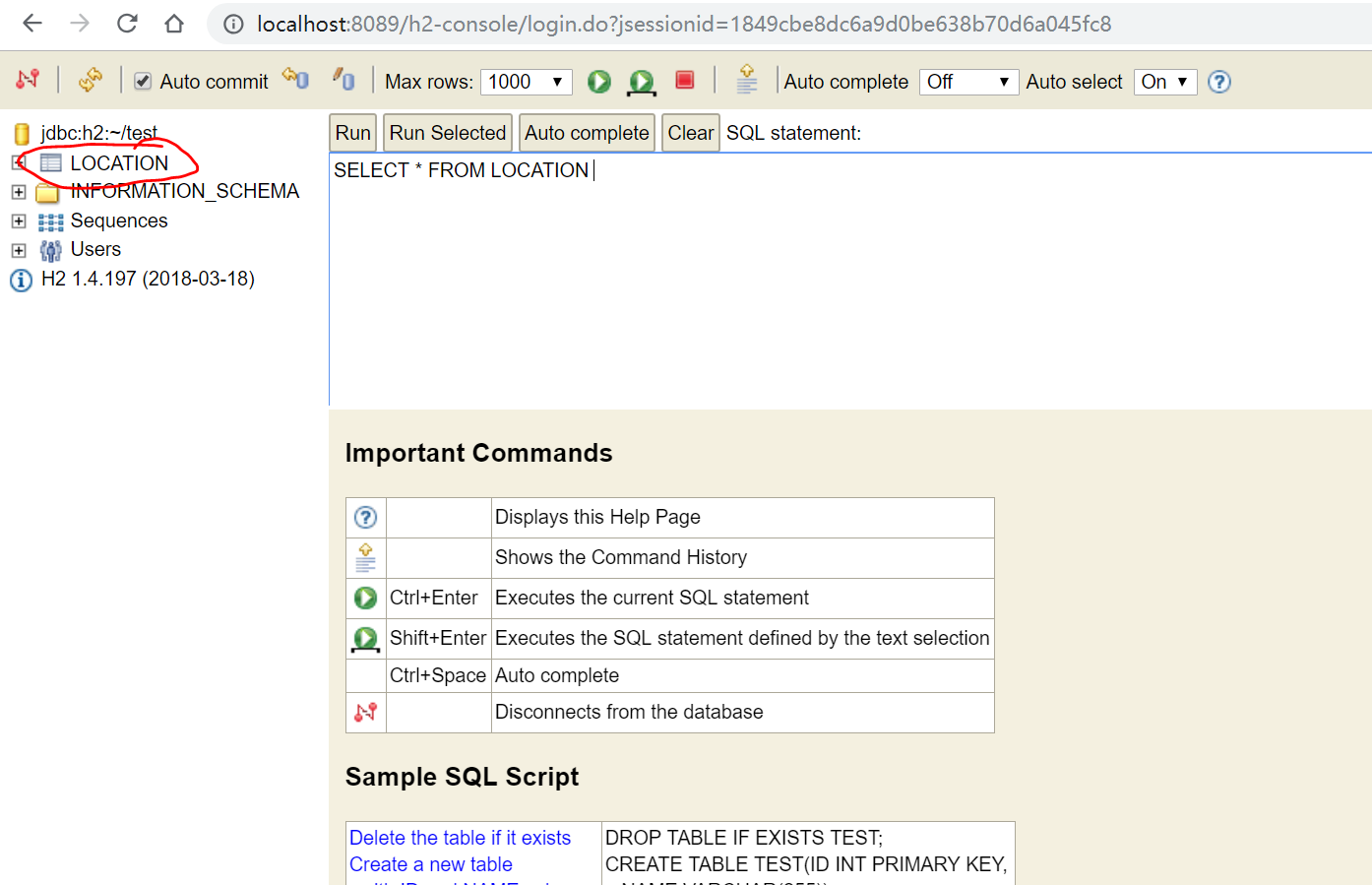
9. 在打开的页面中点击左侧的Location。
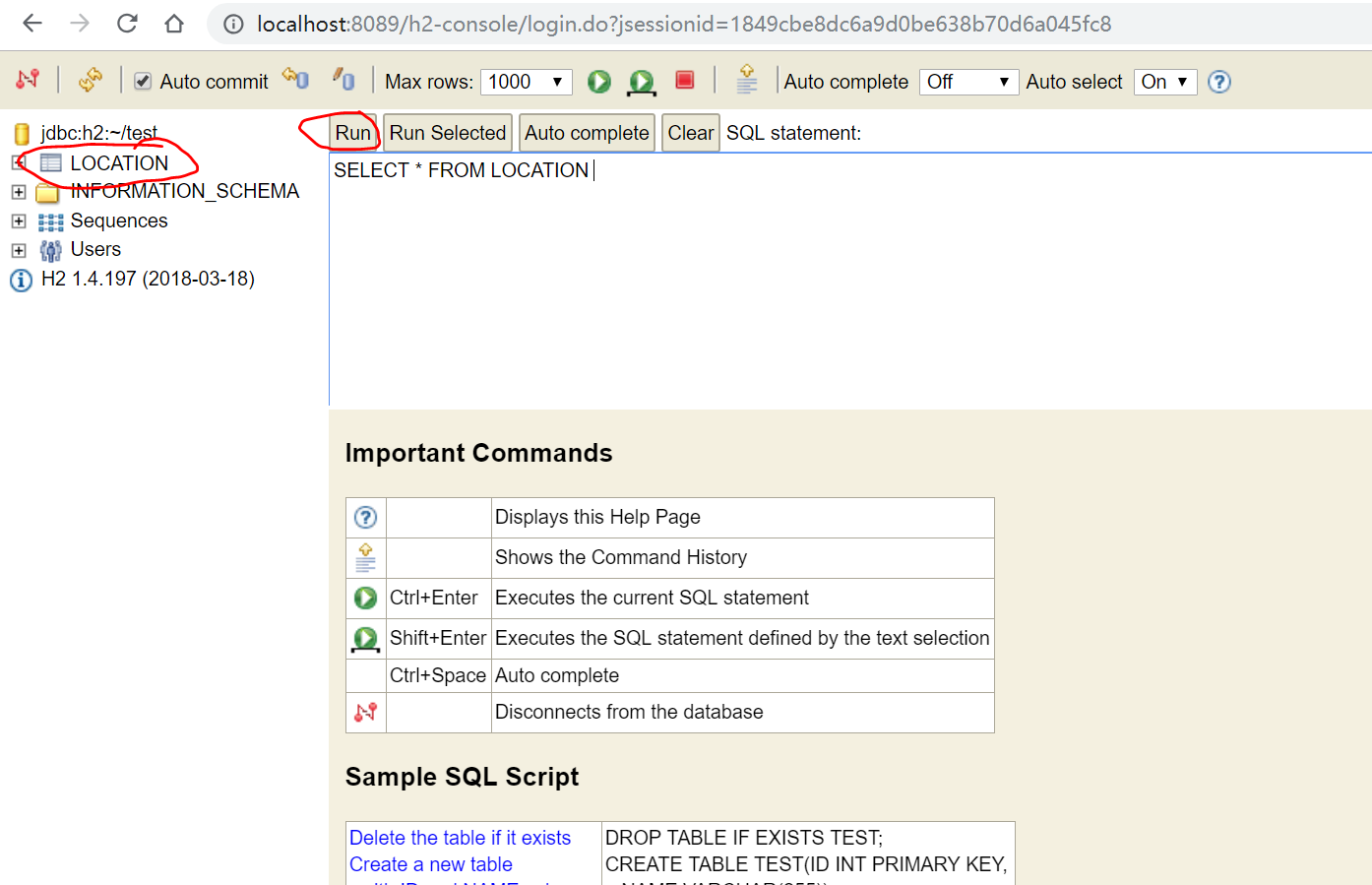
10. 可以看到右侧显示了SQL:
SELECT * FROM USER
点击上面的Run执行。
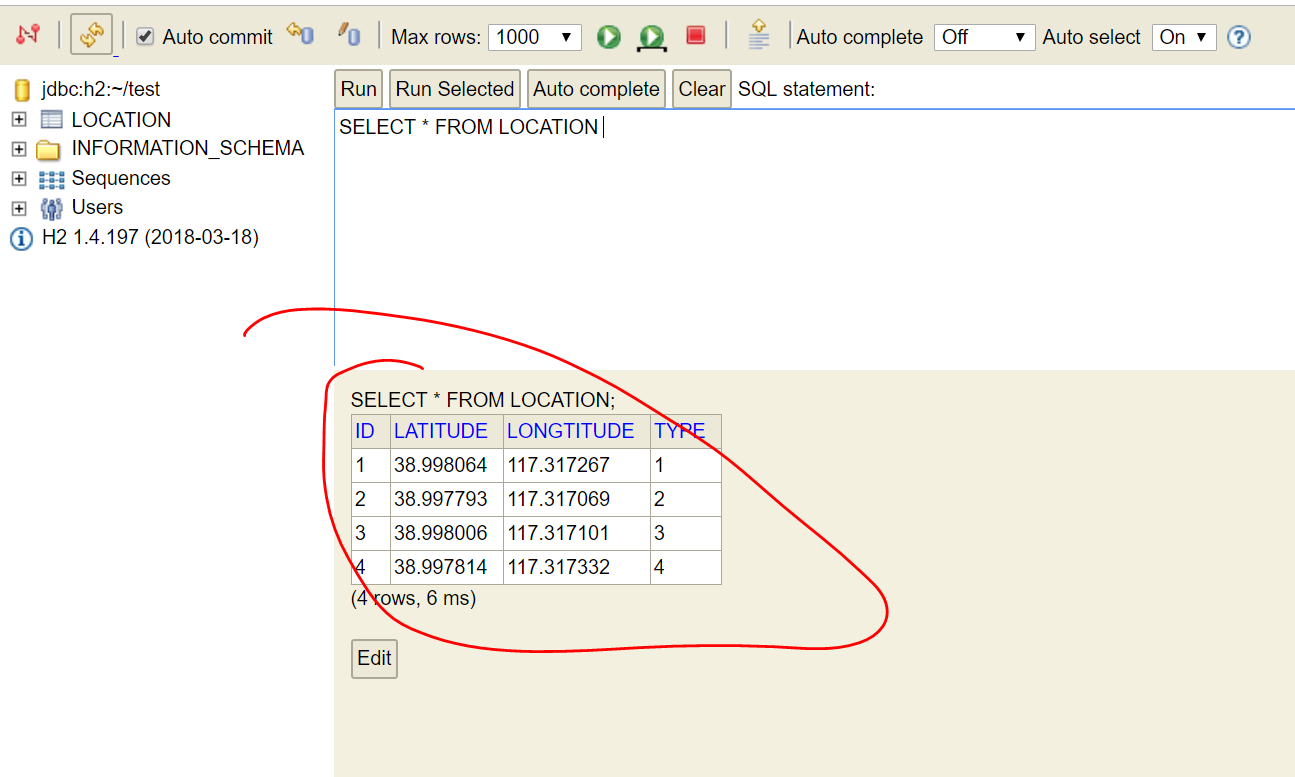
11. 执行完毕后,可以看到下面显示了我们加入的数据。




















 1474
1474











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








