concurrenthashmap
线程安全集合类
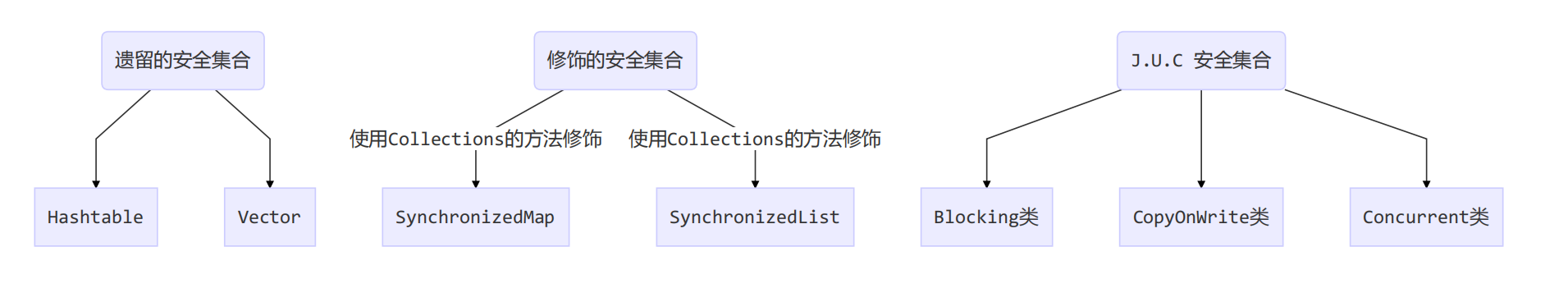
线程安全基本分类
线程安全集合类可以分为三大类:
-
遗留的线程安全集合如
Hashtable,Vector -
使用 Collections 装饰的线程安全集合,如
- Collections.synchronizedCollection
- Collections.synchronizedList
- Collections.synchronizedMap
- Collections.synchronizedSet
- Collections.synchronizedNavigableMap
- Collections.synchronizedNavigableSet
- Collections.synchronizedSortedMap
- Collections.synchronizedSortedSet
-
java.util.concurrent.*
重点介绍 java.util.concurrent.* 下的线程安全集合类,可以发现它们有规律,里面包含三类关键词:Blocking、CopyOnWrite、Concurrent
Blocking大部分实现基于锁,并提供用来阻塞的方法CopyOnWrite之类容器修改开销相对较重Concurrent类型的容器 :- 内部很多操作使用
cas优化,一般可以提供较高吞吐量 - 弱一致性 : 遍历时弱一致性,例如,当利用迭代器遍历时,如果容器发生修改,迭代器仍然可以继续进行遍历,这时内容是旧的
- 求大小弱一致性,size 操作未必是 100% 准确
- 读取弱一致性
- 内部很多操作使用
遍历时如果发生了修改,对于非安全容器来讲,使用 fail-fast 机制也就是让遍历立刻失败,抛出 ConcurrentModifificationException,不再继续遍历
ConcurrentHashMap
计数案例
案例要求
统计26个文件中单词的个数 :
-
一是提供一个 map 集合,用来存放每个单词的计数结果,key 为单词,value 为计数
-
二是提供一组操作,保证计数的安全性,会传递 map 集合以及 单词 List
正确结果输出应该是每个单词出现 200 次 :
{a=200, b=200, c=200, d=200, e=200, f=200, g=200, h=200, i=200, j=200, k=200, l=200, m=200,
n=200, o=200, p=200, q=200, r=200, s=200, t=200, u=200, v=200, w=200, x=200, y=200, z=200}
文件生成 :
package cn.knightzz.concurrent.examples;
import javax.xml.crypto.Data;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* @author 王天赐
* @title: DataGeneration
* @projectName hm-juc-codes
* @description: 数据生成
* @website <a href="http://knightzz.cn/">http://knightzz.cn/</a>
* @github <a href="https://github.com/knightzz1998">https://github.com/knightzz1998</a>
* @create: 2022-09-26 10:10
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class DataGeneration {
static final String ALPHA = "abcedfghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
static final String RESOURCE_PATH = "juc-chapter-08/src/main/resources/tmp/";
public static void main(String[] args) {
int length = ALPHA.length();
int count = 200;
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(length * count);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char ch = ALPHA.charAt(i);
for (int j = 0; j < count; j++) {
list.add(String.valueOf(ch));
}
}
Collections.shuffle(list);
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
try (PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream(RESOURCE_PATH + (i + 1) + ".txt")))) {
String collect = list.subList(i * count, (i + 1) * count).stream()
.collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
out.print(collect);
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
}
代码实现
多线程读取的代码 :
package cn.knightzz.concurrent.examples;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
/**
* @author 王天赐
* @title: FileUtils
* @projectName hm-juc-codes
* @description:
* @website <a href="http://knightzz.cn/">http://knightzz.cn/</a>
* @github <a href="https://github.com/knightzz1998">https://github.com/knightzz1998</a>
* @create: 2022-09-26 10:36
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class FileUtils {
static final String RESOURCE_PATH = "juc-chapter-08/src/main/resources/tmp/";
public static List<String> readFromFile(int i) {
ArrayList<String> words = new ArrayList<>();
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(RESOURCE_PATH + i + ".txt")))) {
while (true) {
String word = in.readLine();
if (word == null) {
break;
}
words.add(word);
}
return words;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
/**
* 多线程读取
*
* @param supplier 提供存储结果的map集合
* @param consumer 用于对数据进行处理
* @param <V>
*/
public static <V> void multithreadedRead(Supplier<Map<String, V>> supplier, BiConsumer<Map<String, V>, List<String>> consumer) {
Map<String, V> counterMap = supplier.get();
// key value
// a 200
// b 200
List<Thread> ts = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 26; i++) {
int idx = i;
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
// 开启多个线程去同时读取并处理数据
List<String> words = readFromFile(idx);
// 调用外部的 consumer 去处理数据
consumer.accept(counterMap, words);
});
ts.add(thread);
}
ts.forEach(t -> t.start());
ts.forEach(t -> {
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
System.out.println(counterMap);
}
基本思路是:
- 检查 map中是否存在 key
- 如果有 : 获取 key -> value , 然后+1
- 如果没有 : 把 key 存入map
主要可能存在并发问题的地方 : map 是共享的, 在判断的时候会出现并发问题 . map 仅能保证某个方法内线程安全, 即线程不会出现上下文切换
multithreadedRead(
() -> new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Integer>(),
(map, words) -> {
for (String word : words) {
Integer value = map.get(word);
if (value != null) {
map.put(word, value+1);
}else {
map.put(word, 0);
}
}
}
);
就比如上面的部分, 虽然 ConcurrentHashMap 里面的方法是线程安全的, 但是多个线程安全的方法放到一起就不是线程安全的了
map.put(word, value+1); 这个方法仅仅能保证方法内部的线程安全, 假设出现下面的情况 :
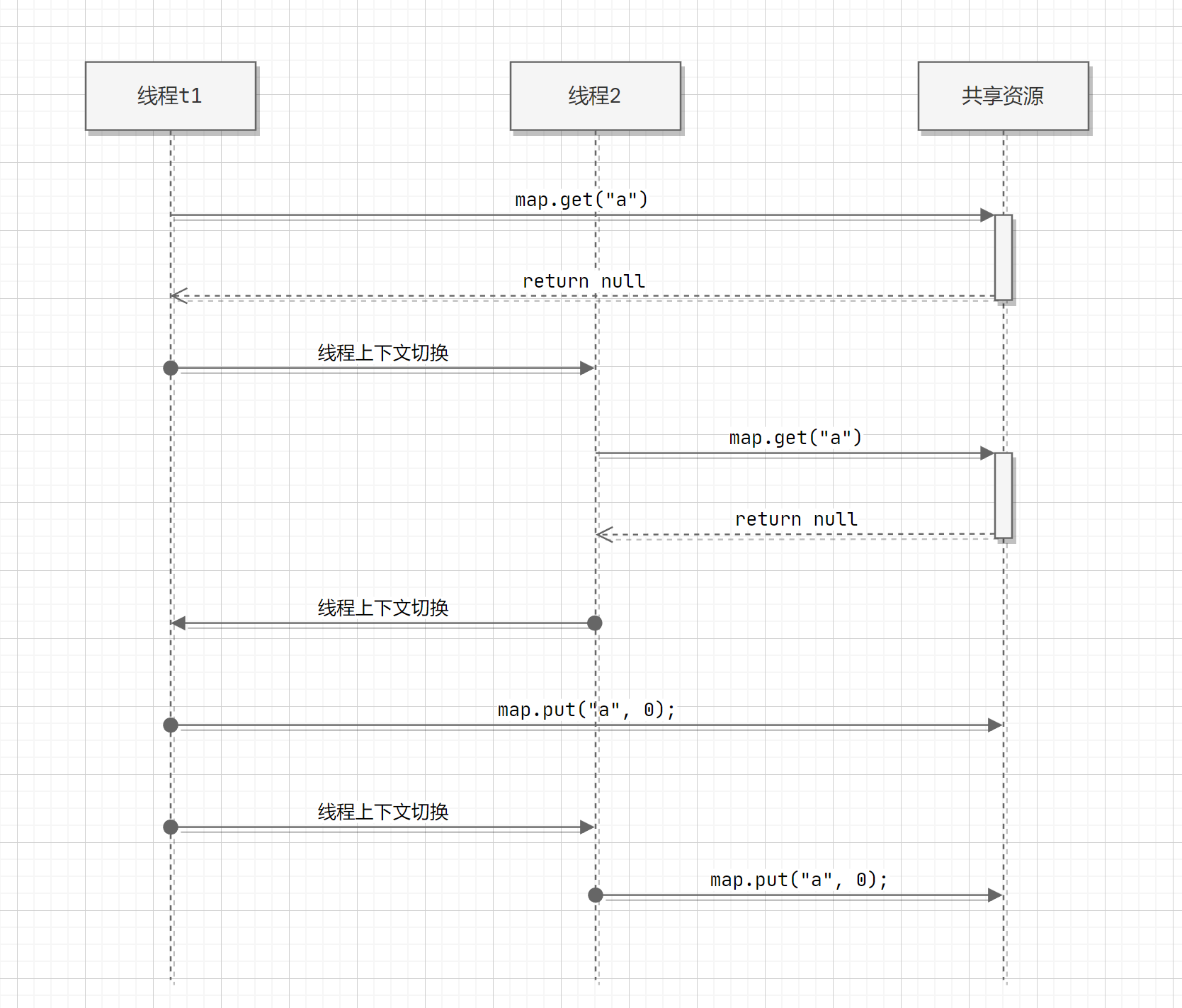
线程安全的实现 :
public static void main(String[] args) {
multithreadedRead(
() -> new ConcurrentHashMap<String, LongAdder>(),
(map, words) -> {
for (String word : words) {
LongAdder longAdder = map.computeIfAbsent(word, (key) -> new LongAdder());
longAdder.increment();
}
}
);
}
multithreadedRead(
() -> new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Integer>(),
(map, words) -> {
for (String word : words) {
map.merge(word, 1, Integer::sum);
}
}
);
执行结果如下 :
{a=200, b=200, c=200, d=200, e=200, f=200, g=200, h=200, i=200, j=200, k=200, l=200, m=200, n=200, o=200, p=200, q=200, r=200, s=200, t=200, u=200, v=200, w=200, x=200, y=200, z=200}
Process finished with exit code 0






















 4966
4966











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










