pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.11.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.gblfy</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-mybatis</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot-mybatis</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--SpringBoot mvc启动器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Mysql数据库驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.28</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--lombok 简化java代码-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.10</version>
</dependency>
<!--druid连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<!--SpringBoot test 启动器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
</project>
首先在 application.properties 中配置数据库基本信息,然后提供两个 DataSource 即可
spring.datasource.one.url=jdbc:mysql:///test01?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.datasource.one.username=root
spring.datasource.one.password=root
spring.datasource.one.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.two.url=jdbc:mysql:///test02?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.datasource.two.username=root
spring.datasource.two.password=root
spring.datasource.two.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
然后再提供两个 DataSource,如下:
import com.alibaba.druid.spring.boot.autoconfigure.DruidDataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.one")
DataSource dsOne() {
return DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.two")
DataSource dsTwo() {
return DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
}
MyBatis 配置
要提供两个 Bean,因此这里两个数据源我将在两个类中分开来配置,首先来看第一个数据源的配置:
mport org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.gblfy.springboot.mybatis.mapper1",sqlSessionFactoryRef = "sqlSessionFactory1",sqlSessionTemplateRef = "sqlSessionTemplate1")
public class MyBatisConfigOne {
@Resource(name = "dsOne")
DataSource dsOne;
@Bean
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory1() {
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
try {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dsOne);
sessionFactory = bean.getObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sessionFactory;
}
@Bean
SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate1() {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory1());
}
}
创建 MyBatisConfigOne 类,首先指明该类是一个配置类,配置类中要扫描的包是 org.javaboy.mybatis.mapper1 ,即该包下的 Mapper 接口将操作 dsOne 中的数据,对应的 SqlSessionFactory 和 SqlSessionTemplate 分别是 sqlSessionFactory1 和 sqlSessionTemplate1,在 MyBatisConfigOne 内部,分别提供 SqlSessionFactory 和 SqlSessionTemplate 即可, SqlSessionFactory 根据 dsOne 创建,然后再根据创建好的SqlSessionFactory 创建一个 SqlSessionTemplate。
这里配置完成后,依据这个配置,再来配置第二个数据源即可:
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.gblfy.springboot.mybatis.mapper2",sqlSessionFactoryRef = "sqlSessionFactory2",sqlSessionTemplateRef = "sqlSessionTemplate2")
public class MyBatisConfigTwo {
@Resource(name = "dsTwo")
DataSource dsTwo;
@Bean
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory2() {
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
try {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dsTwo);
sessionFactory = bean.getObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sessionFactory;
}
@Bean
SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate2() {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory2());
}
}
好了,这样 MyBatis 多数据源基本上就配置好了,接下来只需要在 org.javaboy.mybatis.mapper1 和 org.javaboy.mybatis.mapper2 包中提供不同的 Mapper,Service 中注入不同的 Mapper 就可以操作不同的数据源。
com.gblfy.springboot.mybatis.mapper1中的 mapper:
import com.gblfy.springboot.mybatis.entity.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserMapperOne{
List<User> getAllUser();
}
对应的 XML 文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.gblfy.springboot.mybatis.mapper1.UserMapperOne">
<select id="getAllUser" resultType="com.gblfy.springboot.mybatis.entity.User">
select * from user;
</select>
</mapper>
com.gblfy.springboot.mybatis.mapper2中的 mapper:
import com.gblfy.springboot.mybatis.entity.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> getAllUser();
}
对应的 XML 文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.gblfy.springboot.mybatis.mapper2.UserMapper">
<select id="getAllUser" resultType="com.gblfy.springboot.mybatis.entity.User">
select * from user;
</select>
</mapper>
实体类:
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@Data
public class User implements Serializable {
//主键
private Long id;
//姓名
private String name;
//年龄
private Integer age;
//邮箱
private String email;
//创建时间
private LocalDateTime createTime;
}
数据库脚本;
one
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user;
CREATE TABLE user
(
id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID',
name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
age INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
email VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱',
create_time DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
DELETE FROM user;
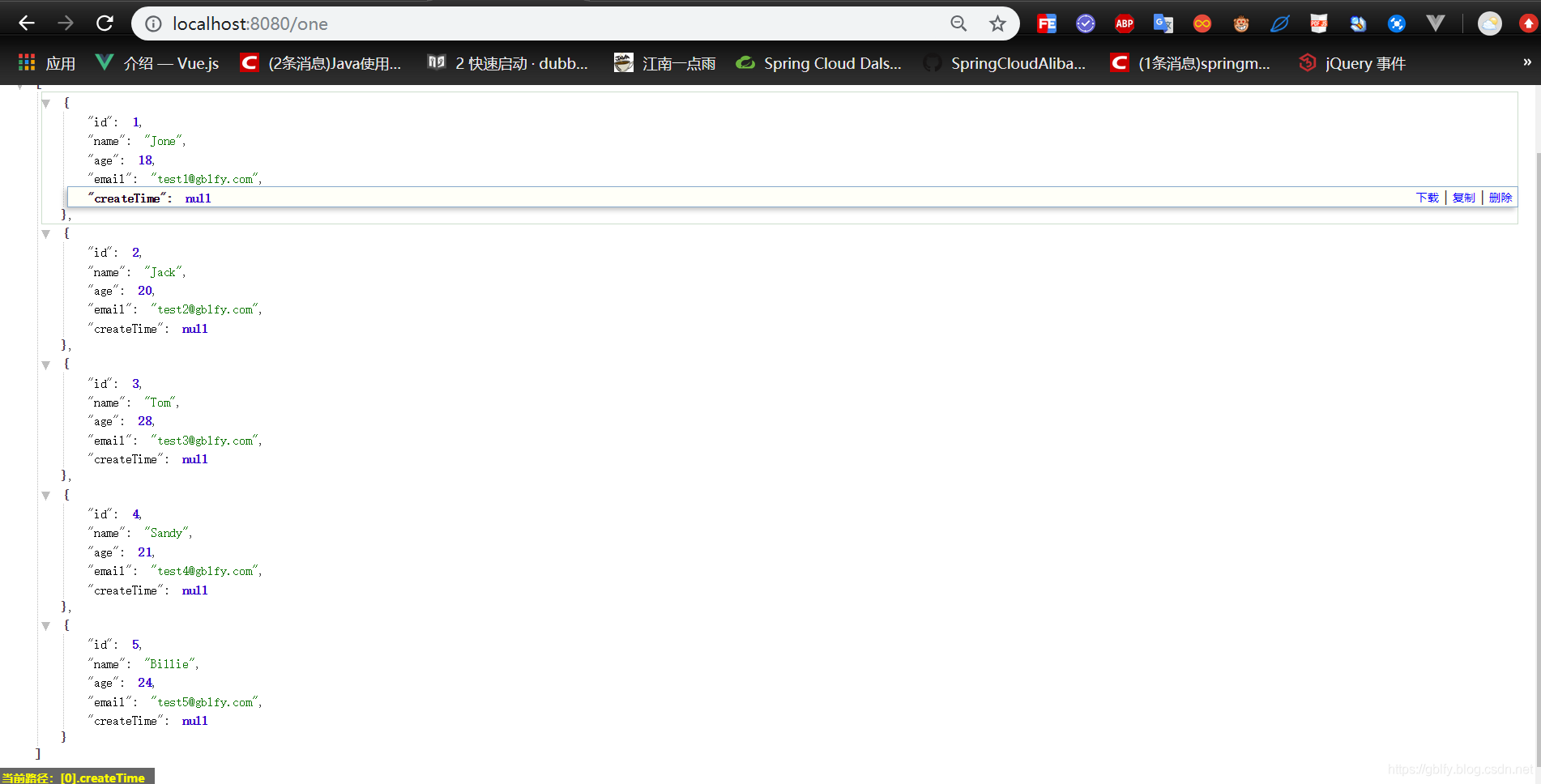
INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email, create_time) VALUES
(1, 'Jone', 18, 'test1@gblfy.com','2019-01-11 14:20:20'),
(2, 'Jack', 20, 'test2@gblfy.com','2019-02-05 11:12:22'),
(3, 'Tom', 28, 'test3@gblfy.com','2019-02-14 08:31:16'),
(4, 'Sandy', 21, 'test4@gblfy.com','2019-01-14 09:15:15'),
(5, 'Billie', 24, 'test5@gblfy.com','2019-01-14 09:48:16');
two
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user;
CREATE TABLE user
(
id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID',
name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
age INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
email VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱',
create_time DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
DELETE FROM user;
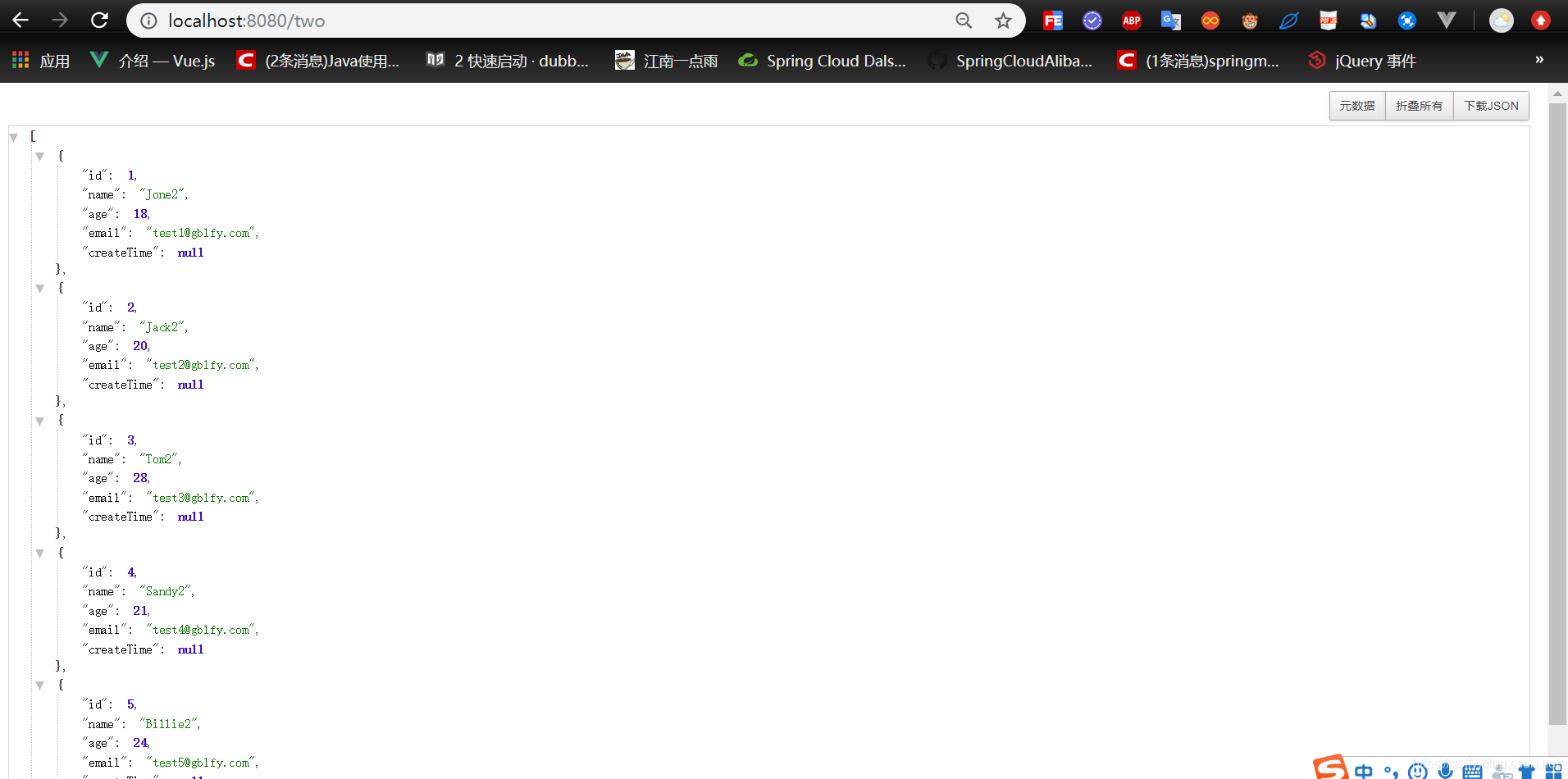
INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email, create_time) VALUES
(1, 'Jone2', 18, 'test1@gblfy.com','2019-01-11 14:20:20'),
(2, 'Jack2', 20, 'test2@gblfy.com','2019-02-05 11:12:22'),
(3, 'Tom2', 28, 'test3@gblfy.com','2019-02-14 08:31:16'),
(4, 'Sandy2', 21, 'test4@gblfy.com','2019-01-14 09:15:15'),
(5, 'Billie2', 24, 'test5@gblfy.com','2019-01-14 09:48:16');
写一个测试controller
import com.gblfy.springboot.mybatis.entity.User;
import com.gblfy.springboot.mybatis.mapper1.UserMapperOne;
import com.gblfy.springboot.mybatis.mapper2.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class PageController {
@Autowired
private UserMapperOne userMapperOne;
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@GetMapping("/one")
public List<User> getOneList() {
return userMapperOne.getAllUser();
}
@GetMapping("/two")
public List<User> getTwoList() {
return userMapper.getAllUser();
}
}
启动项目:
依次访问
http://localhost:8080/one






















 3673
3673











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










