Spring Boot
1. SpringBoot基本应用
1.1 约定优于配置
Build Anything with Spring Boot:Spring Boot is the starting point for building all Spring-based applications. Spring Boot is designed to get you up and running as quickly as possible, with minimal upfront configuration of Spring.
Spring Boot 是所有基于 Spring 开发的项目的起点。Spring Boot 的设计是为了让你尽可能快的跑起来 Spring 应用程序并且尽可能减少你的配置文件。
- 约定优于配置(Convention over Configuration),又称按约定编程,是一种软件设计范式。
本质上是说,系统、类库或框架应该假定合理的默认值,而非要求提供不必要的配置。只有在偏离这一个约定的时候,例如 想要将该表命名为person,才需要写有关这个名字的配置。
约定优于配置简单来理解,就是遵循约定。
1.2 SpringBoot概念
1.2.1 Spring优缺点分析
优点:
Spring是Java企业版(Java Enterprise Edition,JEE,也称J2EE)的轻量级代替品。
无需开发重量级的 Enterprise Java Bean(EJB),Spring为企业级Java开发提供了一种相对简单的方法,通过依赖注入和 面向切面编程,用简单的Java对象(Plain Old Java Object,POJO)实现了EJB的功能
缺点:
- 虽然Spring的组件代码是轻量级的,但它的配置却是重量级的。
一开始,Spring用XML配置,而且是很 多XML配 置。Spring 2.5引入了基于注解的组件扫描,这消除了大量针对应用程序自身组件的显式XML 配置。Spring 3.0引入了基于Java的配置,这是一种类型安全的可重构配置方式,可以代替XML。
所有这些配置都代表了开发时的损耗。因为在思考Spring特性配置和解决业务问题之间需要进行思维切 换,所以编写配置挤占了编写应用程序逻辑的时间。和所有框架一样,Spring实用,但与此同时它要求 的回报也不少。
- 除此之外,项目的依赖管理也是一件耗时耗力的事情。
在环境搭建时,需要分析要导入哪些库的坐标, 而且还需要分析导入与之有依赖关系的其他库的坐标,一旦选错了依赖的版本,随之而来的不兼容问题 就会严重阻碍项目的开发进度。
- SSM的整合:
Spring、Spring MVC、Mybatis、Spring-Mybatis整合包、数据库驱动,引入依赖的数量繁 多、容易存在版本冲突。
1.2.2 Spring Boot解决上述spring问题
基于约定优于配置的思想,可以让开发人员不必在 配置与逻辑 业务之间进行思维的切换,全身心的投入到逻辑业务的代码编写中,从而大大提高了开发的 效率,一定程度上缩短了项目周期。
起步依赖
起步依赖本质上是一个Maven项目对象模型(Project Object Model,POM),定义了对其他库的传递依 赖,这些东西加在一起即支持某项功能。
简单的说,起步依赖就是将具备某种功能的依赖坐标打包到一起,并提供一些默认的功能。
自动配置
springboot的自动配置,指的是springboot,会自动将一些配置类的bean注册进ioc容器,我们可以需 要的地方使用@autowired或者@resource等注解来使用它。
只需要引我们想用功能的包,相关的配置我们完全不用管,springboot会自动注入这些配置bean,我们直接使用这些bean即可
springboot: 简单、快速、方便地搭建项目,对主流开发框架的无配置集成,极大提高了开发、部署效率
1.3 Spring Boot入门案例
需求:请求Controller中的方法,并将返回值响应到页面
(1)依赖管理
<!--
所用的springBoot项目都会直接或者间接的继承spring-boot-starter-parent
1.指定项目的编码格式为UTF-8
2.指定JDK版本为1.8
3.对项目依赖的版本进行管理,当前项目再引入其他常用的依赖时就不需要再指定版本号,避免版本冲突的问题
4.默认的资源过滤和插件管理
-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!--引入Spring Web及Spring MVC相关的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!--可以将project打包为一个可以执行的jar-->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
(2)启动类
/**
* SpringBoot的启动类通常放在二级包中,比如:com.lagou.SpringBootDemo1Application
* 因为SpringBoot项目在做包扫描,会扫描启动类所在的包及其子包下的所有内容。
*/
//标识当前类为SpringBoot项目的启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootDemo1Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//样板代码
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemo1Application.class, args);
}
}
(3)Controller
package com.lagou.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/boot")
public String helloBoot(){
return "Hello Spring Boot";
}
}
1.4 SpringBoot 快速构建
需求:请求Controller中的方法,并将返回值响应到页面
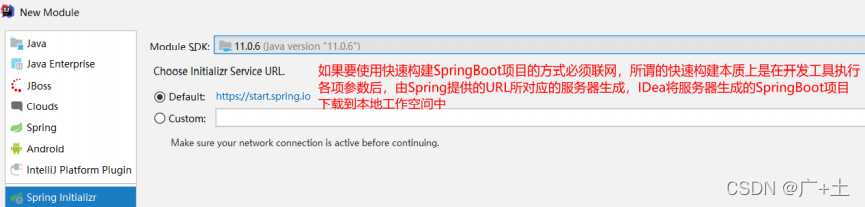
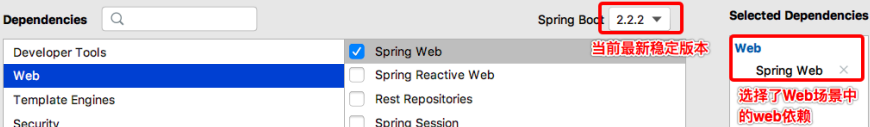
(1)使用Spring Initializr方式构建Spring Boot项目
本质上说,Spring Initializr是一个Web应用,它提供了一个基本的项目结构,能够帮助我们快速构建一个基础的Spring Boot项目
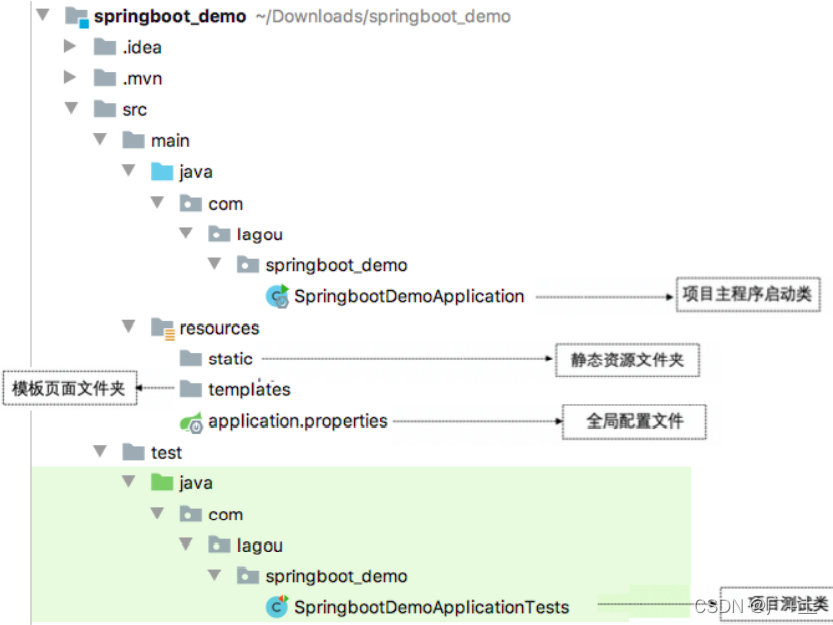
创建好的Spring Boot项目结构如图:
(2) 创建一个用于Web访问的Controller
-
创建一个请求处理控制类com.lagou.controller.HelloController, 并编写一个请求处理方法
-
注意:将项目启动类SpringBootDemoApplication移动到com.lagou包下
@RestController // 该注解为组合注解,等同于Spring中@Controller+@ResponseBody注解
public class DemoController {
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public String demo(){
return "hello spring Boot";
}
}
(3) 运行项目
运行主程序启动类SpringbootDemoApplication,项目启动成功后,在控制台上会发现Spring Boot项目默认启动的端口号为8080,此时,可以在浏览器上访问“http://localhost:8080/hello”。页面输出的内容是“hello Spring Boot”,至此,构建Spring Boot项目就完成了
1.5 单元测试与热部署
开发中,每当完成一个功能接口或业务方法的编写后,通常都会借助单元测试验证该功能是否正确。Spring Boot对项目的单元测试提供了很好的支持,在使用时,需要提前在项目的pom.xml文件中添 加spring-boot-starter-test测试依赖启动器,可以通过相关注解实现单元测试
1.5.1 单元测试
1.添加spring-boot-starter-test测试依赖启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
注意:使用Spring Initializr方式搭建的Spring Boot项目,会自动加入spring-boot-starter-test测试依赖 启动器,无需再手动添加
2.编写单元测试类和测试方法
使用Spring Initializr方式搭建的Spring Boot项目,会在src.test.java测试目录下自动创建与项目主程序 启动类对应的单元测试类
package com.lagou;
import com.lagou.controller.HelloController;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.JUnit4;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
/**
* SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class:Spring运行环境
* JUnit4.class:JUnit运行环境
* SpringRunner.class:Spring Boot运行环境
*/
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) //@RunWith:运行器
@SpringBootTest //标记为当前类为SpringBoot测试类,加载项目的ApplicationContext上下文环境
class Springbootdemo2ApplicationTests {
/**
* 需求:调用HelloController的hello方法
*/
@Autowired
private HelloController helloController;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
String result = helloController.hello();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
1.5.2 热部署
Spring Boot框 架专门提供了进行热部署的依赖启动器,用于进行项目热部署,而无需手动重启项目 。
热部署:在修改完代码之后,不需要重新启动容器,就可以实现更新。
1.添加spring-boot-devtools热部署依赖启动器
<!-- 引入热部署依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. IDEA工具热部署设置
开启Idea的自动编译
File->Settings,选择Build下的Compiler选项,在右侧勾选“Build project automatically”选项将项目设置为自动编译,保存设置
开启Idea的在项目运行中自动编译的功能
在项目任意页面中使用组合快捷键“Ctrl+Shift+Alt+/”打开Maintenance选项框,选中并打开 Registry页面,列表中找到“compiler.automake.allow.when.app.running”,将该选项后的Value值勾选,用于指 定IDEA工具在程序运行过程中自动编译,最后单击【Close】按钮完成设置
3.热部署效果测试
打开http://localhost:8080/hello查看效果;接下来,在不关闭当前项目的情况下,将DemoController 类中的请求处理方法hello()的返回值修改,查看控制台信息会发现项目能够自动构 建和编译,说明项目热部署生效;同时,刷新浏览器后输出内容随之修改,说明项目热部署配置成功
1.6 全局配置文件
- 全局配置文件能够对一些默认配置值进行修改。
- Spring Boot使用一个application.properties或者 application.yaml的文件作为全局配置文件,
- 该文件存放在src/main/resource目录或者类路径 的/config,一般会选择resource目录。
Spring Boot配置文件的命名及其格式:
- application.properties
- application.yaml或application.yml
1.6.1 application.properties配置文件
我们可以在application.properties文件中定义Spring Boot项目的相关属性,当然,这些相关属性可以 是系统属性、环境变量、命令参数等信息,也可以是自定义配置文件名称和位置
#修改tomcat的版本号
server.port=8888
#定义数据库的连接信息 JdbcTemplate
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/lagou
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=wu7787879
接下来,通过一个案例对Spring Boot项目中application.properties配置文件的具体使用进行讲解
(1)将配置属性注入到实体类
public class Pet {
private String type;
private String name;
}
演示将application.properties配置文件中的自定义配置属性(下一步编写)注入到 Person实体类的对应属性中
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private int id; //id
private String name; //名称
private List hobby; //爱好
private String[] family; //家庭成员
private Map map;
private Pet pet; //宠物
}
注解:
- @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “person”):将配置文件中以person开头的属性值通过 setXX()方法注入到实体类对应属性中
- @Component:将当前注入属性值的Person类对象作为Bean组件放到Spring容器中,只有这样才能被@ConfigurationProperties注解进行赋值
(2)编写需要对 Person类设置的配置属性
#自定义配置信息
person.id=1
person.name=王二麻子
person.hobby=read,write
person.family=father,mather
person.map.key1=value1
person.map.key2=value2
person.pet.type=dog
person.pet.name=哈士奇
(3)项目测试类
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) // 测试启动器,并加载Spring Boot测试注解
@SpringBootTest // 标记为Spring Boot单元测试类,并加载项目的ApplicationContext上下文环境
class SpringbootDemoApplicationTests {
// 配置测试
@Autowired
private Person person;
@Test
void configurationTest() {
System.out.println(person);
}
}
测试方法configurationTest()运行成功,同时正确打印出了Person实体类对象,说明 application.properties配置文件属性配置正确,并通过相关注解自动完成了属性注入 。
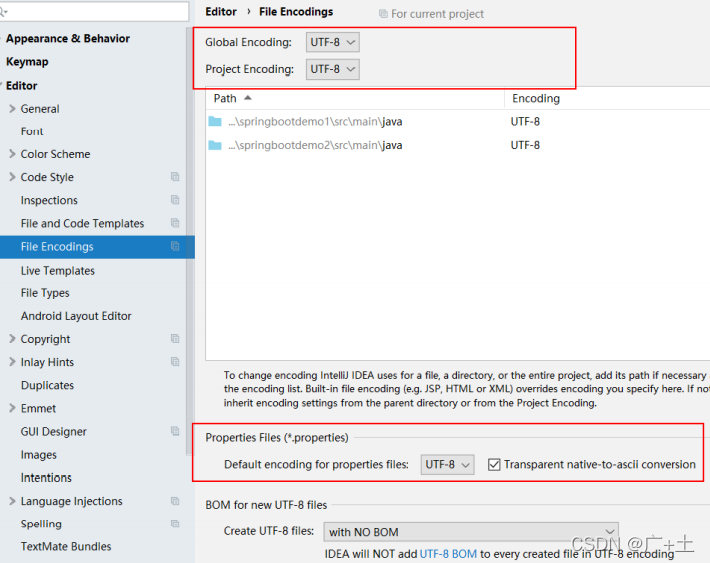
(4)中文乱码问题解决
- 调整文件编码格式:
- 设置Tomcat及Http编码
#解决中文乱码
server.tomcat.uri-encoding=UTF-8
spring.http.encoding.force=true
spring.http.encoding.charset=UTF-8
spring.http.encoding.enabled=true
1.6.2 application.yaml配置文件
-
YAML文件格式是Spring Boot支持的一种JSON文件格式
-
YAML文件的扩展名可以使用.yml或者.yaml
-
application.yml文件使用 “key:(冒号后面必须加空格)value”格式配置属性,使用缩进控制层级关系
-
相较于传统的Properties配置文件,YAML文件以数据为核心,是一种更为直观且容易被电脑识别的数据序列化格式。
-
application.yaml配置文件的工作原理和application.properties是一样的,只不过yaml格式配置文件看起来更简洁一些
(1)value值为普通数据类型(例如数字、字符串、布尔等)
可以直接配置对应的属性值;同时对于字符串类型的属性值,不需要额外添加引号
server:
port: 8080
servlet:
context-path: /hello
(2)value值为数组和单列集合
主要有两种书写方式:缩进式写法和行内式写法。
缩进式
- 写法一(-(空格)属性值)
person:
hobby:
- play
- read
- sleep
- 写法二(英文逗号分隔,最后一个属性值后不加)
person:
hobby:
play,
read,
sleep
行内式
person:
hobby: [play,read,sleep]
行内式写法更加简明、方便。另外,包含属性值的中括 号“[]”还可以进一步省略,在进行属性赋值时,程序会自动匹配和校对
(3)value值为Map集合和对象
缩进式写法的形式按照YAML文件格式编写即可,而行内式写法的属性值要用大括号“{}”包含。
缩进式
person:
map:
k1: v1
k2: v2
行内式
person:
map: {
k1: v1,k2: v2}
演示案例:
(1)编写为Person 类设置的配置属性
注意:本次使用application.yaml配置文件进行测试时需要提前将application.properties配置 文件中编写的配置注释,这是因为application.properties配置文件会覆盖application.yaml配置文件
#对实体类对象Person进行属性配置
person:
id: 1
name: 王二麻子
family:
- 妻
- 妾
hobby:
- play
- read
- sleep
map:
k1: value1
k2: value2
pet:
type: 狗
name: 哈士奇
1.7 配置文件属性值的注入
配置文件的优先级如下: 从低到高(按照下面的声明顺序)
<includes>
<include>**/application*.yml</include>
<include>**/application*.yaml</include>
<include>**/application*.properties</include>
</includes>
1.7.1 使用@ConfigurationProperties注入属性
使用Spring Boot全局配置文件设置属性时:
- Spring Boot已有属性,如服务端口server.port,那么Spring Boot内部会自动扫描并读取这些配置文件中的属性值并覆盖默认属性。
- 用户自定义属性,如自定义的Person实体类属性,还必须在程序中注入这些配置属性方可生效。
@Component
//将配置文件中所有以person开头的配置信息注入当前类中
//前提1:必须保证配置文件中person.xx与当前Person类的属性名一致
//前提2:必须保证当前Person中的属性都具有set方法
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private int id; //id
private String name; //名称
private List hobby; //爱好
private String[] family; //家庭成员
private Map map;
private Pet pet; //宠物
}
- Spring Boot提供的@ConfigurationProperties注解用来快速、方便地将配置文件中的自定义属性值批量 注入到某个Bean对象的多个对应属性中
- 使用@Component和@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “person”)将配置文件中的每个属性 映射到person类组件中。
1.7.2 使用@Value注入属性
- @Value注解是Spring框架提供的,用来读取配置文件中的属性值并逐个注入到Bean对象的对应属性中,Spring Boot框架从Spring框架中对@Value注解进行了默认继承,所以在Spring Boot框架中还可以使用该注解读取和注入配置文件属性值。
@Component
public class Person {
@Value("${person.id}")
private int id;
}
-
使用@Component和@Value注入Person实体类的id属性。其中,@Value不仅可以 将配置文件的属性注入Person的id属性,还可以直接给id属性赋值,这点是@ConfigurationProperties 不支持的
-
使用@Value注解方式需要对每一个属性注入设置,同时又免去了属性的 setXX()方法
-
@Value注 解对于包含Map集合、对象以及YAML文件格式的行内式写法的配置文件的属性注入都不支持,如果赋值会出现错误
1.8 自定义配置文件
Spring Boot会自动加载全局配置文件从而免除我们手动加载的烦恼。但是,如果我们自定义配置文件,Spring Boot是无 法识别这些配置文件的,此时就需要我们手动加载。
1.8.1 使用@PropertySource加载配置文件
-
@PropertySource注解用于指定自定义配置文件的具体位置 和名称
-
如需将自定义配置文件中的属性值注入到对应类的属性中,可使用 @ConfigurationProperties或者@Value注解进行属性值注入
演示:
(1)resources目录下新建test.properties自定义配置文件








 本文详述了Spring Boot的基本应用,包括约定优于配置、Spring Boot的概念与优点、自动配置、快速构建案例、单元测试与热部署。此外,还探讨了Spring Boot的全局配置文件,包括application.properties和YAML格式的配置,以及配置文件属性值的注入。最后,文章介绍了Spring Boot如何整合MyBatis和Redis,以及视图技术Thymeleaf的使用。
本文详述了Spring Boot的基本应用,包括约定优于配置、Spring Boot的概念与优点、自动配置、快速构建案例、单元测试与热部署。此外,还探讨了Spring Boot的全局配置文件,包括application.properties和YAML格式的配置,以及配置文件属性值的注入。最后,文章介绍了Spring Boot如何整合MyBatis和Redis,以及视图技术Thymeleaf的使用。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 85
85











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








