FFmpeg合成流程
示例本程序会⽣成⼀个合成的⾳频和视频流,并将它们编码和封装输出到输出⽂件,输出格式是根据⽂件 扩展名⾃动猜测的。
示例的流程图如下所示。
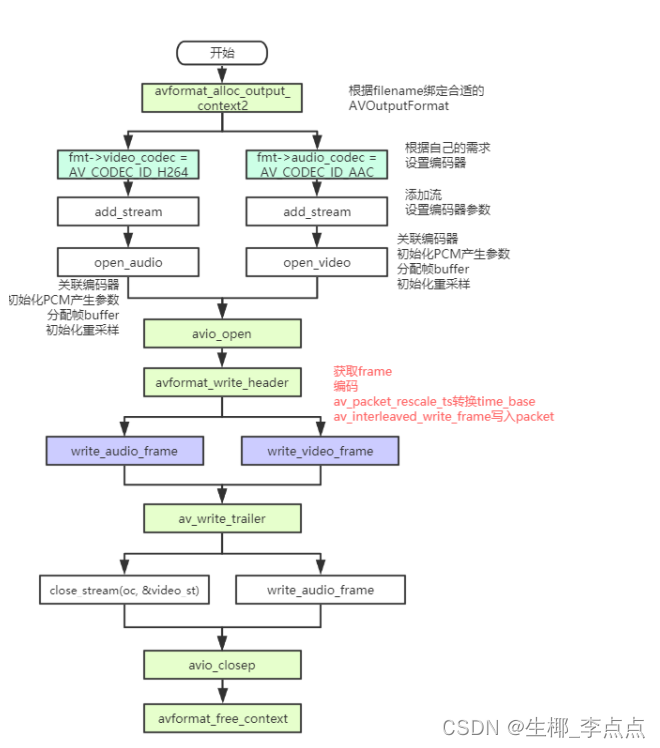
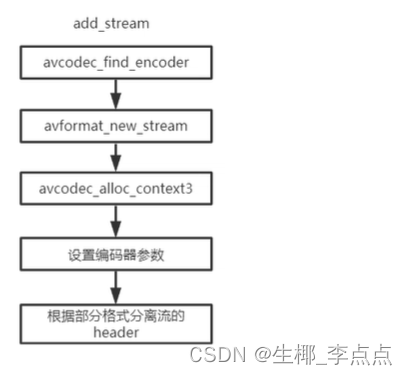
ffmpeg 的 Mux 主要分为 三步操作:
- avformat_write_header : 写⽂件头
- av_write_frame/av_interleaved_write_frame: 写packet
- av_write_trailer : 写⽂件尾
avcodec_parameters_from_context:
将AVCodecContext结构体中码流参数拷⻉到AVCodecParameters结构体中,和avcodec_parameters_to_context刚好相反。
FFmpeg函数:avformat_write_header
int avformat_write_header(AVFormatContext *s, AVDictionary **options)
{
int ret = 0;
int already_initialized = s->internal->initialized;
int streams_already_initialized = s->internal->streams_initialized;
if (!already_initialized)
if ((ret = avformat_init_output(s, options)) < 0)
return ret;
if (!(s->oformat->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE) && s->pb)
avio_write_marker(s->pb, AV_NOPTS_VALUE, AVIO_DATA_MARKER_HEADER);
if (s->oformat->write_header) {
ret = s->oformat->write_header(s);
if (ret >= 0 && s->pb && s->pb->error < 0)
ret = s->pb->error;
if (ret < 0)
goto fail;
flush_if_needed(s);
}
if (!(s->oformat->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE) && s->pb)
avio_write_marker(s->pb, AV_NOPTS_VALUE, AVIO_DATA_MARKER_UNKNOWN);
if (!s->internal->streams_initialized) {
if ((ret = init_pts(s)) < 0)
goto fail;
}
return streams_already_initialized;
fail:
if (s->oformat->deinit)
s->oformat->deinit(s);
return ret;
}
最终调⽤到复⽤器的 write_header,⽐如
AVOutputFormat ff_flv_muxer = {
.name = "flv",
.long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("FLV (Flash Video)"),
.mime_type = "video/x-flv",
.extensions = "flv",
.priv_data_size = sizeof(FLVContext),
.audio_codec = CONFIG_LIBMP3LAME ? AV_CODEC_ID_MP3 : AV_CODEC_ID_ADPCM_SWF,
.video_codec = AV_CODEC_ID_FLV1,
.init = flv_init,
.write_header = flv_write_header,
.write_packet = flv_write_packet,
.write_trailer = flv_write_trailer,
.check_bitstream= flv_check_bitstream,
.codec_tag = (const AVCodecTag* const []) {
flv_video_codec_ids, flv_audio_codec_ids, 0
},
.flags = AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER | AVFMT_VARIABLE_FPS |
AVFMT_TS_NONSTRICT,
.priv_class = &flv_muxer_class,
};
FFmpeg结构体:avformat_alloc_output_context2
函数在在libavformat.h⾥⾯的定义
/**
* Allocate an AVFormatContext for an output format.
* avformat_free_context() can be used to free the context and
* everything allocated by the framework within it.
* * @param *ctx is set to the created format context, or to NULL in
* case of failure
* @param oformat format to use for allocating the context, if NULL
* format_name and filename are used instead
* @param format_name the name of output format to use for allocating the
* context, if NULL filename is used instead
* @param filename the name of the filename to use for allocating the
* context, may be NULL
* @return >= 0 in case of success, a negative AVERROR code in case of
* failure
*/
int avformat_alloc_output_context2(AVFormatContext **ctx, ff_const59 AVOutputFormat *oformat,
const char *format_name, const char *filename);
函数参数的介绍:
- ctx:需要创建的context,返回NULL表示失败。
- oformat:指定对应的AVOutputFormat,如果不指定,可以通过后⾯format_name、filename两个参 数进⾏指定,让ffmpeg⾃⼰推断。
- format_name: 指定⾳视频的格式,⽐如“flv”,“mpeg”等,如果设置为NULL,则由filename进⾏指 定,让ffmpeg⾃⼰推断。
- filename: 指定⾳视频⽂件的路径,如果oformat、format_name为NULL,则ffmpeg内部根据 filename后缀名选择合适的复⽤器,⽐如xxx.flv则使⽤flv复⽤器。
int avformat_alloc_output_context2(AVFormatContext **avctx, ff_const59 AVOutputFormat *oformat,
const char *format, const char *filename)
{
AVFormatContext *s = avformat_alloc_context();
int ret = 0;
*avctx = NULL;
if (!s)
goto nomem;
if (!oformat) {
if (format) {
oformat = av_guess_format(format, NULL, NULL);
if (!oformat) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Requested output format '%s' is not a suitable output format\n", format);
ret = AVERROR(EINVAL);
goto error;
}
} else {
oformat = av_guess_format(NULL, filename, NULL);
if (!oformat) {
ret = AVERROR(EINVAL);
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Unable to find a suitable output format for '%s'\n",
filename);
goto error;
}
}
}
s->oformat = oformat;
if (s->oformat->priv_data_size > 0) {
s->priv_data = av_mallocz(s->oformat->priv_data_size);
if (!s->priv_data)
goto nomem;
if (s->oformat->priv_class) {
*(const AVClass**)s->priv_data= s->oformat->priv_class;
av_opt_set_defaults(s->priv_data);
}
} else
s->priv_data = NULL;
if (filename) {
#if FF_API_FORMAT_FILENAME
FF_DISABLE_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS
av_strlcpy(s->filename, filename, sizeof(s->filename));
FF_ENABLE_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS
#endif
if (!(s->url = av_strdup(filename)))
goto nomem;
}
*avctx = s;
return 0;
nomem:
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Out of memory\n");
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
error:
avformat_free_context(s);
return ret;
}
可以看出,⾥⾯最主要的就两个函数,avformat_alloc_context和av_guess_format,⼀个 是申请内存分配上下⽂,⼀个是通过后⾯两个参数获取AVOutputFormat。
出av_guess_format这个函数会通过filename和short_name来和所有的编码器进⾏⽐对,找 出最接近的编码器然后返回。
ff_const59 AVOutputFormat *av_guess_format(const char *short_name, const char *filename,
const char *mime_type)
{
const AVOutputFormat *fmt = NULL;
AVOutputFormat *fmt_found = NULL;
void *i = 0;
int score_max, score;
/* specific test for image sequences */
#if CONFIG_IMAGE2_MUXER
if (!short_name && filename &&
av_filename_number_test(filename) &&
ff_guess_image2_codec(filename) != AV_CODEC_ID_NONE) {
return av_guess_format("image2", NULL, NULL);
}
#endif
/* Find the proper file type. */
score_max = 0;
while ((fmt = av_muxer_iterate(&i))) {
score = 0;
if (fmt->name && short_name && av_match_name(short_name, fmt->name))
score += 100;
if (fmt->mime_type && mime_type && !strcmp(fmt->mime_type, mime_type))
score += 10;
if (filename && fmt->extensions &&
av_match_ext(filename, fmt->extensions)) {
score += 5;
}
if (score > score_max) {
score_max = score;
fmt_found = (AVOutputFormat*)fmt;
}
}
return fmt_found;
}
FFmpeg结构体:AVOutputFormat
1.描述
AVOutpufFormat表示输出⽂件容器格式,AVOutputFormat 结构主要包含的信息有:封装名称描述,编 码格式信息(video/audio 默认编码格式,⽀持的编码格式列表),⼀些对封装的操作函数 (write_header,write_packet,write_tailer等)。 ffmpeg⽀持各种各样的输出⽂件格式,MP4,FLV,3GP等等。⽽ AVOutputFormat 结构体则保存了这 些格式的信息和⼀些常规设置。 每⼀种封装对应⼀个 AVOutputFormat 结构,ffmpeg将AVOutputFormat 按照链表存储:
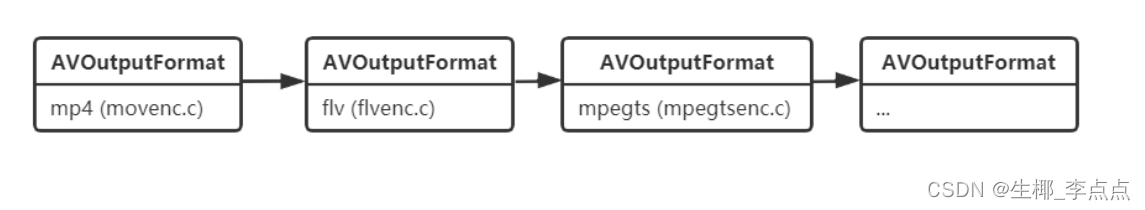
2.结构体定义
/**
* @addtogroup lavf_encoding
* @{
*/
typedef struct AVOutputFormat {
const char *name;
/**
* Descriptive name for the format, meant to be more human-readable
* than name. You should use the NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL() macro
* to define it.
*/
const char *long_name;
const char *mime_type;
const char *extensions; /**< comma-separated filename extensions */
/* output support */
enum AVCodecID audio_codec; /**< default audio codec */
enum AVCodecID video_codec; /**< default video codec */
enum AVCodecID subtitle_codec; /**< default subtitle codec */
/**
* can use flags: AVFMT_NOFILE, AVFMT_NEEDNUMBER,
* AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER, AVFMT_NOTIMESTAMPS, AVFMT_VARIABLE_FPS,
* AVFMT_NODIMENSIONS, AVFMT_NOSTREAMS, AVFMT_ALLOW_FLUSH,
* AVFMT_TS_NONSTRICT, AVFMT_TS_NEGATIVE
*/
int flags;
/**
* List of supported codec_id-codec_tag pairs, ordered by "better
* choice first". The arrays are all terminated by AV_CODEC_ID_NONE.
*/
const struct AVCodecTag * const *codec_tag;
const AVClass *priv_class; ///< AVClass for the private context
/*****************************************************************
* No fields below this line are part of the public API. They
* may not be used outside of libavformat and can be changed and
* removed at will.
* New public fields should be added right above.
*****************************************************************
*/
/**
* The ff_const59 define is not part of the public API and will
* be removed without further warning.
*/
#if FF_API_AVIOFORMAT
#define ff_const59
#else
#define ff_const59 const
#endif
ff_const59 struct AVOutputFormat *next;
/**
* size of private data so that it can be allocated in the wrapper
*/
int priv_data_size;
int (*write_header)(struct AVFormatContext *);
/**
* Write a packet. If AVFMT_ALLOW_FLUSH is set in flags,
* pkt can be NULL in order to flush data buffered in the muxer.
* When flushing, return 0 if there still is more data to flush,
* or 1 if everything was flushed and there is no more buffered
* data.
*/
int (*write_packet)(struct AVFormatContext *, AVPacket *pkt);
int (*write_trailer)(struct AVFormatContext *);
/**
* Currently only used to set pixel format if not YUV420P.
*/
int (*interleave_packet)(struct AVFormatContext *, AVPacket *out,
AVPacket *in, int flush);
/**
* Test if the given codec can be stored in this container.
*
* @return 1 if the codec is supported, 0 if it is not.
* A negative number if unknown.
* MKTAG('A', 'P', 'I', 'C') if the codec is only supported as AV_DISPOSITION_ATTACHED_PIC
*/
int (*query_codec)(enum AVCodecID id, int std_compliance);
void (*get_output_timestamp)(struct AVFormatContext *s, int stream,
int64_t *dts, int64_t *wall);
/**
* Allows sending messages from application to device.
*/
int (*control_message)(struct AVFormatContext *s, int type,
void *data, size_t data_size);
/**
* Write an uncoded AVFrame.
*
* See av_write_uncoded_frame() for details.
*
* The library will free *frame afterwards, but the muxer can prevent it
* by setting the pointer to NULL.
*/
int (*write_uncoded_frame)(struct AVFormatContext *, int stream_index,
AVFrame **frame, unsigned flags);
/**
* Returns device list with it properties.
* @see avdevice_list_devices() for more details.
*/
int (*get_device_list)(struct AVFormatContext *s, struct AVDeviceInfoList *device_list);
/**
* Initialize device capabilities submodule.
* @see avdevice_capabilities_create() for more details.
*/
int (*create_device_capabilities)(struct AVFormatContext *s, struct AVDeviceCapabilitiesQuery *caps);
/**
* Free device capabilities submodule.
* @see avdevice_capabilities_free() for more details.
*/
int (*free_device_capabilities)(struct AVFormatContext *s, struct AVDeviceCapabilitiesQuery *caps);
enum AVCodecID data_codec; /**< default data codec */
/**
* Initialize format. May allocate data here, and set any AVFormatContext or
* AVStream parameters that need to be set before packets are sent.
* This method must not write output.
*
* Return 0 if streams were fully configured, 1 if not, negative AVERROR on failure
*
* Any allocations made here must be freed in deinit().
*/
int (*init)(struct AVFormatContext *);
/**
* Deinitialize format. If present, this is called whenever the muxer is being
* destroyed, regardless of whether or not the header has been written.
*
* If a trailer is being written, this is called after write_trailer().
*
* This is called if init() fails as well.
*/
void (*deinit)(struct AVFormatContext *);
/**
* Set up any necessary bitstream filtering and extract any extra data needed
* for the global header.
* Return 0 if more packets from this stream must be checked; 1 if not.
*/
int (*check_bitstream)(struct AVFormatContext *, const AVPacket *pkt);
} AVOutputFormat;
3.常⻅变量及其作⽤
- const char *name; // 复⽤器名称
- const char *long_name;//格式的描述性名称,易于阅读。
- enum AVCodecID audio_codec; //默认的⾳频编解码器
- enum AVCodecID video_codec; //默认的视频编解码器
- enum AVCodecID subtitle_codec; //默认的字幕编解码器
⼤部分复⽤器都有默认的编码器,所以⼤家如果要调整编码器类型则需要⾃⼰⼿动指定。
比如
AVOutputFormat ff_flv_muxer = {
.name = "flv",
.long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("FLV (Flash Video)"),
.mime_type = "video/x-flv",
.extensions = "flv",
.priv_data_size = sizeof(FLVContext),
.audio_codec = CONFIG_LIBMP3LAME ? AV_CODEC_ID_MP3 : AV_CODEC_ID_ADPCM_SWF,
.video_codec = AV_CODEC_ID_FLV1,
.init = flv_init,
.write_header = flv_write_header,
.write_packet = flv_write_packet,
.write_trailer = flv_write_trailer,
.check_bitstream= flv_check_bitstream,
.codec_tag = (const AVCodecTag* const []) {
flv_video_codec_ids, flv_audio_codec_ids, 0
},
.flags = AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER | AVFMT_VARIABLE_FPS |
AVFMT_TS_NONSTRICT,
.priv_class = &flv_muxer_class,
};
AVOutputFormat ff_mpegts_muxer = {
.name = "mpegts",
.long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("MPEG-TS (MPEG-2 Transport Stream)"),
.mime_type = "video/MP2T",
.extensions = "ts,m2t,m2ts,mts",
.priv_data_size = sizeof(MpegTSWrite),
.audio_codec = AV_CODEC_ID_MP2,
.video_codec = AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG2VIDEO,
.init = mpegts_init,
.write_packet = mpegts_write_packet,
.write_trailer = mpegts_write_end,
.deinit = mpegts_deinit,
.check_bitstream = mpegts_check_bitstream,
.flags = AVFMT_ALLOW_FLUSH | AVFMT_VARIABLE_FPS | AVFMT_NODIMENSIONS,
.priv_class = &mpegts_muxer_class,
};
int (*write_header)(struct AVFormatContext *);
int (*write_packet)(struct AVFormatContext *, AVPacket *pkt);//写⼀个数据包。 如果在标志中设 置AVFMT_ALLOW_FLUSH,则pkt可以为NULL。
int (*write_trailer)(struct AVFormatContext *);
int (*interleave_packet)(struct AVFormatContext *, AVPacket *out, AVPacket *in, int flush);
int (*control_message)(struct AVFormatContext *s, int type, void *data, size_t data_size);//允 许从应⽤程序向设备发送消息。
int (*write_uncoded_frame)(struct AVFormatContext *, int stream_index, AVFrame **frame, unsigned flags);//写⼀个未编码的AVFrame。
int (*init)(struct AVFormatContext *);//初始化格式。 可以在此处分配数据,并设置在发送数据包之前 需要设置的任何AVFormatContext或AVStream参数。
void (*deinit)(struct AVFormatContext *);//取消初始化格式。
int (*check_bitstream)(struct AVFormatContext *, const AVPacket *pkt);//设置任何必要的⽐特流 过滤,并提取全局头部所需的任何额外数据。
FFmpeg函数:avformat_new_stream
AVStream 即是流通道。例如我们将 H264 和 AAC 码流存储为MP4⽂件的时候,就需要在 MP4⽂件中 增加两个流通道,⼀个存储Video:H264,⼀个存储Audio:AAC。(假设H264和AAC只包含单个流通道)。
/**
* Add a new stream to a media file.
* * When demuxing, it is called by the demuxer in read_header(). If the
* flag AVFMTCTX_NOHEADER is set in s.ctx_flags, then it may also
* be called in read_packet().
* * When muxing, should be called by the user before avformat_write_header().
* * User is required to call avcodec_close() and avformat_free_context() to
* clean up the allocation by avformat_new_stream().
* * @param s media file handle
* @param c If non-NULL, the AVCodecContext corresponding to the new stream
* will be initialized to use this codec. This is needed for e.g. codec-specific
* defaults to be set, so codec should be provided if it is known.
* * @return newly created stream or NULL on error.
*/
AVStream *avformat_new_stream(AVFormatContext *s, const AVCodec *c);
avformat_new_stream 在 AVFormatContext 中创建 Stream 通道。
关联的结构体
AVFormatContext :
- unsigned int nb_streams; 记录stream通道数⽬。
- AVStream **streams; 存储stream通道。
- AVStream : int index; 在AVFormatContext 中所处的通道索引
avformat_new_stream之后便在 AVFormatContext ⾥增加了 AVStream 通道(相关的index已经被设 置了)。之后,我们就可以⾃⾏设置 AVStream 的⼀些参数信息。例如 : codec_id , format ,bit_rate ,width , height
FFmpeg函数:av_interleaved_write_frame
函数原型:int av_interleaved_write_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt);
说明:将数据包写⼊输出媒体⽂件,并确保正确的交织(保持packet dts的增⻓性)。 该函数会在内部根据需要缓存packet,以确保输出⽂件中的packet按dts递增的顺序正确交织。如果⾃⼰ 进⾏交织则应调⽤av_write_frame()。
参数:
| s | 媒体⽂件句柄 |
|---|---|
| pkt | 要写⼊的packet。 如果packet使⽤引⽤参考计数的内存⽅式,则此函数将获取此引⽤权(可以理解为 move了reference),并在内部在合适的时候进⾏释放。此函数返回后,调⽤者不得 通过此引⽤访问数据。如果packet没有引⽤计数,libavformat将进⾏复制。 此参数可以为NULL(在任何时候,不仅在结尾),以刷新交织队列。 Packet的stream_index字段必须设置为s-> streams中相应流的索引。 时间戳记(pts,dts)必须设置为stream’s timebase中的正确值(除⾮输出格式⽤ AVFMT_NOTIMESTAMPS标志标记,然后可以将其设置为AV_NOPTS_VALUE)。 同⼀stream后续packet的dts必须严格递增(除⾮输出格式⽤ AVFMT_TS_NONSTRICT标记,则它们只必须不减少)。duration也应设置(如果已 知)。 |
返回值:成功时为0,错误时为负AVERROR。即使此函数调⽤失败,Libavformat仍将始终释放该 packet。
FFmpeg函数:av_compare_ts
/**
* Compare two timestamps each in its own time base.
* * @return One of the following values:
* - -1 if `ts_a` is before `ts_b`
* - 1 if `ts_a` is after `ts_b`
* - 0 if they represent the same position
* * @warning
* The result of the function is undefined if one of the timestamps is outside
* the `int64_t` range when represented in the other's timebase.
*/
int av_compare_ts(int64_t ts_a, AVRational tb_a, int64_t ts_b, AVRational tb_b);
返回值:
- -1 ts_a 在ts_b之前
- 1 ts_a 在ts_b之后
- 0 ts_a 在ts_b同⼀位置
⽤伪代码:return ts_a == ts_b ? 0 : ts_a < ts_b ? -1 : 1
MediaInfo分析⽂件写⼊
这⾥只是分析avformat_write_header和av_write_trailer的作⽤。
flv
只写avformat_write_header
000 File Header (9 bytes)
000 FLV header (9 bytes)
000 Signature: FLV
003 Version: 1 (0x01)
004 Flags: 5 (0x05)
005 Video: Yes
005 Audio: Yes
005 Size: 9 (0x00000009)
009 -------------------------
009 --- FLV, accepted ---
009 -------------------------
009 Meta - onMetaData - 12 elements (288 bytes)
009 Header (15 bytes)
009 PreviousTagSize: 0 (0x00000000)
00D Type: 18 (0x12)
00E BodyLength: 273 (0x000111)
011 Timestamp_Base: 0 (0x000000)
014 Timestamp_Extended: 0 (0x00)
015 StreamID: 0 (0x000000)
018 Type: 2 (0x02) - SCRIPTDATASTRING
019 Value_Size: 10 (0x000A)
01B Value: onMetaData
025 Type: 8 (0x08) -SCRIPTDATAVARIABLE[ECMAArrayLength]
026 ECMAArrayLength: 12 (0x0000000C)
02A duration (19 bytes)
02A StringLength: 8 (0x0008)
02C StringData: duration
034 Type: 0 (0x00) - DOUBLE
035 Value: 0.000
03D width - 352 (16 bytes)
03D StringLength: 5 (0x0005)
03F StringData: width
044 Type: 0 (0x00) - DOUBLE
045 Value: 352.000
04D height - 288 (17 bytes)
04D StringLength: 6 (0x0006)
04F StringData: height
055 Type: 0 (0x00) - DOUBLE
056 Value: 288.000
05E videodatarate - 390625 (24 bytes)
05E StringLength: 13 (0x000D)
060 StringData: videodatarate
06D Type: 0 (0x00) - DOUBLE
06E Value: 390.625
076 videocodecid - 2 (23 bytes)
076 StringLength: 12 (0x000C)
078 StringData: videocodecid
084 Type: 0 (0x00) - DOUBLE
085 Value: 2.000
08D audiodatarate - 62500 (24 bytes)
08D StringLength: 13 (0x000D)
08F StringData: audiodatarate
09C Type: 0 (0x00) - DOUBLE
09D Value: 62.500
0A5 audiosamplerate - 44100 (26 bytes)
0A5 StringLength: 15 (0x000F)
0A7 StringData: audiosamplerate
0B6 Type: 0 (0x00) - DOUBLE
0B7 Value: 44100.000
0BF audiosamplesize - 16 (26 bytes)
0BF StringLength: 15 (0x000F)
0C1 StringData: audiosamplesize
0D0 Type: 0 (0x00) - DOUBLE
0D1 Value: 16.000
0D9 stereo - 1 (0x1) (10 bytes)
0D9 StringLength: 6 (0x0006)
0DB StringData: stereo
0E1 Type: 1 (0x01) - UI8
0E2 Value: 1 (0x01)
0E3 audiocodecid - 2 (23 bytes)
0E3 StringLength: 12 (0x000C)
0E5 StringData: audiocodecid
0F1 Type: 0 (0x00) - DOUBLE
0F2 Value: 2.000
0FA encoder - Lavf58.29.100 (25 bytes)
0FA StringLength: 7 (0x0007)
0FC StringData: encoder
103 Type: 2 (0x02) - SCRIPTDATASTRING
104 Value_Size: 13 (0x000D)
106 Value: Lavf58.29.100
113 filesize (19 bytes)
113 StringLength: 8 (0x0008)
115 StringData: filesize
11D Type: 0 (0x00) - DOUBLE
11E Value: 0.000
129 End Of File (4 bytes)
129 Header (4 bytes)
129 PreviousTagSize: 284 (0x0000011C)
12D ------------------------
12D --- FLV, filling ---
12D ------------------------
12D -------------------------
12D --- FLV, finished ---
12D -------------------------
avformat_write_header+ av_write_trailer 对于FLV⽽⾔没有任何变化。
mp4
avformat_write_header
00 File Type (32 bytes)
00 Header (8 bytes)
00 Size: 32 (0x00000020)
04 Name: ftyp
08 MajorBrand: isom
0C MajorBrandVersion: 512 (0x00000200)
10 CompatibleBrand: isom
14 CompatibleBrand: iso2
18 CompatibleBrand: avc1
1C CompatibleBrand: mp41
20 ----------------------------
20 --- MPEG-4, accepted ---
20 ----------------------------
20 Free space (8 bytes)
20 Header (8 bytes)
20 Size: 8 (0x00000008)
24 Name: free
28 Junk (4 bytes)
28 Header (4 bytes)
28 Size: 0 (0x00000000)
2C Problem (4 bytes)
2C Header (4 bytes)
2C Size: 1835295092 (0x6D646174)
30 Size is wrong: 0 (0x00000000)
30 ---------------------------
30 --- MPEG-4, filling ---
30 ---------------------------
30 ----------------------------
30 --- MPEG-4, finished ---
30 ----------------------------
avformat_write_header+av_write_trailer
000 File Type (32 bytes)
000 Header (8 bytes)
000 Size: 32 (0x00000020)
004 Name: ftyp
008 MajorBrand: isom
00C MajorBrandVersion: 512 (0x00000200)
010 CompatibleBrand: isom
014 CompatibleBrand: iso2
018 CompatibleBrand: avc1
01C CompatibleBrand: mp41
020 ----------------------------
020 --- MPEG-4, accepted ---
020 ----------------------------
020 Free space (8 bytes)
020 Header (8 bytes)
020 Size: 8 (0x00000008)
024 Name: free
028 Data (8 bytes)
028 Header (8 bytes)
028 Size: 8 (0x00000008)
02C Name: mdat
030 File header (214 bytes)
030 Header (8 bytes)
030 Size: 214 (0x000000D6)
034 Name: moov
038 Movie header (108 bytes)
038 Header (8 bytes)
038 Size: 108 (0x0000006C)
03C Name: mvhd
040 Version: 0 (0x00)
041 Flags: 0 (0x000000)
044 Creation time: 0 (0x00000000) -
048 Modification time: 0 (0x00000000) -
04C Time scale: 1000 (0x000003E8) - 1000 Hz
050 Duration: 0 (0x00000000) - 0 ms
054 Preferred rate: 65536 (0x00010000) - 1.000
058 Preferred volume: 256 (0x0100) - 1.000
05A Reserved: (10 bytes)
064 Matrix structure (36 bytes)
064 a (width scale): 1.000
068 b (width rotate): 0.000
06C u (width angle): 0.000
070 c (height rotate): 0.000
074 d (height scale): 1.000
078 v (height angle): 0.000
07C x (position left): 0.000
080 y (position top): 0.000
084 w (divider): 1.000
088 Preview time: 0 (0x00000000)
08C Preview duration: 0 (0x00000000)
090 Poster time: 0 (0x00000000)
094 Selection time: 0 (0x00000000)
098 Selection duration: 0 (0x00000000)
09C Current time: 0 (0x00000000)
0A0 Next track ID: 2 (0x00000002)
0A4 User Data (98 bytes)
0A4 Header (8 bytes)
0A4 Size: 98 (0x00000062)
0A8 Name: udta
0AC Metadata (90 bytes)
0AC Header (8 bytes)
0AC Size: 90 (0x0000005A)
0B0 Name: meta
0B4 Version: 0 (0x00)
0B5 Flags: 0 (0x000000)
0B8 Metadata Header (33 bytes)
0B8 Header (8 bytes)
0B8 Size: 33 (0x00000021)
0BC Name: hdlr
0C0 Version: 0 (0x00)
0C1 Flags: 0 (0x000000)
0C4 Type (Quicktime):
0C8 Metadata type: mdir
0CC Manufacturer: appl
0D0 Component reserved flags: 0 (0x00000000)
0D4 Component reserved flags mask: 0 (0x00000000)
0D8 Component type name:
0D9 List (45 bytes)
0D9 Header (8 bytes)
0D9 Size: 45 (0x0000002D)
0DD Name: ilst
0E1 Element (37 bytes)
0E1 Header (8 bytes)
0E1 Size: 37 (0x00000025)
0E5 Name: ﹖oo
0E9 Data - Encoded_Application (29 bytes)
0E9 Header (8 bytes)
0E9 Size: 29 (0x0000001D)
0ED Name: data
0F1 Kind: 1 (0x00000001) - UTF8
0F5 Language: 0 (0x00000000)
0F9 Value: Lavf58.29.100
106 ---------------------------
106 --- MPEG-4, filling ---
106 ---------------------------
106 ----------------------------
106 --- MPEG-4, finished ---
106 ----------------------------
FFmpeg时间戳详解
原⽂地址::https://www.cnblogs.com/leisure_chn/p/10584910.html 编者注:相对原⽂有⼀定的改动。
1.I帧/P帧/B帧
- I帧:
I帧(Intra-coded picture, 帧内编码帧,常称为关键帧)包含⼀幅完整的图像信息,属于帧内编码图 像,不含运动⽮量,在解码时不需要参考其他帧图像。因此在I帧图像处可以切换频道,⽽不会导致图像丢 失或⽆法解码。I帧图像⽤于阻⽌误差的累积和扩散。在闭合式GOP中,每个GOP的第⼀个帧⼀定是I帧, 且当前GOP的数据不会参考前后GOP的数据。 - P帧:
P帧(Predictive-coded picture, 预测编码图像帧)是帧间编码帧,利⽤之前的I帧或P帧进⾏预测编 码。 - B帧:
B帧(Bi-directionally predicted picture, 双向预测编码图像帧)是帧间编码帧,利⽤之前和(或)之 后的I帧或P帧进⾏双向预测编码。B帧不可以作为参考帧。 B帧具有更⾼的压缩率,但需要更多的缓冲时间以及更⾼的CPU占⽤率,因此B帧适合本地存储以及视频点 播,⽽不适⽤对实时性要求较⾼的直播系统。
2. DTS和PTS
DTS(Decoding Time Stamp, 解码时间戳),表示压缩帧的解码时间。
PTS(Presentation Time Stamp, 显示时间戳),表示将压缩帧解码后得到的原始帧的显示时间。 ⾳频中DTS和PTS是相同的。视频中由于B帧需要双向预测,B帧依赖于其前和其后的帧,因此含B帧的视 频解码顺序与显示顺序不同,即DTS与PTS不同。当然,不含B帧的视频,其DTS和PTS是相同的。下图以 ⼀个开放式GOP示意图为例,说明视频流的解码顺序和显示顺序
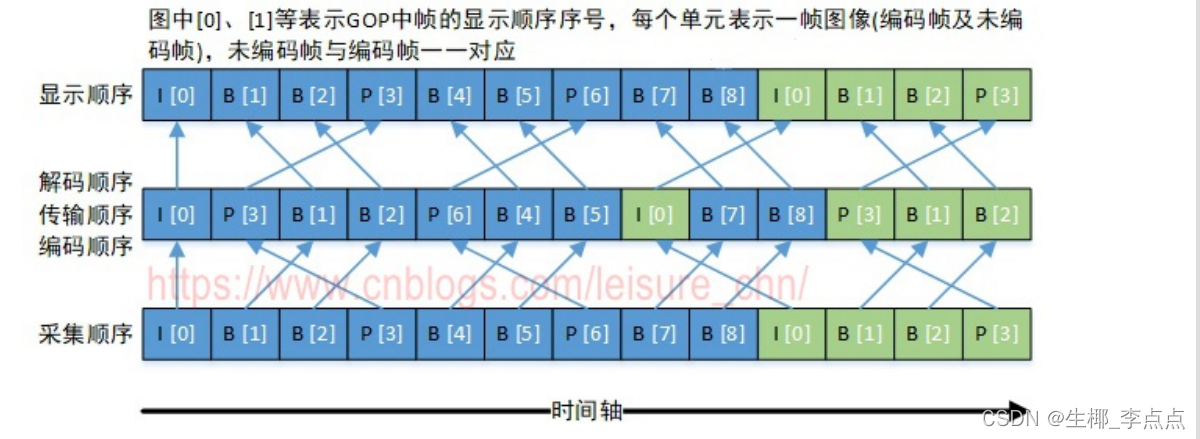
采集顺序指图像传感器采集原始信号得到图像帧的顺序。
编码顺序指编码器编码后图像帧的顺序。存储到磁盘的本地视频⽂件中图像帧的顺序与编码顺序相同。
传输顺序指编码后的流在⽹络中传输过程中图像帧的顺序。
解码顺序指解码器解码图像帧的顺序。
显示顺序指图像帧在显示器上显示的顺序。
采集顺序与显示顺序相同。编码顺序、传输顺序和解码顺序相同。
以图中“B[1]”帧为例进⾏说明,“B[1]”帧解码时需要参考“I[0]”帧和“P[3]”帧,因此“P[3]”帧必须 ⽐“B[1]”帧先解码。这就导致了解码顺序和显示顺序的不⼀致,后显示的帧需要先解码。
3. FFmpeg中的时间基与时间戳
3.1 时间基与时间戳的概念
在FFmpeg中,时间基(time_base)是时间戳(timestamp)的单位,时间戳值乘以时间基,可以得到实际的 时刻值(以秒等为单位)。例如,如果⼀个视频帧的dts是40,pts是160,其time_base是1/1000秒,那么 可以计算出此视频帧的解码时刻是40毫秒(40/1000),显示时刻是160毫秒(160/1000)。FFmpeg中时间戳 (pts/dts)的类型是int64_t类型,把⼀个time_base看作⼀个时钟脉冲,则可把dts/pts看作时钟脉冲的计 数。
3.2 三种时间基tbr、tbn和tbc
不同的封装格式具有不同的时间基。在FFmpeg处理⾳视频过程中的不同阶段,也会采⽤不同的时间基。 FFmepg中有三种时间基,命令⾏中tbr、tbn和tbc的打印值就是这三种时间基的倒数:
tbn:对应容器中的时间基。值是AVStream.time_base的倒数
tbc:对应编解码器中的时间基。值是AVCodecContext.time_base的倒数
tbr:从视频流中猜算得到,可能是帧率或场率(帧率的2倍)
3.3 内部时间基AV_TIME_BASE
除以上三种时间基外,FFmpeg还有⼀个内部时间基AV_TIME_BASE(以及分数形式的 AV_TIME_BASE_Q)
/**
* Internal time base represented as integer
*/
#define AV_TIME_BASE 1000000
/**
* Internal time base represented as fractional value
*/
#define AV_TIME_BASE_Q (AVRational){1, AV_TIME_BASE}
AV_TIME_BASE及AV_TIME_BASE_Q⽤于FFmpeg内部函数处理,使⽤此时间基计算得到时间值表示的 是微秒。
3.4 时间值形式转换
av_q2d()将时间从AVRational形式转换为double形式。AVRational是分数类型,double是双精度浮点数 类型,转换的结果单位是秒。转换前后的值基于同⼀时间基,仅仅是数值的表现形式不同⽽已。 av_q2d()实现如下:
/**
* Convert an AVRational to a `double`.
* @param a AVRational to convert
* @return `a` in floating-point form
* @see av_d2q()
*/
static inline double av_q2d(AVRational a){
return a.num / (double) a.den;
}
使用方法
AVStream stream;
AVPacket packet;
packet播放时刻值:timestamp(单位秒) = packet.pts * av_q2d(stream.time_bas e);
packet播放时⻓值:duration(单位秒) = packet.duration * av_q2d(stream.time _base);
3.5 时间基转换函数
av_rescale_q
av_rescale_q()⽤于不同时间基的转换,⽤于将时间值从⼀种时间基转换为另⼀种时间基。 将a数值由 bq时间基转成 cq的时间基,通过返回结果获取以cq时间基表示的新数值。
/**
* Rescale a 64-bit integer by 2 rational numbers.
*
* The operation is mathematically equivalent to `a * bq / cq`.
*
* This function is equivalent to av_rescale_q_rnd() with #AV_ROUND_NEAR_INF.
*
* @see av_rescale(), av_rescale_rnd(), av_rescale_q_rnd()
*/
int64_t av_rescale_q(int64_t a, AVRational bq, AVRational cq) av_const;
av_rescale_rnd
int64_t av_rescale_rnd(int64_t a, int64_t b, int64_t c, enum AVRounding rnd); 它的作⽤是计算 “a * b / c” 的值并分五种⽅式来取整 (具体的⽤途⽤哪个不⽤那么纠结)
- AV_ROUND_ZERO = 0, // Round toward zero. 趋近于0, round(2.5) 为 2, ⽽ round(-2.5) 为 -2
- AV_ROUND_INF = 1, // Round away from zero. 趋远于0 round(3.5)=4, round(-3.5)=-4
- AV_ROUND_DOWN = 2, // Round toward -infinity.向负⽆穷⼤⽅向 [-2.9, -1.2, 2.4, 5.6, 7.0, 2.4] -> [-3, -2, 2, 5, 7, 2]
- AV_ROUND_UP = 3, // Round toward +infinity. 向正⽆穷⼤⽅向[-2.9, -1.2, 2.4, 5.6, 7.0, 2.4] -> [-2, -1, 3, 6, 7, 3]
- AV_ROUND_NEAR_INF = 5, // Round to nearest and halfway cases away from zero. // 四 舍五⼊,⼩于0.5取值趋向0,⼤于0.5取值趋远于0
av_packet_rescale_ts()
⽤于将AVPacket中各种时间值从⼀种时间基转换为另⼀种时间基。
/**
* Convert valid timing fields (timestamps / durations) in a packet from one
* timebase to another. Timestamps with unknown values (AV_NOPTS_VALUE) will be
* ignored.
*
* @param pkt packet on which the conversion will be performed
* @param tb_src source timebase, in which the timing fields in pkt are
* expressed
* @param tb_dst destination timebase, to which the timing fields will be
* converted
*/
void av_packet_rescale_ts(AVPacket *pkt, AVRational tb_src, AVRational tb_dst);
3.6 转封装过程中的时间基转换
容器中的时间基(AVStream.time_base,3.2节中的tbn)定义如下:
typedef struct AVStream {
int index; /**< stream index in AVFormatContext */
/**
* Format-specific stream ID.
* decoding: set by libavformat
* encoding: set by the user, replaced by libavformat if left unset
*/
int id;
#if FF_API_LAVF_AVCTX
/**
* @deprecated use the codecpar struct instead
*/
attribute_deprecated
AVCodecContext *codec;
#endif
void *priv_data;
/**
* This is the fundamental unit of time (in seconds) in terms
* of which frame timestamps are represented.
*
* decoding: set by libavformat
* encoding: May be set by the caller before avformat_write_header() to
* provide a hint to the muxer about the desired timebase. In
* avformat_write_header(), the muxer will overwrite this field
* with the timebase that will actually be used for the timestamps
* written into the file (which may or may not be related to the
* user-provided one, depending on the format).
*/
AVRational time_base;
/**
* Decoding: pts of the first frame of the stream in presentation order, in stream time base.
* Only set this if you are absolutely 100% sure that the value you set
* it to really is the pts of the first frame.
* This may be undefined (AV_NOPTS_VALUE).
* @note The ASF header does NOT contain a correct start_time the ASF
* demuxer must NOT set this.
*/
int64_t start_time;
/**
* Decoding: duration of the stream, in stream time base.
* If a source file does not specify a duration, but does specify
* a bitrate, this value will be estimated from bitrate and file size.
*
* Encoding: May be set by the caller before avformat_write_header() to
* provide a hint to the muxer about the estimated duration.
*/
int64_t duration;
int64_t nb_frames; ///< number of frames in this stream if known or 0
...
AVStream.time_base是AVPacket中pts和dts的时间单位,输⼊流与输出流中time_base按如下⽅式确 定:
- 对于输⼊流:打开输⼊⽂件后,调⽤avformat_find_stream_info()可获取到每个流中的time_base
- 对于输出流:打开输出⽂件后,调⽤avformat_write_header()可根据输出⽂件封装格式确定每个流的 time_base并写⼊输出⽂件中
不同封装格式具有不同的时间基,在转封装(将⼀种封装格式转换为另⼀种封装格式)过程中,时间基转换相 关代码如下:
av_read_frame(ifmt_ctx, &pkt);
pkt.pts = av_rescale_q_rnd(pkt.pts, in_stream->time_base, out_stream- >time_base,
AV_ROUND_NEAR_INF|AV_ROUND_PASS_MINMAX);
pkt.dts = av_rescale_q_rnd(pkt.dts, in_stream->time_base, out_stream- >time_base,
AV_ROUND_NEAR_INF|AV_ROUND_PASS_MINMAX);
pkt.duration = av_rescale_q(pkt.duration, in_stream->time_base, out_s tream->time_base);
下⾯的代码具有和上⾯代码相同的效果:
// 从输⼊⽂件中读取packet
av_read_frame(ifmt_ctx, &pkt);
// 将packet中的各时间值从输⼊流封装格式时间基转换到输出流封装格式时间基
av_packet_rescale_ts(&pkt, in_stream->time_base, out_stream->time_bas e);
这⾥流⾥的时间基 in_stream->time_base 和 out_stream->time_base ,是容器中的时间基,就 是3.2节中的tbn。
例如,flv封装格式的time_base为{1,1000},ts封装格式的time_base为{1,90000}
我们编写程序将flv封装格式转换为ts封装格式,抓取原⽂件(flv)的前四帧显示时间戳:
think@opensuse> ffprobe -show_frames -select_streams v tnmil3.flv | grep pkt_pts
ffprobe version 4.1 Copyright (c) 2007-2018 the FFmpeg developers
Input #0, flv, from 'tnmil3.flv':
Metadata:
encoder : Lavf58.20.100
Duration: 00:00:03.60, start: 0.017000, bitrate: 513 kb/s
Stream #0:0: Video: h264 (High),yuv420p(progressive), 784x480,25 fps, 25 tbr, 1k tbn, 50 tbc
Stream #0:1: Audio: aac (LC), 44100 Hz, stereo, fltp, 128 kb/s
pkt_pts=80
pkt_pts_time=0.080000
pkt_pts=120
pkt_pts_time=0.120000
pkt_pts=160
pkt_pts_time=0.160000
pkt_pts=200
pkt_pts_time=0.200000
再抓取转换的⽂件(ts)的前四帧显示时间戳:
think@opensuse> ffprobe -show_frames -select_streams v tnmil3.ts | g rep pkt_pts
ffprobe version 4.1 Copyright (c) 2007-2018 the FFmpeg developers
Input #0, mpegts, from 'tnmil3.ts':
Duration: 00:00:03.58, start: 0.017000, bitrate: 619 kb/s
Program 1
Metadata:
service_name : Service01
service_provider: FFmpeg
Stream #0:0[0x100]: Video: h264 (High) ([27][0][0][0] / 0x001B), yuv420p(progressive), 784x480, 25 fps, 25 tbr, 90k tbn, 50 tbc
Stream #0:1[0x101]: Audio: aac (LC) ([15][0][0][0] / 0x000F), 44 100 Hz, stereo, fltp, 127 kb/s
pkt_pts=7200
pkt_pts_time=0.080000
pkt_pts=10800
pkt_pts_time=0.120000
pkt_pts=14400
pkt_pts_time=0.160000
pkt_pts=18000
pkt_pts_time=0.200000
可以发现,对于同⼀个视频帧,它们时间基(tbn)不同因此时间戳(pkt_pts)也不同,但是计算出来的时刻值 (pkt_pts_time)是相同的。
看第⼀帧的时间戳,计算关系:80×{1,1000} == 7200×{1,90000} == 0.080000
3.7转码过程中的时间基转换
编解码器中的时间基(AVCodecContext.time_base,3.2节中的tbc)定义如下:
typedef struct AVCodecContext {
...
uint8_t *extradata;
int extradata_size;
/**
* This is the fundamental unit of time (in seconds) in terms
* of which frame timestamps are represented. For fixed-fps content,
* timebase should be 1/framerate and timestamp increments should be
* identically 1.
* This often, but not always is the inverse of the frame rate or field rate
* for video. 1/time_base is not the average frame rate if the frame rate is not
* constant.
*
* Like containers, elementary streams also can store timestamps, 1/time_base
* is the unit in which these timestamps are specified.
* As example of such codec time base see ISO/IEC 14496-2:2001(E)
* vop_time_increment_resolution and fixed_vop_rate
* (fixed_vop_rate == 0 implies that it is different from the framerate)
*
* - encoding: MUST be set by user.
* - decoding: the use of this field for decoding is deprecated.
* Use framerate instead.
*/
AVRational time_base;
...
}
上述注释指出,AVCodecContext.time_base是帧率(视频帧)的倒数,每帧时间戳递增1,那么tbc就等于 帧率。编码过程中,应由⽤户设置好此参数。解码过程中,此参数已过时,建议直接使⽤帧率倒数⽤作时间基
这⾥有⼀个问题:按照此处注释说明,帧率为25的视频流,tbc理应为25,但实际值却为50,不知作何解 释?是否tbc已经过时,不具参考意义?
根据注释中的建议,实际使⽤时,在视频解码过程中,我们不使⽤AVCodecContext.time_base,⽽⽤帧 率倒数作时间基,在视频编码过程中,我们将AVCodecContext.time_base设置为帧率的倒数。
3.7.1视频流
视频按帧播放,所以解码后的原始视频帧时间基为 1/framerate。 视频解码过程中的时间基转换处理(darren注:该段没有参考意义,packet的pts到底什么,要看实际的 情况,从av_read_frame读取的packet,是以AVSteam->time_base,送给解码器之前没有必要转成 AVcodecContext->time_base, 需要注意的是avcodec_receive_frame后以AVSteam->time_base为 单位即可。)
AVFormatContext *ifmt_ctx;
AVStream *in_stream;
AVCodecContext *dec_ctx;
AVPacket packet;
AVFrame *frame;
// 从输⼊⽂件中读取编码帧
av_read_frame(ifmt_ctx, &packet);
// 时间基转换
int raw_video_time_base = av_inv_q(dec_ctx->framerate);
av_packet_rescale_ts(packet, in_stream->time_base, raw_video_time_ba se);
// 解码
avcodec_send_packet(dec_ctx, packet)
avcodec_receive_frame(dec_ctx, frame);
视频编码过程中的时间基转换处理(darren:编码的时候frame如果以AVstream为time_base送编码器, 则avcodec_receive_packet读取的时候也是以转成AVSteam->time_base,本质来讲就是具体情况具体 分析,没必要硬套流程):
AVFormatContext *ofmt_ctx;
AVStream *out_stream;
AVCodecContext *dec_ctx;
AVCodecContext *enc_ctx;
AVPacket packet;
AVFrame *frame;
// 编码
avcodec_send_frame(enc_ctx, frame);
avcodec_receive_packet(enc_ctx, packet);
// 时间基转换
packet.stream_index = out_stream_idx;
enc_ctx->time_base = av_inv_q(dec_ctx->framerate);
av_packet_rescale_ts(&opacket, enc_ctx->time_base, out_stream->time_ base);
// 将编码帧写⼊输出媒体⽂件
av_interleaved_write_frame(o_fmt_ctx, &packet);
3.7.2⾳频流
darren:对于⾳频流也是类似的,本质来讲就是具体情况具体分析,没必要硬套流程,⽐如ffplay 解码播 放时就是AVSteam的time_base为基准的packet进⼊到编码器,然后出来的frame再⽤AVSteam的 time_base讲对应的pts转成秒, 但是要注意的是ffplay做了⼀个⽐较隐秘的设置:avctx- >pkt_timebase = ic->streams[stream_index]->time_base; 即是对应的codeccontext⾃⼰对 pkt_timebase设置和AVStream⼀样的time_base。
⾳频按采样点播放,所以解码后的原始⾳频帧时间基为 1/sample_rate ⾳频解码过程中的时间基转换处理:
AVFormatContext *ifmt_ctx;
AVStream *in_stream;
AVCodecContext *dec_ctx;
AVPacket packet;
AVFrame *frame;
// 从输⼊⽂件中读取编码帧
av_read_frame(ifmt_ctx, &packet);
// 时间基转换
int raw_audio_time_base = av_inv_q(dec_ctx->sample_rate);
av_packet_rescale_ts(packet, in_stream->time_base, raw_audio_time_ba se);
// 解码
avcodec_send_packet(dec_ctx, packet)
avcodec_receive_frame(dec_ctx, frame);
⾳频编码过程中的时间基转换处理:
AVFormatContext *ofmt_ctx;
AVStream *out_stream;
AVCodecContext *dec_ctx;
AVCodecContext *enc_ctx;
AVPacket packet; 6 AVFrame *frame;
// 编码
avcodec_send_frame(enc_ctx, frame);
avcodec_receive_packet(enc_ctx, packet);
// 时间基转换
packet.stream_index = out_stream_idx;
enc_ctx->time_base = av_inv_q(dec_ctx->sample_rate);
av_packet_rescale_ts(&opacket, enc_ctx->time_base, out_stream->time_ base);
// 将编码帧写⼊输出媒体⽂件
av_interleaved_write_frame(o_fmt_ctx, &packet);
代码
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <libavutil/avassert.h>
#include <libavutil/channel_layout.h>
#include <libavutil/opt.h>
#include <libavutil/mathematics.h>
#include <libavutil/timestamp.h>
#include <libavformat/avformat.h>
#include <libswscale/swscale.h>
#include <libswresample/swresample.h>
#define STREAM_DURATION 5.0 //流时长 单位秒
#define STREAM_FRAME_RATE 25 /* 25 images/s */
#define STREAM_PIX_FMT AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P /* default pix_fmt */
#define SCALE_FLAGS SWS_BICUBIC // scale flag
// 封装单个输出AVStream
typedef struct OutputStream
{
AVStream *st; // 代表一个stream, 1路audio或1路video都代表独立的steam
AVCodecContext *enc; // 编码器上下文
/* pts of the next frame that will be generated */
int64_t next_pts;
int samples_count; // 音频的采样数量累计
AVFrame *frame; // 重采样后的frame, 视频叫scale
AVFrame *tmp_frame; // 重采样前
float t, tincr, tincr2; // 这几个参数用来生成PCM和YUV用的
struct SwsContext *sws_ctx; // 图像scale
struct SwrContext *swr_ctx; // 音频重采样
} OutputStream;
static void log_packet(const AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx, const AVPacket *pkt)
{
AVRational *time_base = &fmt_ctx->streams[pkt->stream_index]->time_base;
printf("pts:%s pts_time:%s dts:%s dts_time:%s duration:%s duration_time:%s stream_index:%d\n",
av_ts2str(pkt->pts), av_ts2timestr(pkt->pts, time_base),
av_ts2str(pkt->dts), av_ts2timestr(pkt->dts, time_base),
av_ts2str(pkt->duration), av_ts2timestr(pkt->duration, time_base),
pkt->stream_index);
}
static int write_frame(AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx, const AVRational *time_base,
AVStream *st, AVPacket *pkt)
{
/* rescale output packet timestamp values from codec to stream timebase */
// 将packet的timestamp由codec to stream timebase pts_before = -1024
av_packet_rescale_ts(pkt, *time_base, st->time_base);
pkt->stream_index = st->index; // pts_before * 1/44100 = pts_after *1/1000
// pts_after = pts_before * 1/44100 * 1000 = -1024 * 1/44100 * 1000 = -23
/* Write the compressed frame to the media file. */
log_packet(fmt_ctx, pkt);
return av_interleaved_write_frame(fmt_ctx, pkt);
}
//增加输出流,返回AVStream,并给codec赋值,但此时codec并未打开
static void add_stream(OutputStream *ost, AVFormatContext *oc,
AVCodec **codec,
enum AVCodecID codec_id)
{
AVCodecContext *codec_ctx;
int i;
/* 查找编码器 */
*codec = avcodec_find_encoder(codec_id); //通过codec_id找到编码器
if (!(*codec))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not find encoder for '%s'\n",
avcodec_get_name(codec_id));
exit(1);
}
// 新建码流 绑定到 AVFormatContext stream->index 有设置
ost->st = avformat_new_stream(oc, NULL); // 创建一个流成分
if (!ost->st)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate stream\n");
exit(1);
}
/* 为什么要 -1呢?每次调用avformat_new_stream的时候nb_streams+1
但id是从0开始, 比如第1个流:对应流id = nb_streams(1) -1 = 0
第2个流:对应流id = nb_streams(2) -1 = 1
*/
ost->st->id = oc->nb_streams - 1;
codec_ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(*codec); // 创建编码器上下文
if (!codec_ctx)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not alloc an encoding context\n");
exit(1);
}
ost->enc = codec_ctx;
// 初始化编码器参数
switch ((*codec)->type)
{
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO:
codec_ctx->codec_id = codec_id;
codec_ctx->sample_fmt = (*codec)->sample_fmts ? // 采样格式
(*codec)->sample_fmts[0] : AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP;
codec_ctx->bit_rate = 64000; // 码率
codec_ctx->sample_rate = 44100; // 采样率
if ((*codec)->supported_samplerates)
{
codec_ctx->sample_rate = (*codec)->supported_samplerates[0];
for (i = 0; (*codec)->supported_samplerates[i]; i++)
{
if ((*codec)->supported_samplerates[i] == 44100)
codec_ctx->sample_rate = 44100;
}
}
codec_ctx->channel_layout = AV_CH_LAYOUT_STEREO;
codec_ctx->channels = av_get_channel_layout_nb_channels(codec_ctx->channel_layout);
if ((*codec)->channel_layouts)
{
codec_ctx->channel_layout = (*codec)->channel_layouts[0];
for (i = 0; (*codec)->channel_layouts[i]; i++) {
if ((*codec)->channel_layouts[i] == AV_CH_LAYOUT_STEREO)
codec_ctx->channel_layout = AV_CH_LAYOUT_STEREO;
}
}
codec_ctx->channels = av_get_channel_layout_nb_channels(codec_ctx->channel_layout);
// 设置timebase, 使用采样率
ost->st->time_base = (AVRational){ 1, codec_ctx->sample_rate };
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO:
codec_ctx->codec_id = codec_id;
codec_ctx->bit_rate = 400000;
/* Resolution must be a multiple of two. */
codec_ctx->width = 352; // 分辨率
codec_ctx->height = 288;
codec_ctx->max_b_frames = 1;
/* timebase: This is the fundamental unit of time (in seconds) in terms
* of which frame timestamps are represented. For fixed-fps content,
* timebase should be 1/framerate and timestamp increments should be
* identical to 1. */
ost->st->time_base = (AVRational){ 1, STREAM_FRAME_RATE }; // 时基
codec_ctx->time_base = ost->st->time_base; // 为什么这里需要设置
codec_ctx->gop_size = STREAM_FRAME_RATE; //
codec_ctx->pix_fmt = STREAM_PIX_FMT;
break;
default:
break;
}
/* Some formats want stream headers to be separate. */
if (oc->oformat->flags & AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER)
codec_ctx->flags |= AV_CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER; //
}
/**************************************************************/
/* audio output */
static AVFrame *alloc_audio_frame(enum AVSampleFormat sample_fmt,
uint64_t channel_layout,
int sample_rate, int nb_samples)
{
AVFrame *frame = av_frame_alloc();
int ret;
if (!frame)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error allocating an audio frame\n");
exit(1);
}
frame->format = sample_fmt;
frame->channel_layout = channel_layout;
frame->sample_rate = sample_rate;
frame->nb_samples = nb_samples;
if (nb_samples)
{
ret = av_frame_get_buffer(frame, 0);
if (ret < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error allocating an audio buffer\n");
exit(1);
}
}
return frame;
}
static void open_audio(AVFormatContext *oc, AVCodec *codec, OutputStream *ost, AVDictionary *opt_arg)
{
AVCodecContext *codec_ctx;
int nb_samples;
int ret;
AVDictionary *opt = NULL;
codec_ctx = ost->enc;
/* open it */
av_dict_copy(&opt, opt_arg, 0);
// 1. 关联编码器 会设置codec_ctx->time_base
ret = avcodec_open2(codec_ctx, codec, &opt);
av_dict_free(&opt);
if (ret < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not open audio codec: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
exit(1);
}
/* init signal generator */
// 2. 初始化产生PCM的参数
ost->t = 0;
ost->tincr = 2 * M_PI * 110.0 / codec_ctx->sample_rate;
/* increment frequency by 110 Hz per second */
ost->tincr2 = 2 * M_PI * 110.0 / codec_ctx->sample_rate / codec_ctx->sample_rate;
// 每次需要的samples
// if (codec_ctx->codec->capabilities & AV_CODEC_CAP_VARIABLE_FRAME_SIZE)
// nb_samples = 10000; // 支持可变FRAME size的编码器极少,直接注释掉
// else
nb_samples = codec_ctx->frame_size;
// signal generator -> PCM -> ost->tmp_frame -> swr_convert重采样 -> ost->frame -> 编码器
// 分配送给编码器的帧, 并申请对应的buffer
ost->frame = alloc_audio_frame(codec_ctx->sample_fmt, codec_ctx->channel_layout,
codec_ctx->sample_rate, nb_samples);
// 分配送给信号生成PCM的帧, 并申请对应的buffer
ost->tmp_frame = alloc_audio_frame(AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16, codec_ctx->channel_layout,
codec_ctx->sample_rate, nb_samples);
/* copy the stream parameters to the muxer */
ret = avcodec_parameters_from_context(ost->st->codecpar, codec_ctx);
if (ret < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not copy the stream parameters\n");
exit(1);
}
/* create resampler context 创建重采样器 */
ost->swr_ctx = swr_alloc();
if (!ost->swr_ctx)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate resampler context\n");
exit(1);
}
/* set options */
av_opt_set_int (ost->swr_ctx, "in_channel_count", codec_ctx->channels, 0);
av_opt_set_int (ost->swr_ctx, "in_sample_rate", codec_ctx->sample_rate, 0);
av_opt_set_sample_fmt(ost->swr_ctx, "in_sample_fmt", AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16, 0);
av_opt_set_int (ost->swr_ctx, "out_channel_count", codec_ctx->channels, 0);
av_opt_set_int (ost->swr_ctx, "out_sample_rate", codec_ctx->sample_rate, 0);
av_opt_set_sample_fmt(ost->swr_ctx, "out_sample_fmt", codec_ctx->sample_fmt, 0);
/* initialize the resampling context */
if ((ret = swr_init(ost->swr_ctx)) < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize the resampling context\n");
exit(1);
}
}
/* Prepare a 16 bit dummy audio frame of 'frame_size' samples and
* 'nb_channels' channels. */
static AVFrame *get_audio_frame(OutputStream *ost)
{
AVFrame *frame = ost->tmp_frame;
int j, i, v;
int16_t *q = (int16_t*)frame->data[0];
/* check if we want to generate more frames */
// 44100 * {1, 44100} = 1 -》44100*5 * {1, 44100} = 5
// 5 *{1,1} = 5
if (av_compare_ts(ost->next_pts, ost->enc->time_base,
STREAM_DURATION, (AVRational){ 1, 1 }) >= 0)
return NULL;
for (j = 0; j <frame->nb_samples; j++)
{
v = (int)(sin(ost->t) * 10000);
for (i = 0; i < ost->enc->channels; i++)
*q++ = v;
ost->t += ost->tincr;
ost->tincr += ost->tincr2;
}
frame->pts = ost->next_pts; // 使用samples作为计数 设置pts 0, nb_samples(1024) 2048
ost->next_pts += frame->nb_samples; // 音频PTS使用采样samples叠加
return frame;
}
/*
* encode one audio frame and send it to the muxer
* return 1 when encoding is finished, 0 otherwise
*/
static int write_audio_frame(AVFormatContext *oc, OutputStream *ost)
{
AVCodecContext *codec_ctx;
AVPacket pkt = { 0 }; // data and size must be 0;
AVFrame *frame;
int ret;
int got_packet;
int dst_nb_samples;
av_init_packet(&pkt);
codec_ctx = ost->enc;
frame = get_audio_frame(ost);
if (frame)
{
/* convert samples from native format to destination codec format, using the resampler */
/* compute destination number of samples */
dst_nb_samples = av_rescale_rnd(swr_get_delay(ost->swr_ctx, codec_ctx->sample_rate) + frame->nb_samples,
codec_ctx->sample_rate, codec_ctx->sample_rate, AV_ROUND_UP);
av_assert0(dst_nb_samples == frame->nb_samples);
/* when we pass a frame to the encoder, it may keep a reference to it
* internally;
* make sure we do not overwrite it here
*/
ret = av_frame_make_writable(ost->frame);
if (ret < 0)
exit(1);
/* convert to destination format */
ret = swr_convert(ost->swr_ctx,
ost->frame->data, dst_nb_samples,
(const uint8_t **)frame->data, frame->nb_samples);
if (ret < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error while converting\n");
exit(1);
}
frame = ost->frame;
// 转换time_base
frame->pts = av_rescale_q(ost->samples_count, (AVRational){1, codec_ctx->sample_rate},
codec_ctx->time_base);
ost->samples_count += dst_nb_samples;
}
ret = avcodec_encode_audio2(codec_ctx, &pkt, frame, &got_packet);
if (ret < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error encoding audio frame: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
exit(1);
}
if (got_packet)
{
ret = write_frame(oc, &codec_ctx->time_base, ost->st, &pkt);
if (ret < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error while writing audio frame: %s\n",
av_err2str(ret));
exit(1);
}
}
// frame == NULL 读取不到frame(比如读完了5秒的frame); got_packet == 0 没有帧了
return (frame || got_packet) ? 0 : 1;
}
/**************************************************************/
/* video output */
static AVFrame *alloc_picture(enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt, int width, int height)
{
AVFrame *picture;
int ret;
picture = av_frame_alloc();
if (!picture)
return NULL;
picture->format = pix_fmt;
picture->width = width;
picture->height = height;
/* allocate the buffers for the frame data */
ret = av_frame_get_buffer(picture, 32);
if (ret < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate frame data.\n");
exit(1);
}
return picture;
}
static void open_video(AVFormatContext *oc, AVCodec *codec, OutputStream *ost, AVDictionary *opt_arg)
{
int ret;
AVCodecContext *codec_ctx = ost->enc;
AVDictionary *opt = NULL;
av_dict_copy(&opt, opt_arg, 0);
/* open the codec */
// 1. 关联编码器
ret = avcodec_open2(codec_ctx, codec, &opt);
av_dict_free(&opt);
if (ret < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not open video codec: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
exit(1);
}
// 2. 分配帧buffer
/* allocate and init a re-usable frame */
ost->frame = alloc_picture(codec_ctx->pix_fmt, codec_ctx->width, codec_ctx->height);
if (!ost->frame)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate video frame\n");
exit(1);
}
/* If the output format is not YUV420P, then a temporary YUV420P
* picture is needed too. It is then converted to the required
* output format. */
ost->tmp_frame = NULL;
if (codec_ctx->pix_fmt != AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P)
{
// 编码器格式需要的数据不是 AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P才需要 调用图像scale
ost->tmp_frame = alloc_picture(AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, codec_ctx->width, codec_ctx->height);
if (!ost->tmp_frame)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate temporary picture\n");
exit(1);
}
}
/* copy the stream parameters to the muxer */
ret = avcodec_parameters_from_context(ost->st->codecpar, codec_ctx);
if (ret < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not copy the stream parameters\n");
exit(1);
}
}
/* Prepare a dummy image. */
static void fill_yuv_image(AVFrame *pict, int frame_index,
int width, int height)
{
int x, y, i;
i = frame_index;
/* Y */
for (y = 0; y < height; y++)
for (x = 0; x < width; x++)
pict->data[0][y * pict->linesize[0] + x] = x + y + i * 3;
/* Cb and Cr */
for (y = 0; y < height / 2; y++)
{
for (x = 0; x < width / 2; x++) {
pict->data[1][y * pict->linesize[1] + x] = 128 + y + i * 2;
pict->data[2][y * pict->linesize[2] + x] = 64 + x + i * 5;
}
}
}
static AVFrame *get_video_frame(OutputStream *ost)
{
AVCodecContext *codec_ctx = ost->enc;
/* check if we want to generate more frames */
// 我们测试时只产生STREAM_DURATION(这里是5.0秒)的视频数据
if (av_compare_ts(ost->next_pts, codec_ctx->time_base,
STREAM_DURATION, (AVRational){ 1, 1 }) >= 0)
return NULL;
/* when we pass a frame to the encoder, it may keep a reference to it
* internally; make sure we do not overwrite it here */
if (av_frame_make_writable(ost->frame) < 0)
exit(1);
if (codec_ctx->pix_fmt != AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P)
{
/* as we only generate a YUV420P picture, we must convert it
* to the codec pixel format if needed */
if (!ost->sws_ctx)
{
ost->sws_ctx = sws_getContext(codec_ctx->width, codec_ctx->height,
AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P,
codec_ctx->width, codec_ctx->height,
codec_ctx->pix_fmt,
SCALE_FLAGS, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (!ost->sws_ctx) {
fprintf(stderr
,
"Could not initialize the conversion context\n");
exit(1);
}
}
fill_yuv_image(ost->tmp_frame, ost->next_pts, codec_ctx->width, codec_ctx->height);
sws_scale(ost->sws_ctx, (const uint8_t * const *) ost->tmp_frame->data,
ost->tmp_frame->linesize, 0, codec_ctx->height, ost->frame->data,
ost->frame->linesize);
} else {
fill_yuv_image(ost->frame, ost->next_pts, codec_ctx->width, codec_ctx->height);
}
ost->frame->pts = ost->next_pts++; // 为什么+1? 单位是 1/25 = 40ms
// 0 1 2 -> 0 40ms 80ms
return ost->frame;
}
/*
* encode one video frame and send it to the muxer
* return 1 when encoding is finished, 0 otherwise
*/
static int write_video_frame(AVFormatContext *oc, OutputStream *ost)
{
int ret;
AVCodecContext *codec_ctx;
AVFrame *frame;
int got_packet = 0;
AVPacket pkt = { 0 };
codec_ctx = ost->enc;
frame = get_video_frame(ost);
av_init_packet(&pkt);
/* encode the image */
ret = avcodec_encode_video2(codec_ctx, &pkt, frame, &got_packet);
if (ret < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error encoding video frame: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
exit(1);
}
if (got_packet)
{
ret = write_frame(oc, &codec_ctx->time_base, ost->st, &pkt);
}
else
{
ret = 0;
}
if (ret < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error while writing video frame: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
exit(1);
}
// 这里之所以有两个判断条件
// frame非NULL: 表示还在产生YUV数据帧
// got_packet为1: 编码器还有缓存的帧
return (frame || got_packet) ? 0 : 1;
}
static void close_stream(AVFormatContext *oc, OutputStream *ost)
{
avcodec_free_context(&ost->enc);
av_frame_free(&ost->frame);
av_frame_free(&ost->tmp_frame);
sws_freeContext(ost->sws_ctx);
swr_free(&ost->swr_ctx);
}
/**************************************************************/
/* media file output */
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
OutputStream video_st = { 0 }; // 封装视频编码相关的
OutputStream audio_st = { 0 }; // 封装音频编码相关的
const char *filename; // 输出文件
// AVOutputFormat ff_flv_muxer
AVOutputFormat *fmt; // 输出文件容器格式, 封装了复用规则,AVInputFormat则是封装了解复用规则
AVFormatContext *oc;
AVCodec *audio_codec, *video_codec;
int ret;
int have_video = 0, have_audio = 0;
int encode_video = 0, encode_audio = 0;
AVDictionary *opt = NULL;
int i;
if (argc < 2)
{
printf("usage: %s output_file\n"
"API example program to output a media file with libavformat.\n"
"This program generates a synthetic audio and video stream, encodes and\n"
"muxes them into a file named output_file.\n"
"The output format is automatically guessed according to the file extension.\n"
"Raw images can also be output by using '%%d' in the filename.\n"
"\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
filename = argv[1];
for (i = 2; i+1 < argc; i+=2)
{
if (!strcmp(argv[i], "-flags") || !strcmp(argv[i], "-fflags"))
av_dict_set(&opt, argv[i]+1, argv[i+1], 0);
}
/* 分配AVFormatContext并根据filename绑定合适的AVOutputFormat */
avformat_alloc_output_context2(&oc, NULL, NULL, filename);
if (!oc)
{
// 如果不能根据文件后缀名找到合适的格式,那缺省使用flv格式
printf("Could not deduce output format from file extension: using flv.\n");
avformat_alloc_output_context2(&oc, NULL, "flv", filename);
}
if (!oc)
return 1;
fmt = oc->oformat; // 获取绑定的AVOutputFormat
// 我们音视频课程音视频编解码主要涉及H264和AAC, 所以我们指定为H264+AAC
fmt->video_codec = AV_CODEC_ID_H264; // 指定编码器
fmt->audio_codec = AV_CODEC_ID_AAC; // 指定编码器
/* 使用指定的音视频编码格式增加音频流和视频流 */
if (fmt->video_codec != AV_CODEC_ID_NONE)
{
add_stream(&video_st, oc, &video_codec, fmt->video_codec);
have_video = 1;
encode_video = 1;
}
if (fmt->audio_codec != AV_CODEC_ID_NONE)
{
add_stream(&audio_st, oc, &audio_codec, fmt->audio_codec);
have_audio = 1;
encode_audio = 1;
}
/* Now that all the parameters are set, we can open the audio and
* video codecs and allocate the necessary encode buffers. */
if (have_video)
open_video(oc, video_codec, &video_st, opt);
if (have_audio)
open_audio(oc, audio_codec, &audio_st, opt);
av_dump_format(oc, 0, filename, 1);
/* open the output file, if needed */
if (!(fmt->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE))
{
// 打开对应的输出文件,没有则创建
ret = avio_open(&oc->pb, filename, AVIO_FLAG_WRITE);
if (ret < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not open '%s': %s\n", filename,
av_err2str(ret));
return 1;
}
}
// audio AVstream->base_time = 1/44100, video AVstream->base_time = 1/25
/* 写头部. 到底做了什么操作呢? 对应steam的time_base被改写 和封装格式有关系*/
ret = avformat_write_header(oc, &opt);// base_time audio = 1/1000 video = 1/1000
if (ret < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error occurred when opening output file: %s\n",
av_err2str(ret));
return 1;
}
while (encode_video || encode_audio)
{
/* select the stream to encode */
if (encode_video && // video_st.next_pts值 <= audio_st.next_pts时
(!encode_audio || av_compare_ts(video_st.next_pts, video_st.enc->time_base,
audio_st.next_pts, audio_st.enc->time_base) <= 0)) {
printf("\nwrite_video_frame\n");
encode_video = !write_video_frame(oc, &video_st);
}
else
{
printf("\nwrite_audio_frame\n");
encode_audio = !write_audio_frame(oc, &audio_st);
}
}
/* Write the trailer, if any. The trailer must be written before you
* close the CodecContexts open when you wrote the header; otherwise
* av_write_trailer() may try to use memory that was freed on
* av_codec_close(). */
av_write_trailer(oc);
/* Close each codec. */
if (have_video)
close_stream(oc, &video_st);
if (have_audio)
close_stream(oc, &audio_st);
if (!(fmt->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE))
/* Close the output file. */
avio_closep(&oc->pb);
/* free the stream */
avformat_free_context(oc);
return 0;
}






















 3785
3785











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








