- 二叉树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
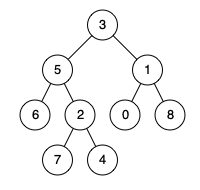
示例 1:
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出: 3
解释: 节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3。
示例 2:
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
输出: 5
解释: 节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。

图中第三点的两个情况不太好理解,也不用去理解
关键在于递归采用的是后序遍历的方式,由于需要先知道左右子树的情况,然后决定向上返回什么。因此「后序遍历」的思想是很关键,
由于是从底层向上逐渐返回,所以要对应判断左右,left,right 的输出情况,根据其取值特点,决定返回什么,
所以所担心的,若都在右节点,同时离root又很远,会不会返回root,这种情况就不存在了。
强调一点就是,只要分别位于root两边,root一定为所寻找的点
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;//作为边界条件
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(left == null) return right;
if(right == null) return left;
return root;//即都不为null
}
}
2.先dfs遍历一遍
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
HashMap<Integer, TreeNode> map = new HashMap<>();
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
dfs(root);//先遍历一遍,标记
while(p!= null){
visited.add(p.val);
p = map.get(p.val);
}
while (q != null){
if(visited.contains(q.val)) return q;
q = map.get(q.val);
}
return null;//如果上面没有返回,说明没有公共节点
}
void dfs(TreeNode root){//存储所有的点的父亲节点
if(root.left != null){//这里必须要提前判断,下面容易空指针
map.put(root.left.val, root);
dfs(root.left);
}
if(root.right != null){
map.put(root.right.val, root);
dfs(root.right);
}
}
}
其实,上面的解法还是有问题的,如果存在值相同的,必然map不容易查找
class Solution {
HashMap<TreeNode, TreeNode> map = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
dfs(root);
HashSet<TreeNode> set = new HashSet<>();
while(p != null){
set.add(p);
p = map.get(p);
}
while(q!= null){
if(set.contains(q)) return q;
q = map.get(q);
}
return null;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root.left != null){
map.put(root.left, root);
dfs(root.left);
}
if(root.right != null){
map.put(root.right, root);
dfs(root.right);
}
}
}






















 881
881











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








