springboot源码解析之自定义参数解析
有需要互关的小伙伴,关注一下,有关必回关,争取今年认证早日拿到博客专家
标签:源码:springboot
自定义参数
@Data
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Pet pet;
}
Controller代码
@RequestMapping("/savePerson")
@ResponseBody
public Object savePerson(Person person) {
System.out.println("person = " + person);
return person;
}
get请求(能收到)
/savePerson?name=李四&age=18&pet.petName=黑皇&pet.petAge=3
person = Person(name=李四, age=18, pet=Pet(petName=黑皇, petAge=3))
post请求-前端传参形式form-data(能收到)
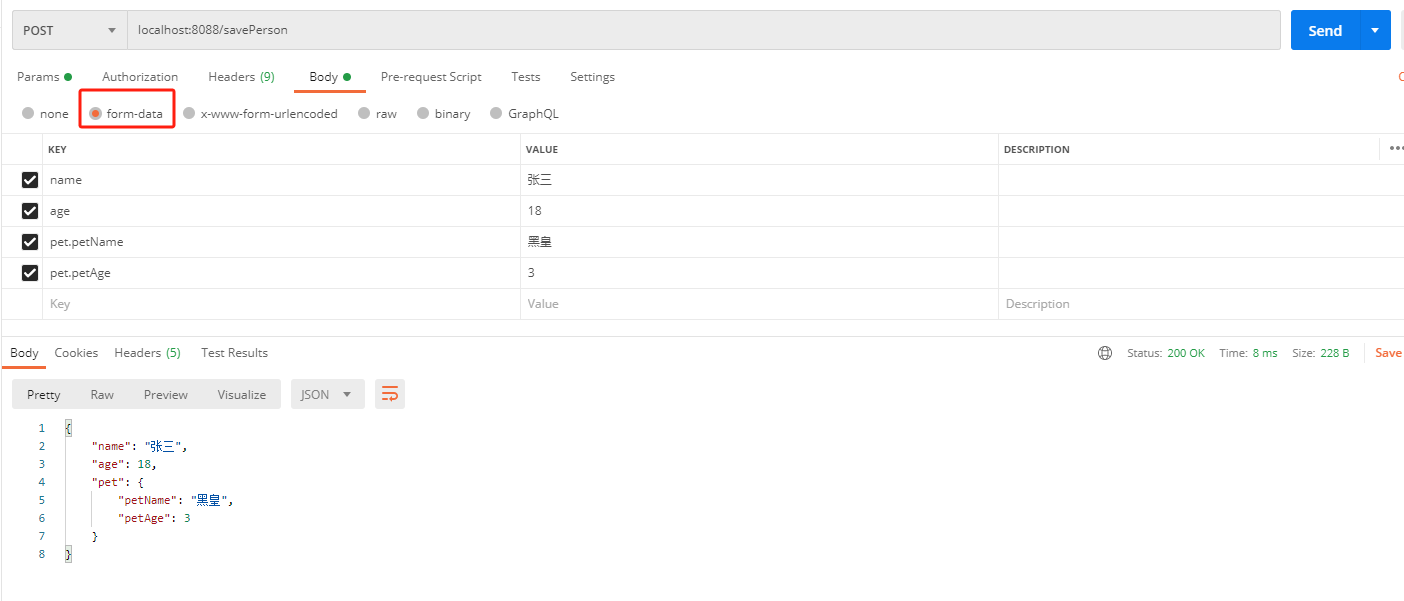
控制台输出
{
"name": "张三",
"age": 18,
"pet": {
"petName": "黑皇",
"petAge": 3
}
}
post请求-前端传参形式json(收不到)
为啥呢?因为不管是get请求还是post请求,传给后端的都是key-value对,json对象是一个整体
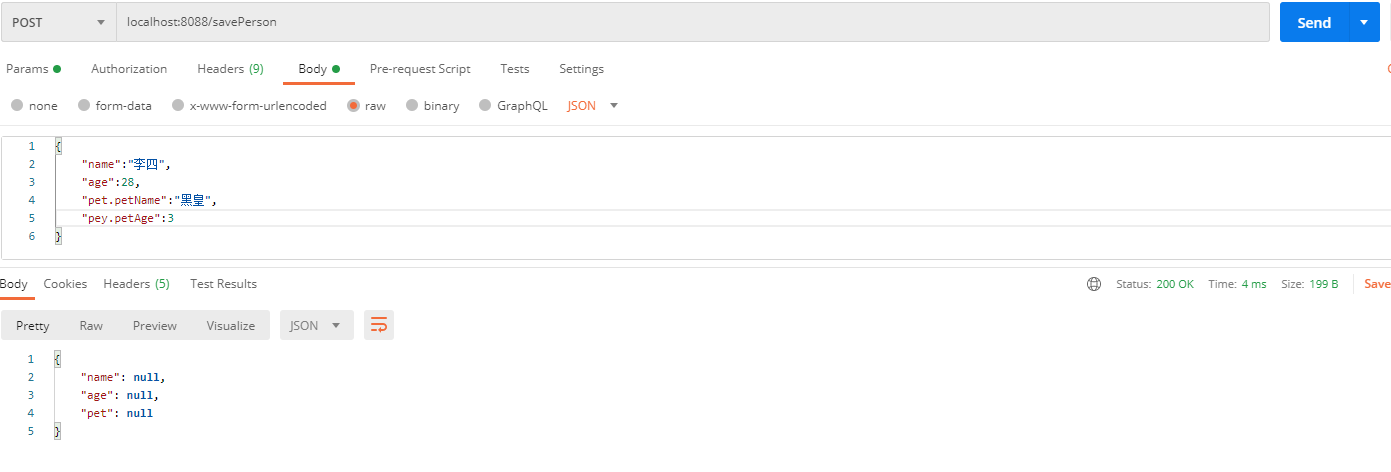
person = Person(name=null, age=null, pet=null)
参数解析流程
先直接上结论吧,数据解析的过程太长了
- 从参数解析器组里拿到自定义参数的解析器ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor(循环遍历参数解析器组,找到能支持的)
- 然后通过反射创建出一个空的参数对象(这里就是Person)
- 创建数据绑定器,数据绑定器里面封装了刚刚创建的对象Person,还有参数的名称person,以及请求(WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, attribute, name)😉,在创建数据绑定器的过程中还会给数据绑定器设置数据转换器(http传输的key-value均为字符串,需要将字符串解析为参数所需要的类型,比如将age = "18"转为age=18)
- 通过数据绑定器将请求中的数据绑定到刚刚创建的Person对象里
26个默认参数解析器
- org.springframework.web.method.annotation.ErrorsMethodArgumentResolver@78b6a2d
- org.springframework.web.method.annotation.ExpressionValueMethodArgumentResolver@6e058e2e
- org.springframework.web.method.annotation.MapMethodProcessor@4739b98d
- org.springframework.web.method.annotation.ModelMethodProcessor@3ba3a6c
- org.springframework.web.method.annotation.RequestHeaderMapMethodArgumentResolver@5a90bb5a
- org.springframework.web.method.annotation.RequestHeaderMethodArgumentResolver@2b585515
- org.springframework.web.method.annotation.RequestParamMapMethodArgumentResolver@1a758e21
- org.springframework.web.method.annotation.RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver@19275a1e
- org.springframework.web.method.annotation.RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver@1e07c615
- org.springframework.web.method.annotation.SessionStatusMethodArgumentResolver@2c2cd73f
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.HttpEntityMethodProcessor@7a9ffe46
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.MatrixVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver@680b4f35
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.MatrixVariableMethodArgumentResolver@4a73a9f5
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.PathVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver@4ba4c6f9
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver@4c005168
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RedirectAttributesMethodArgumentResolver@2081310e
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestAttributeMethodArgumentResolver@39d2ae1f
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestPartMethodArgumentResolver@1d213998
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor@1376fd7e
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletCookieValueMethodArgumentResolver@32cde714
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor@54d87fc5
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor@a7ba90b
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletRequestMethodArgumentResolver@21628d4d
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletResponseMethodArgumentResolver@578f7858
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.SessionAttributeMethodArgumentResolver@4f092a2e
- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.UriComponentsBuilderMethodArgumentResolver@275003f9
注意有两个ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor对象org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor@54d87fc5和org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor@a7ba90b,一个负责解析ModelAttribute注解,一个负责解析自定义类型,且解析ModelAttribute注解注解的顺序在前面
自定义参数的解析器
ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor
public class ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor extends ModelAttributeMethodProcessor {
// ...
}
ModelAttributeMethodProcessor
public class ModelAttributeMethodProcessor implements HandlerMethodArgumentResolver, HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler {
// ...
private final boolean annotationNotRequired;
@Override
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
// 参数上有ModelAttribute注解或者没有ModelAttribute注解并且不是简单类型(在参数解析器组中有两个ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor对象,一个annotationNotRequired == false,优先级高,一个annotationNotRequired == true 优先级低,自定义参数解析用的是annotationNotRequired == true 的)
return (parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class) ||
(this.annotationNotRequired && !BeanUtils.isSimpleProperty(parameter.getParameterType())));
}
@Override
@Nullable
public final Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
Assert.state(mavContainer != null, "ModelAttributeMethodProcessor requires ModelAndViewContainer");
Assert.state(binderFactory != null, "ModelAttributeMethodProcessor requires WebDataBinderFactory");
// 获取到参数的name
String name = ModelFactory.getNameForParameter(parameter);
ModelAttribute ann = parameter.getParameterAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class);
if (ann != null) {
mavContainer.setBinding(name, ann.binding());
}
Object attribute = null;
BindingResult bindingResult = null;
if (mavContainer.containsAttribute(name)) {
attribute = mavContainer.getModel().get(name);
}
else {
// Create attribute instance
try {
// 通过反射创建一个参数类型的空对象 测试代码会在这里创建出一个空Person对象
attribute = createAttribute(name, parameter, binderFactory, webRequest);
}
catch (BindException ex) {
if (isBindExceptionRequired(parameter)) {
// No BindingResult parameter -> fail with BindException
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, expose null/empty value and associated BindingResult
if (parameter.getParameterType() == Optional.class) {
attribute = Optional.empty();
}
bindingResult = ex.getBindingResult();
}
}
if (bindingResult == null) {
// Bean property binding and validation;
// skipped in case of binding failure on construction.
// 这里binder的具体类型为ExtendedServletRequestDataBinder
WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, attribute, name);
if (binder.getTarget() != null) {
if (!mavContainer.isBindingDisabled(name)) {
// 将请求中的数据 绑定到 binder中的target中,也就是 person对象上
bindRequestParameters(binder, webRequest);
}
validateIfApplicable(binder, parameter);
if (binder.getBindingResult().hasErrors() && isBindExceptionRequired(binder, parameter)) {
throw new BindException(binder.getBindingResult());
}
}
// Value type adaptation, also covering java.util.Optional
if (!parameter.getParameterType().isInstance(attribute)) {
attribute = binder.convertIfNecessary(binder.getTarget(), parameter.getParameterType(), parameter);
}
bindingResult = binder.getBindingResult();
}
// Add resolved attribute and BindingResult at the end of the model
Map<String, Object> bindingResultModel = bindingResult.getModel();
mavContainer.removeAttributes(bindingResultModel);
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(bindingResultModel);
return attribute;
}
// 调用绑定器的绑定
protected void bindRequestParameters(WebDataBinder binder, NativeWebRequest request) {
((WebRequestDataBinder) binder).bind(request);
}
// ...
}
数据绑定器
用于将请求中的key-value数据通过类型转换,反射绑定到new 出来的参数对象上,数据绑定的流程还是很麻烦的
ExtendedServletRequestDataBinder
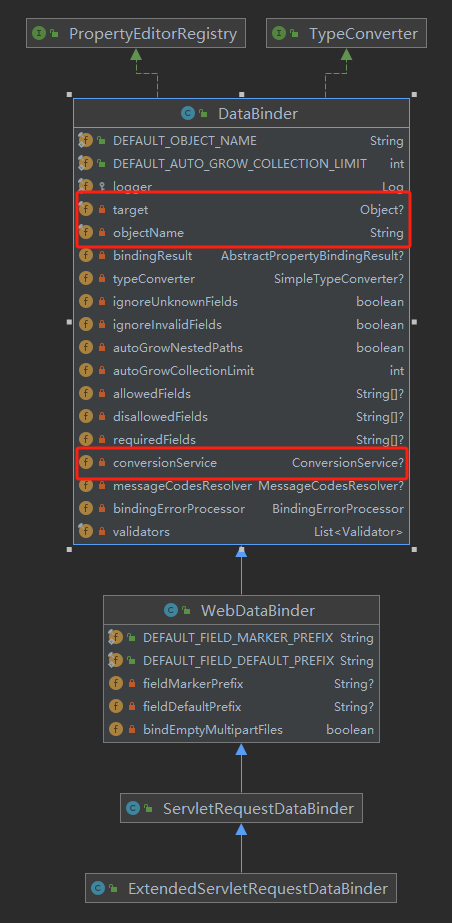
ExtendedServletRequestDataBinder中重要属性说明
-
target:要绑定的目标对象(传给方法的参数对象),也就是代码里面的attribute,这里就是Person对象
-
objectName:参数名称
-
conversionService:消息转换器,http请求,超文本传输请求,一切皆文本(也不知道这么理解对不对),收到的参数不管是数字还是日期,都是字符串的形式,需要通过转换器转为实际方法入参所需要的,默认有124个
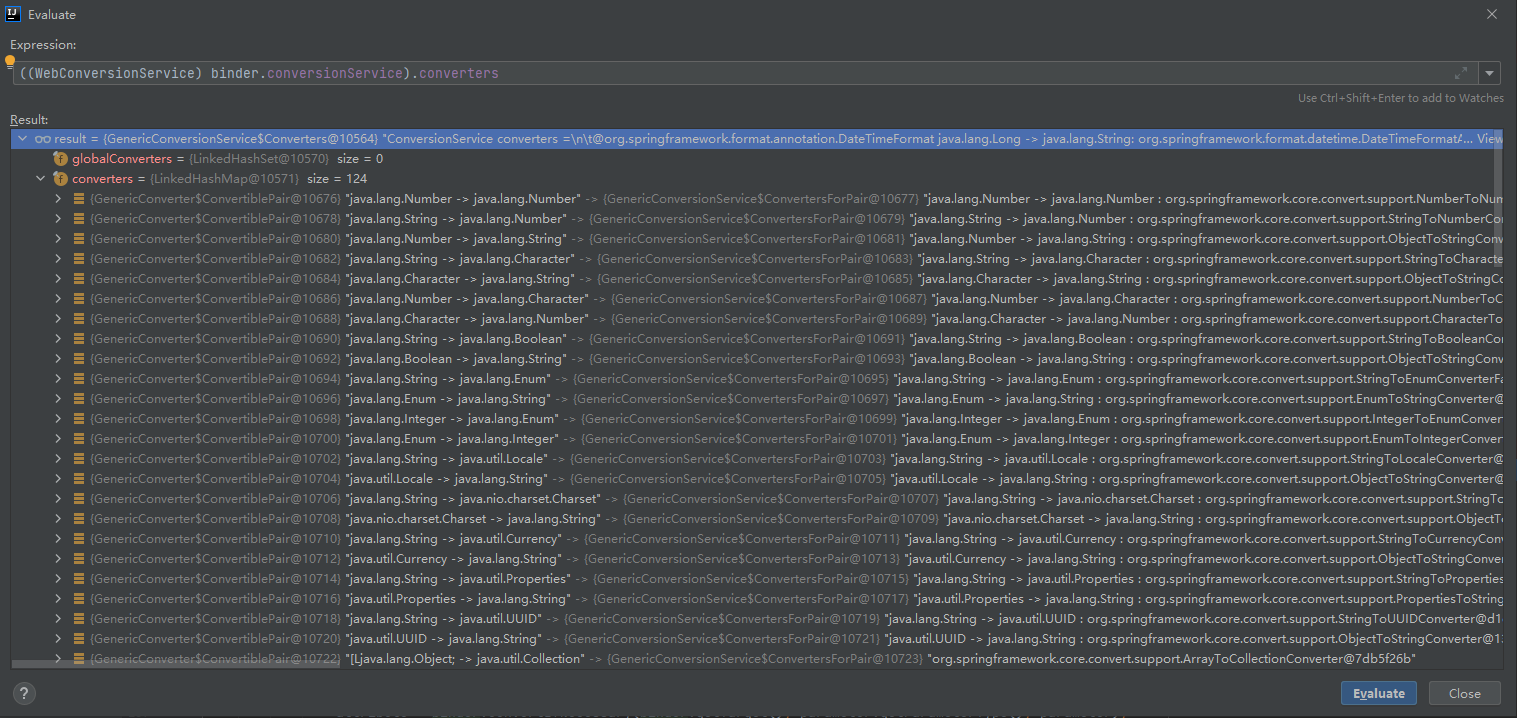
数据绑定器的数据绑定过程
public class WebRequestDataBinder extends WebDataBinder {
public void bind(WebRequest request) {
// 这里就能拿到 请求参数中的key-value对,不管是get请求还是post请求的form-data格式的,都是key-value形式的
MutablePropertyValues mpvs = new MutablePropertyValues(request.getParameterMap());
if (isMultipartRequest(request) && request instanceof NativeWebRequest) {
MultipartRequest multipartRequest = ((NativeWebRequest) request).getNativeRequest(MultipartRequest.class);
if (multipartRequest != null) {
bindMultipart(multipartRequest.getMultiFileMap(), mpvs);
}
else {
HttpServletRequest servletRequest = ((NativeWebRequest) request).getNativeRequest(HttpServletRequest.class);
if (servletRequest != null) {
bindParts(servletRequest, mpvs);
}
}
}
// 绑定数据
doBind(mpvs);
}
@Override
protected void doBind(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
checkFieldDefaults(mpvs);
checkFieldMarkers(mpvs);
super.doBind(mpvs);
}
}
public class DataBinder implements PropertyEditorRegistry, TypeConverter {
protected void doBind(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
checkAllowedFields(mpvs);
checkRequiredFields(mpvs);
// 应用属性和属性的值
applyPropertyValues(mpvs);
}
protected void applyPropertyValues(MutablePropertyValues mpvs) {
try {
// Bind request parameters onto target object.
getPropertyAccessor().setPropertyValues(mpvs, isIgnoreUnknownFields(), isIgnoreInvalidFields());
}
catch (PropertyBatchUpdateException ex) {
// Use bind error processor to create FieldErrors.
for (PropertyAccessException pae : ex.getPropertyAccessExceptions()) {
getBindingErrorProcessor().processPropertyAccessException(pae, getInternalBindingResult());
}
}
}
protected ConfigurablePropertyAccessor getPropertyAccessor() {
return getInternalBindingResult().getPropertyAccessor();
}
}
public abstract class AbstractPropertyAccessor extends TypeConverterSupport implements ConfigurablePropertyAccessor {
@Override
public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, boolean ignoreUnknown, boolean ignoreInvalid)
throws BeansException {
List<PropertyAccessException> propertyAccessExceptions = null;
List<PropertyValue> propertyValues = (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues ?
((MutablePropertyValues) pvs).getPropertyValueList() : Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues()));
for (PropertyValue pv : propertyValues) {
try {
// This method may throw any BeansException, which won't be caught
// here, if there is a critical failure such as no matching field.
// We can attempt to deal only with less serious exceptions.
// pv里面就封装了key-value信息
setPropertyValue(pv);
}
catch (NotWritablePropertyException ex) {
if (!ignoreUnknown) {
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, just ignore it and continue...
}
catch (NullValueInNestedPathException ex) {
if (!ignoreInvalid) {
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, just ignore it and continue...
}
catch (PropertyAccessException ex) {
if (propertyAccessExceptions == null) {
propertyAccessExceptions = new ArrayList<>();
}
propertyAccessExceptions.add(ex);
}
}
// If we encountered individual exceptions, throw the composite exception.
if (propertyAccessExceptions != null) {
PropertyAccessException[] paeArray = propertyAccessExceptions.toArray(new PropertyAccessException[0]);
throw new PropertyBatchUpdateException(paeArray);
}
}
@Override
public void setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) throws BeansException {
setPropertyValue(pv.getName(), pv.getValue());
}
}
巴拉巴拉又长又丑,中间还有一个数据类型的转换,如果请求过来的age = "18"是数字类型,调用转换服务转为实际参数需要的类型age = 18
BeanWrapperImpl
public class BeanWrapperImpl extends AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor implements BeanWrapper {
@Override
public void setValue(final @Nullable Object value) throws Exception {
// 拿到set方法 这里拿到了person对象的setAge方法
final Method writeMethod = (this.pd instanceof GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor ?
((GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor) this.pd).getWriteMethodForActualAccess() :
this.pd.getWriteMethod());
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
return null;
});
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () ->
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value), acc);
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException ex) {
throw ex.getException();
}
}
else {
// 设置方法为可访问的
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(writeMethod);
// 调用person的setAge方法给 person对象赋值
writeMethod.invoke(getWrappedInstance(), value);
}
}
}
解析自定义参数的调用栈还是蛮长的
自定义转换器Converter
当前端传的参数为"/savePerson?name=李四&age=18&pet=黑皇,3"时,spring试图将字符串"黑皇,3"转为Pet对象,默认的转换器里面没有一个将字符串转为pet对象的,所以就会报错
2024-03-10 11:40:58 - WARN - [io-8088-exec-4] .support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver. logException 199 : Resolved [org.springframework.validation.BindException: org.springframework.validation.BeanPropertyBindingResult: 1 errors
Field error in object 'person' on field 'pet': rejected value [黑皇,3]; codes [typeMismatch.person.pet,typeMismatch.pet,typeMismatch.com.lxw.study.entity.Pet,typeMismatch]; arguments [org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable: codes [person.pet,pet]; arguments []; default message [pet]]; default message [Failed to convert property value of type 'java.lang.String' to required type 'com.lxw.study.entity.Pet' for property 'pet'; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalStateException: Cannot convert value of type 'java.lang.String' to required type 'com.lxw.study.entity.Pet' for property 'pet': no matching editors or conversion strategy found]]
添加自定义转换器
package com.lxw.study.config;
import com.lxw.study.entity.Pet;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter;
import org.springframework.format.FormatterRegistry;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class WebConfig {
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer() {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
registry.addConverter(new Converter<String, Pet>() {
@Override
public Pet convert(String source) {
if (StringUtils.hasText(source)) {
Pet pet = new Pet();
pet.setPetName(source.split(",")[0]);
pet.setPetAge(Integer.parseInt(source.split(",")[1]));
return pet;
}
return null;
}
});
}
};
}
}
再次请求就ok了,注意Converter的包是org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter






















 888
888











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








