Netty
BIO
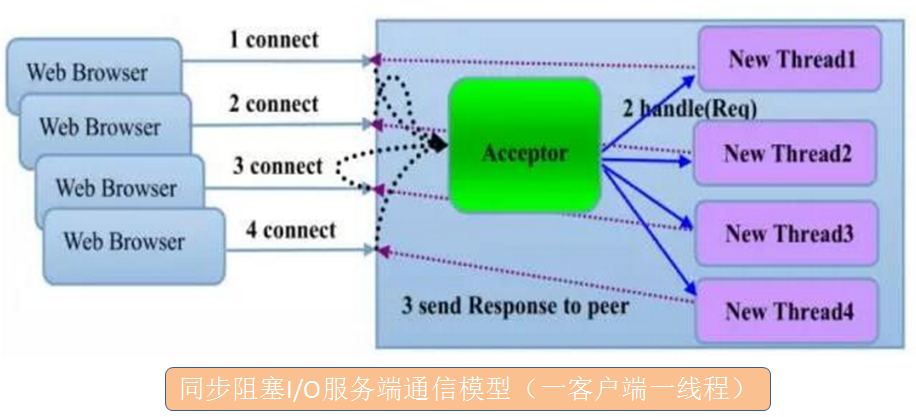
同步阻塞式I/O:每当有一个新的客户端请求接入时,服务器必须创建一个新的线程处理新接入的客户端链路,一个线程只能处理一个客户端连接。
缺点:在高性能服务器应用领域,往往需要面向成千上万个客户端的并发连接,这种模型无法满足高性能能、高并发接入的场景。
伪异步I/O
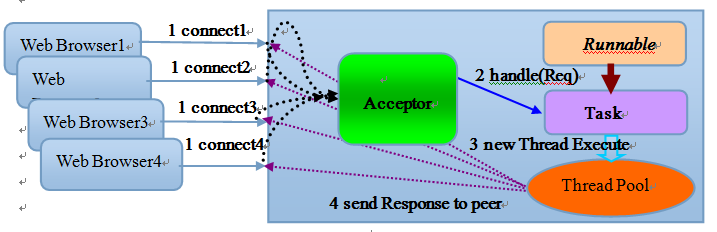
当有新的客户端接入时,将客户端的socket封装成一个task(该任务实现java.lang.Runnable接口)投递到后端的线程池中进行处理,JDK的线程池维护一个消息队列和N个活跃的线程,对消息队列中的任务进行处理。由于线程池可以设置队列的大小和最大线程数,因此,它的资源占用是可控的,无论多少个客户端并发访问,都不会导致资源的耗尽和宕机。
缺点:读写操作都是同步阻塞的,阻塞时间取决对方I/O线程的处理速度和网络I/O的传输速度。
- 服务端处理缓慢,返回应答消息耗费60s,平时只需要10ms。
- 采用伪异步I/O的线程正在读取故障服务节点的响应,由于读取输入流是阻塞的,它将会被同步阻塞60s。
- 假如所有的可用线程采用阻塞队列实现,当队列积满之后,后续入队列的操作将被阻塞。
- 由于前端只有一个Accptor线程接受客户端接入,它被阻塞在线程池的同步阻塞队列之后,新的客户端请求消息将被拒绝,客户端会发生大量的连接超时。
NIO
同步非阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个请求一个线程,即客户端发送的连接请求都会注册到多路复用器上,多路复用器轮询到连接有I/O请求时才启动一个线程进行处理。
在电子技术(特别是数字电路)中,数据选择器(英语:multiplexer,简称:MUX[1]),或称多路复用器,是一种可以从多个模拟或数字输入信号中选择一个信号进行输出的器件。[2] 一个有 2n 输入端的数据选择器有 n 个可选择的输入-输出线路,可以通过控制端来选择其中一个信号被选择作为输出。[3] 数据选择器主要用于增加一定量的时间和带宽内的可以通过网络发送的数据量。[2]
数据选择器使多个信号共享一个设备或资源,例如一个模拟数字转换器或一个传输线,而不必给每一个输入信号配备一个设备。
缓冲区Buffer
- Buffer是一个对象,数据写入和读取都要先经过缓冲区,通过缓冲区经行操作。
- 缓冲区实质上是一个数组,但还提供了对数据结构化访问以及维护读写位置等信息。
- ByteBuffer: 字节缓冲数组
- CharBuffer: 字符缓冲区
- ShortBuffer: 短整型缓冲区
- IntBuffer: 整形缓冲区
- LongBuffer: 长整形缓冲区
- FloatBuffer: 浮点型缓冲区
- DoubleBuffer: 双精度浮点型缓冲区
通道Channel
- Channel是通道,网络数据通过Channel读取和写入。通道可用于读、写或者两者同时进行。
多路复用器Selector
- Selector提供选择已经就绪的任务的能力:Selector会不断轮询注册在其上的Channel,如果某个Channel上面发生读或者写事件,这个Channel就处于就绪状态,会被Selector轮询出来,然后通过SelectionKey可以获取就绪的Channel集合,进行后续的I/O操作。
- 一个多路复用器可以同时轮询多个Channel,一个线程负责Selector的轮询,就可以接入成千上万的客户端。
AIO
回调函数
- JDK底层通过线程池ThreadPoolExecutor来执行回调通知,异步回调通知类由sun.nio.ch.AsynchronousChannelGroupImpl实现,它经过层层调用,最终回调com.phei.netty.aio.AsyncTimeClientHandler$1.complete(例子的方法),完成回调通知。
- 异步Socket Channel是被动执行的对象,我们不需要想NIO编程那样创建一个独立的I/O线程来处理读写操作。对于AsynchronousServerSocketChannel和AsynchronousSocketChannel,它们都由JDK的线程池负责回调并驱动读写操作。
ByteBuf
与NIO ByteBuffer类似,使用ByteBuffer往往需要在读写之间通过flip切换。ByteBuf里维护两个index,一个readerIndex,一个writerIndex;readerIndex writerIndex capactiy 的三者的关系是:
0 <=readerIndex <=writerIndex <= capacity
1.如何工作
ByteBuf维护了两个不同的索引:readerIndex用于读取,writerIndex用于写入。

-
**从ByteBuf读取时:**它的readerIndex将会被递增已经被读取的字节数。
-
**写入ByteBuf时:**它的wirterIndex也会被递增。
-
当往byteBuf写入一个byte时,writerIndex++,从bytebuf读一个byte时,readerIndex++;
-
如果读取字节直到 readerIndex 达到 和 writerIndex 同样的值时,将会到达“可以读取的”数据的末尾。就 如同试图读取超出数组末尾的数据一样,试图读取超出该点的数据将会触发一个IndexOutOfBoundsException。
-
ByteBuf与JDK的ByteBuffer的最大区别之一就是:
- netty的ByteBuf采取了读/写索引分离,一个初始化的ByteBuf的readerIndex和writerIndex都处于0位置。
- 当读索引和写索引处于同一位置时,如果我们继续读取,就会抛出异常IndexOutOfBoundsException。
- 对于ByteBuf的任何读写操作都会分别单独的维护读索引和写索引。maxCapacity最大容量默认的限制就是Integer.MAX_VALUE。
2.
1.Heap Buffer 堆缓冲区
ByteBuf将数据存储在JVM的堆空间,通过将数据存储在数组中实现的。
-
堆缓冲的优点是:由于数据存储在JVM的堆中可以快速创建和快速释放,并且提供了数组的直接快速访问的方法。
-
堆缓冲缺点是:每次读写数据都要先将数据拷贝到直接缓冲区再进行传递。
2.Direct Buffer 直接缓冲区
NIO 在 JDK 1.4 中引入的 ByteBuffer 类允许 JVM 实现通过本地调用来分配内存。这主要是为了避免在每次调用本地 I/O 操作之前(或者之后)将缓冲区的内容复 制到一个中间缓冲区(或者从中间缓冲区把内容复制到缓冲区)。
Direct Buffer在堆之外直接分配内存,直接缓冲区不会占用堆的容量。事实上,在通过套接字发送它之前,JVM将会在内部把你的缓冲 区复制到一个直接缓冲区中。所以如果使用直接缓冲区可以节约一次拷贝。
(1)Direct Buffer的优点是:在使用Socket传递数据时性能很好,由于数据直接在内存中,不存在从JVM拷贝数据到直接缓冲区的过程,性能好。
(2)缺点是:相对于基于堆的缓冲区,它们的分配和释放都较为昂贵。如果你 正在处理遗留代码,你也可能会遇到另外一个缺点:因为数据不是在堆上,所以你不得不进行一 次复制。
虽然netty的Direct Buffer有这个缺点,但是netty通过内存池来解决这个问题。直接缓冲池不支持数组访问数据,但可以通过间接的方式访问数据数组:
ByteBuf directBuf = ...;
if (!directBuf.hasArray()) {
int length = directBuf.readableBytes();
byte[] array = new byte[length];
directBuf.getBytes(directBuf.readerIndex(), array);
handleArray(array, 0, length);
}
不过对于一些IO通信线程中读写缓冲时建议使用DirectByteBuffer,因为这涉及到大量的IO数据读写。对于后端的业务消息的编解码模块使用HeapByteBuffer。
3.Composite Buffer 复合缓冲区
第三种也是最后一种模式使用的是复合缓冲区,它为多个 ByteBuf 提供一个聚合视图。在 这里你可以根据需要添加或者删除 ByteBuf 实例,这是一个 JDK 的 ByteBuffer 实现完全缺 失的特性。
Netty 通过一个 ByteBuf 子类——CompositeByteBuf——实现了这个模式,它提供了一 个将多个缓冲区表示为单个合并缓冲区的虚拟表示
Netty提供了Composite ByteBuf来处理复合缓冲区。例如:一条消息由Header和Body组成,将header和body组装成一条消息发送出去。下图显示了Composite ByteBuf组成header和body:

//组合缓冲区
CompositeByteBuf compBuf = Unpooled.compositeBuffer();
//堆缓冲区
ByteBuf heapBuf = Unpooled.buffer(8);
//直接缓冲区
ByteBuf directBuf = Unpooled.directBuffer(16);
//添加ByteBuf到CompositeByteBuf
compBuf.addComponents(heapBuf, directBuf);
//删除第一个ByteBuf
compBuf.removeComponent(0);
Iterator<ByteBuf> iter = compBuf.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iter.next().toString());
}
//使用数组访问数据
if(!compBuf.hasArray()){
int len = compBuf.readableBytes();
byte[] arr = new byte[len];
compBuf.getBytes(0, arr);
}
4.随机访问索引getByte(i),i是随机值
ByteBuf提供读/写索引,从0开始的索引,第一个字节索引是0,最后一个字节的索引是capacity-1,下面给出一个示例遍历ByteBuf的字节:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个16字节的buffer,这里默认是创建heap buffer
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.buffer(16);
//写数据到buffer
for(int i=0; i<16; i++){
buf.writeByte(i+1);
}
//读数据
for(int i=0; i<buf.capacity(); i++){
System.out.print(buf.getByte(i)+", ");
}
}
/***output:
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,
*/
这里有一点需要注意的是:通过那些需要一个索引值参数的方法(getByte(i))之一索引访问byte时不会改变真实的读索引和写索引,我们可以通过ByteBuf的readerIndex()或则writerIndex()函数来分别推进读索引和写索引。
5.顺序访问索引
@Override
public ByteBuf writeByte(int value) {
ensureAccessible();//检验是否可以写入
ensureWritable0(1);
_setByte(writerIndex++, value);//这里写索引自增了
return this;
}
@Override
public byte readByte() {
checkReadableBytes0(1);
int i = readerIndex;
byte b = _getByte(i);
readerIndex = i + 1;//这里读索引自增了
return b;
}
虽然 ByteBuf 同时具有读索引和写索引,但是 JDK 的 ByteBuffer 却只有一个索引,这 也就是为什么必须调用 flip()方法来在读模式和写模式之间进行切换的原因。
首先图 5-3 展示了 ByteBuf 是如何被它的两个索引划分成 3 个区域的

了解ByteBuf更多内容
3.源码分析:
- 调用discardReadBytes之后被读过的空间将被释放,readerIndex = 0;调用clear操作之后整个ByteBuf空间将被释放,0 = readerIndex = writerIndex;
1.官网三例子:Discard
public class DiscardServer {
private int port;
public DiscardServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void run() throws InterruptedException {
//这个是用于serversocketchannel的eventloop
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//这个是用于处理accept到的channel
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();//初始化服务的配置
//设置时间循环对象,前者用来处理accept事件,后者用于处理已经建立的连接的io
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//设定通讯模式为NIO,同步非阻塞
/**
* childHandler是服务的Bootstrap独有的方法。是用于提供处理对象的。可以一次性
* 增加若干个处理逻辑。是类似责任链模式的处理方式。增加A,B两个处理逻辑,在处理 *客户端请求数据的时候
* 根据A->B顺序依次处理
*
* ChannelInitializer 用于提供处理器的一个模型对象
* 其中定义了一个方法,initChannel方法。
* 该方法是用于初始化处理逻辑责任链条的。
* 可以保证服务端的Bootstrap只初始化一次处理器,尽量提供处理逻辑的重用。
* 避免反复的创建处理器对象,节约资源开销。
*/
//为accept channel的pipeline预添加的inboundhandler
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
//当新连接accept的时候,这个方法会调用
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new DiscardServerHandler()); //在这里配置具体数据接收方法的处理
}
})
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)//设定缓冲区大小,缓冲区的单位是字节
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
/**bind方法 绑定监听端口。ServerBootstrap可以绑定多个监听端口。多次调用bind方法即可
*sync 开始监听逻辑。返回一个ChannelFuture.返回结果代表的是监听成功后的一个对应的未来 *结果
*bind方法会创建一个serverchannel,并且会将当前的channel注册到eventloop上面,
*会为其绑定本地端口,并对其进行初始化,为其的pipeline加一些默认的handler
*可以使用ChannelFuture实现后续的服务器和客户端的交互。
*/
ChannelFuture future = b.bind(port).sync();//绑定端口
System.out.println("server start...");
//相当于在这里阻塞,直到serverchannel关闭
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
/**
* shutdownGracefully 方法是一个安全关闭的方法。可以保证不放弃任何一个已接收的客户端请求。
*/
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int port;
if (args.length > 0) {
port = Integer.parseInt( args[0]);
} else {
port = 8080;
}
new DiscardServer(port).run();
}
}
-
ServerBootstrap的group方法:
//这里parent用于执行server的accept时间事件,child才是用于执行获取的channel连接的事件
public ServerBootstrap group(EventLoopGroup parentGroup, EventLoopGroup childGroup) {
super.group(parentGroup);
if (childGroup == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("childGroup");
}
if (this.childGroup != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("childGroup set already");
}
this.childGroup = childGroup;
return this;
}
-
channel方法:该方法主要是用于构造用于产生channel的工厂类,在我们这段代码说白了就是用于实例化serversocketchannel的工厂类。。。
//构造serversocketchannel factory public B channel(Class<? extends C> channelClass) { if (channelClass == null) { throw new NullPointerException("channelClass"); } return channelFactory(new BootstrapChannelFactory<C>(channelClass)); //构造工厂类 } /** * {@link ChannelFactory} which is used to create {@link Channel} instances from * when calling {@link #bind()}. This method is usually only used if {@link #channel(Class)} * is not working for you because of some more complex needs. If your {@link Channel} implementation * has a no-args constructor, its highly recommend to just use {@link #channel(Class)} for * simplify your code. */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public B channelFactory(ChannelFactory<? extends C> channelFactory) { if (channelFactory == null) { throw new NullPointerException("channelFactory"); } if (this.channelFactory != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("channelFactory set already"); } this.channelFactory = channelFactory; //设置 return (B) this; } -
childHandler方法:
//设置childHandler,这个是当有channel accept之后为其添加的handler public ServerBootstrap childHandler(ChannelHandler childHandler) { if (childHandler == null) { throw new NullPointerException("childHandler"); } this.childHandler = childHandler; return this; } -
ServerBootstrap的其他方法
2.Netty_TCP拆包粘包的解决方案:
1).TCP粘包/拆包发生的原因
-
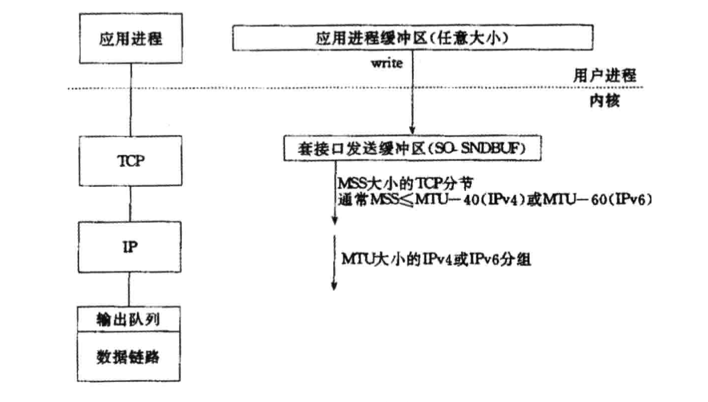
应用程序write写入的字节大小大于套接口发送缓冲区大小;
-
进行MSS大小的TCP分段;
-
以太网帧的payload大于MTU进行IP分片;
2).DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
.....
.....
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel sc) throws Exception {
//设置特殊分隔符,并使用工具类,将String类型的$_转成ByeteBuf类型的数据
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("$_".getBytes());
/* DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder
* 作用主要是从特殊分隔符处,将报文进行拆分
* 2个参数:
* 第一个参数是指特殊分割符的最大长度
* 第二个参数是指特殊分隔符
*/
sc.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024, buf));
//设置字符串形式的解码
sc.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
sc.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
});
......
......
}
}
public class ServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(" server channel active... ");
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
String request = (String)msg;
System.out.println("Server :" + msg);
String response = "服务器响应:" + msg + "$_";
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(response.getBytes()));
}
......
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
......
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel sc) throws Exception {
//
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("$_".getBytes());
sc.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024, buf));
sc.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
sc.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
});
......
}
}
public class ClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter{
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("client channel active... ");
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
try {
String response = (String)msg;
System.out.println("Client: " + response);
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
.....
}
3).利用LineBasedFrameDecoder解决粘包问题:
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { // (4)
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new TimeServerHandler());
}
})
- LineBasedFrameDecoder的工作原理是它依次遍历ByteBuf中的刻可读字节,判断看是否有“/n” 或者 “/r/n”,如果有,就一此为位置结束位置,从可读索引到结束位置区间的字节就组成了一行。它是以换行符为结束标志的解码器,支持携带结束符或者不携带结束符两种解码方式,同时支持配置单行的最大长度。如果连续读取到最大长度后仍然没有发现换行符,就会抛出异常,同时忽略掉之前读到的异常码流。
- StringDecoder的功能非常简单,就是将接收到的对象转换成字符串,然后继续调用后面的Handler。LineBasedFrameDecoder + StringDecoder组合就是按行切换的文本解码器,它被设计用来支持TCP的粘包和拆包。
4).FixedLengthFrameDecoder
用于固定长度的消息编解码
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(20));
3.MessagePack编解码
- 将对象比如BOJO进行编解码以利于网络中进行传输。平常我们也会将编解码说成是序列化/反序列化
- 定义:当进行远程跨进程服务调用时,需要把被传输的java对象编码为字节数组或者ByteBuffer对象。而当远程服务读取到ByteBuffer对象或者字节数组时,需要将其解码为发送时的java对象。这被称为java对象编解码技术。比如java的序列化
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("frameDecoder", new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(65535,0, 2, 0, 2));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("msgpack decoder", new MsgpackDecoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("frameEncoder", new LengthFieldPrepender(2));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("msgpack encoder", new MsgpackEncoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new EchoClientHandler(sendNumber));
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
UserInfo[] infos = UserInfo();
for (UserInfo info : infos) {
ctx.write(info);
}
ctx.flush();
}
4.Protobuf编解码
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufDecoder(SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq.getDefaultInstance()));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufVarint32LengthFieldPrepender());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufEncoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new SubReqServerHandler());
}
···
5.JBoss 的 Marshalling编解码器
- 支持半包和粘包的处理
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.bulidMarshallingDecoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingEncoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new SubReqClientHandler());
}
public class MarshallingCodeCFactory {
public static MarshallingDecoder bulidMarshallingDecoder() {
//serial表示创建的是Java序列化工厂对象
final MarshallerFactory marshallerFactory = Marshalling.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
UnmarshallerProvider provider = new DefaultUnmarshallerProvider(marshallerFactory, configuration);
MarshallingDecoder decoder = new MarshallingDecoder(provider, 1024);
return decoder;
}
public static MarshallingEncoder buildMarshallingEncoder() {
final MarshallerFactory marshallerFactory = Marshalling.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
MarshallerProvider provider = new DefaultMarshallerProvider(marshallerFactory, configuration);
MarshallingEncoder encoder = new MarshallingEncoder(provider);
return encoder;
}
}
6.HTTP文件服务器
public class HttpFileServer {
private static final String DEFAULT_URL = "/src/main/java/com/example/nettydemo/";
private void run(final int port, final String url) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//HTTP请求消息解码器
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("http-decoder", new HttpRequestDecoder());
//将多个消息转换为单一的FullHttpRequest或者FullHttpResponse
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("http-aggregator", new HttpObjectAggregator(65536));
//HTTP响应消息编码器
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("http-encoder", new HttpResponseEncoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("http-chunked", new ChunkedWriteHandler());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("fileServerHandler", new HttpFileServerHandler(url));
}
});
ChannelFuture f = b.bind("10.21.23.112", port).sync();
System.out.println("HTTP文件目录服务器启动,网址是 : " + "http://10.21.23.112:" + port + url);
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int port = 8080;
if (args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
}
}
String url = DEFAULT_URL;
if (args.length > 1) url = args[1];
new HttpFileServer().run(port, url);
}
}
public class HttpFileServerHandler extends
SimpleChannelInboundHandler<FullHttpRequest> {
private final String url;
public HttpFileServerHandler(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
@Override
public void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
FullHttpRequest request) throws Exception {
//对HTTP请求消息的解码结果进行判断,如果解码失败,直接构造HTTP400错误返回
if (!request.decoderResult().isSuccess()) {
sendError(ctx, BAD_REQUEST);
return;
}
//对请求的方法进行判断,如果不是从浏览器或者表单设置为GET发起的请求,构造405错误返回
if (request.method() != GET) {
sendError(ctx, METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED);
return;
}
final String uri = request.uri();
//对url进行包装
final String path = sanitizeUri(uri);
//如果uri不合法返回403
if (path == null) {
sendError(ctx, FORBIDDEN);
return;
}
//使用新组装的uri路径构造File对象
File file = new File(path);
//如果文件不存在或者是系统隐藏文件,则构造404错误
if (file.isHidden() || !file.exists()) {
sendError(ctx, NOT_FOUND);
return;
}
//如果文件是目录,则发送目录的链接给客户端浏览器。
if (file.isDirectory()) {
if (uri.endsWith("/")) {
sendListing(ctx, file);
} else {
sendRedirect(ctx, uri + '/');
}
return;
}
//如果用户在浏览器上点击超链接直接打开或者下载文件,会执行以下代码:多超链接的文件进行合法性判断,如果不是合法文件则返回403
if (!file.isFile()) {
sendError(ctx, FORBIDDEN);
return;
}
//使用随机文件读写类以只读的方式打开文件,,如果文件打开失败,则返回404
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = null;
try {
randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");// 以只读的方式打开文件
} catch (FileNotFoundException fnfe) {
sendError(ctx, NOT_FOUND);
return;
}
//获取文件长度,构造成功的HTTP应答消息,在消息头中设置content length和content type
long fileLength = randomAccessFile.length();
HttpResponse response = new DefaultHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, OK);
setContentLength(response, fileLength);
setContentTypeHeader(response, file);
if (isKeepAlive(request)) {
response.headers().set(CONNECTION);
}
ctx.write(response);
ChannelFuture sendFileFuture;
//通过Netty的ChunkedFile对象直接将文件写入到发送缓冲区中。
sendFileFuture = ctx.write(new ChunkedFile(randomAccessFile, 0,
fileLength, 8192), ctx.newProgressivePromise());
//如果发送完成打印“Transfer progress”
sendFileFuture.addListener(new ChannelProgressiveFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationProgressed(ChannelProgressiveFuture future,
long progress, long total) {
if (total < 0) { // total unknown
System.err.println("Transfer progress: " + progress);
} else {
System.err.println("Transfer progress: " + progress + " / "
+ total);
}
}
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelProgressiveFuture future)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("Transfer complete.");
}
});
//使用chunked编码,最后需要发送一个编码结束的空消息体
ChannelFuture lastContentFuture = ctx
.writeAndFlush(LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT);
if (!isKeepAlive(request)) {
lastContentFuture.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
if (ctx.channel().isActive()) {
sendError(ctx, INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}
private static final Pattern INSECURE_URI = Pattern.compile(".*[<>&\"].*");
private String sanitizeUri(String uri) {
try {
//对url进行解码,使用UTF-8字符集
uri = URLDecoder.decode(uri, "UTF-8");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
try {
uri = URLDecoder.decode(uri, "ISO-8859-1");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e1) {
throw new Error();
}
}
//如果uri与允许访问的uri一致或者是其子目录(文件),则校验通过,否则返回空
if (!uri.startsWith(url)) {
return null;
}
if (!uri.startsWith("/")) {
return null;
}
//将硬编码的文件路径分隔符替换为本地操作系统的文件路径分隔符
uri = uri.replace('/', File.separatorChar);
if (uri.contains(File.separator + '.')
|| uri.contains('.' + File.separator) || uri.startsWith(".")
|| uri.endsWith(".") || INSECURE_URI.matcher(uri).matches()) {
return null;
}
return System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator + uri;
}
private static final Pattern ALLOWED_FILE_NAME = Pattern
.compile("[A-Za-z0-9][-_A-Za-z0-9\\.]*");
private static void sendListing(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, File dir) {
//创建“成功”的HTTP响应消息
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, OK);
//设置消息头的类型为“text/html;charset=UTF-8”
response.headers().set(CONTENT_TYPE, "text/html; charset=UTF-8");
//用于构造响应消息体
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder();
String dirPath = dir.getPath();
buf.append("<!DOCTYPE html>\r\n");
buf.append("<html><head><title>");
buf.append(dirPath);
buf.append(" 目录:");
buf.append("</title></head><body>\r\n");
buf.append("<h3>");
buf.append(dirPath).append(" 目录:");
buf.append("</h3>\r\n");
buf.append("<ul>");
buf.append("<li>链接:<a href=\"../\">..</a></li>\r\n");
for (File f : dir.listFiles()) {
if (f.isHidden() || !f.canRead()) {
continue;
}
String name = f.getName();
if (!ALLOWED_FILE_NAME.matcher(name).matches()) {
continue;
}
buf.append("<li>链接:<a href=\"");
buf.append(name);
buf.append("\">");
buf.append(name);
buf.append("</a></li>\r\n");
}
buf.append("</ul></body></html>\r\n");
ByteBuf buffer = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(buf, CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
response.content().writeBytes(buffer);
buffer.release();
ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
private static void sendRedirect(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String newUri) {
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, FOUND);
response.headers().set(LOCATION, newUri);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
private static void sendError(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
HttpResponseStatus status) {
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1,
status, Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Failure: " + status.toString()
+ "\r\n", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
response.headers().set(CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain; charset=UTF-8");
ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
private static void setContentTypeHeader(HttpResponse response, File file) {
MimetypesFileTypeMap mimeTypesMap = new MimetypesFileTypeMap();
response.headers().set(CONTENT_TYPE,
mimeTypesMap.getContentType(file.getPath()));
}
}
错误原因:Order依赖于其它三个Address、Shipping、Customer要按顺序排练这四个类
F:\IntelliJ IDEA 2018.1.6\WorkSpace\netty-demo\target\classes\com\example\nettydemo>
java -Djava.ext.dirs=C:\Users\clear\Desktop\jibx\lib org.jibx.binding.generator.BindGen -t C:\aa -b bind.xml -v httpxml.Order
Using class loading paths:
.
F:\JDK8\\lib
F:\JDK8\\lib\tools.jar
.
Using source loading paths:
Starting from classes:
httpxml.Order
Output to directory C:\aa
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
at org.jibx.custom.classes.SharedValueBase.fillType(SharedValueBase.java:357)
at org.jibx.custom.classes.ValueCustom.fillDetails(ValueCustom.java:316)
at org.jibx.custom.classes.ClassCustom.apply(ClassCustom.java:800)
at org.jibx.custom.classes.GlobalCustom.addClassCustomization(GlobalCustom.java:377)
at org.jibx.binding.generator.BindGen.checkInclude(BindGen.java:163)
at org.jibx.binding.generator.BindGen.expandReferences(BindGen.java:208)
at org.jibx.binding.generator.BindGen.findReferences(BindGen.java:1010)
at org.jibx.binding.generator.BindGen.generate(BindGen.java:1124)
at org.jibx.binding.generator.BindGen.main(BindGen.java:1302)
7.WebSocket
特点
- 单一的TCP连接,采用全双工模式通信。
- 对代理、防火墙和路由器透明。
- 无头部信息、Cookie和身份验证。
- 无安全开销。
- 通过“ping/pong”帧保持链路激活。
- 服务器可以主动传递消息给客户端,不再需要客户端轮询。
1.连接建立:

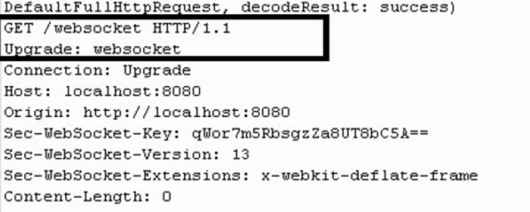
- 握手成功后,服务端和客户端就可以通过“message”的方式进行通信了,一个消息由一个或多个帧组成,WebSocket的消息并不一定对应一个特定的网络层的帧,它可以被分割成多个帧或者被合并。帧都有自己的类型,属于同一个消息的多个帧具有相同类型的数据。
2.WebSocket协议开发
-
服务端
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast("http-codec", new HttpServerCodec()) .addLast("aggregator", new HttpObjectAggregator(65536)) .addLast("http-chunked", new ChunkedWriteHandler()) .addLast("handler", new WebSocketServerHandler()); } }); -
WebSocketServerHandler
public class WebSocketServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Object> { private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(WebSocketServerHandler.class.getName()); private WebSocketServerHandshaker handshaker; @Override protected void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Object o) throws Exception { if (o instanceof FullHttpRequest) { handleHttpRequest(channelHandlerContext, (FullHttpRequest) o); } else if (o instanceof WebSocketFrame) { handleWebFrame(channelHandlerContext, (WebSocketFrame) o); } } @Override public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { ctx.flush(); } private void handleHttpRequest(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest req) { //判断是否是websocket请求 if (!req.decoderResult().isSuccess() || (!"websocket".equals(req.headers().get("Upgrade")))) { sendHttpResponse(ctx, req , new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.BAD_REQUEST)); return; } WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory webSocketServerHandshakerFactory = new WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory( "ws://loclahost:8080/websocket", null, false); handshaker = webSocketServerHandshakerFactory.newHandshaker(req); if (handshaker == null) { WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory.sendUnsupportedVersionResponse(ctx.channel()); } else { //构造握手响应信息返回给客户端,同时将WebSocket相关的编码和解码器动态添加到ChannelPipeline中 handshaker.handshake(ctx.channel(), req); } } private static void sendHttpResponse(ChannelHandlerContext context, FullHttpRequest req, FullHttpResponse res) { // 返回应答给客户端 if (res.status().code() != 200) { ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(res.status().toString(), CharsetUtil.UTF_8); res.content().writeBytes(buf); buf.release(); setContentLength(res, res.content().readableBytes()); } // 如果是非Keep-Alive,关闭连接 ChannelFuture f = context.channel().writeAndFlush(res); if (!isKeepAlive(req) || res.status().code() != 200) { f.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); } } private void handleWebFrame(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, WebSocketFrame o) { if (o instanceof CloseWebSocketFrame) { handshaker.close(channelHandlerContext.channel(), ((CloseWebSocketFrame) o).retain()); return; } if (o instanceof PingWebSocketFrame) { channelHandlerContext.channel().write(new PongWebSocketFrame(o.content().retain())); return; } if (!(o instanceof TextWebSocketFrame)) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException( String.format("%s frame types not supported", o.getClass().getName())); } String request = ((TextWebSocketFrame) o).text(); if (logger.isLoggable(Level.FINE)) { logger.fine(String.format("%s received %s", channelHandlerContext.channel(), request)); } channelHandlerContext.channel().write( new TextWebSocketFrame(request + " , 欢迎使用Netty WebSocket服务,现在时刻:" + new java.util.Date().toString())); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }






















 551
551

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








