目录
2.1.1. org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint
2.1.2. org.aopalliance.intercept.JoinPoint
2.5. ReflectiveMethodInvocation
3.1.1. AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice
3.1.3. AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice
3.1.5. AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice
3.2. DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry
3.2.1. MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
3.2.2. AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor
3.2.3. ThrowsAdviceInterceptor
1. 前言
在上篇文章:Spring AOP源码分析篇四:JDK动态代理(JdkDynamicAopProxy)和CGLIB代理(ObjenesisCglibAopProxy)_程序源仔的博客-CSDN博客
我们知道了代理对象创建好后,其拦截方法的操作都是交给MethodInvocation去做,jdk的JdkDynamicAopProxy是交给ReflectiveMethodInvocation,CGLIB的ObjenesisCglibAopProxy是交给CglibMethodInvocation。
MethodInvocation是AOP联盟包里的,包路径为org.aopalliance.intercepet.MethodInvocation
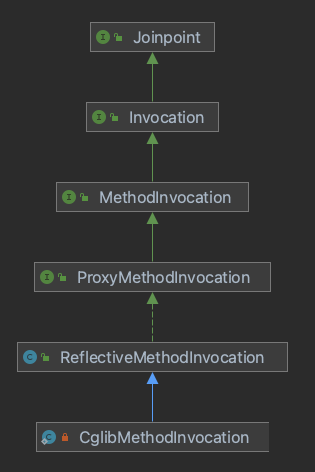
下面将会逐一介绍图中的类
2. JoinPoint
2.1. JoinPoint
我们要注意,有两个不同包路径的joinpint!!!
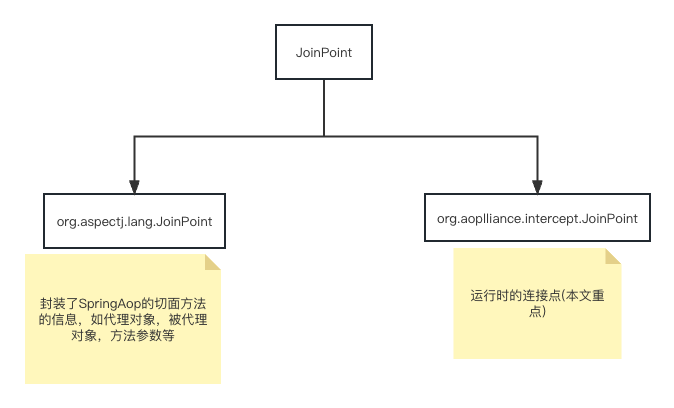
2.1.1. org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint
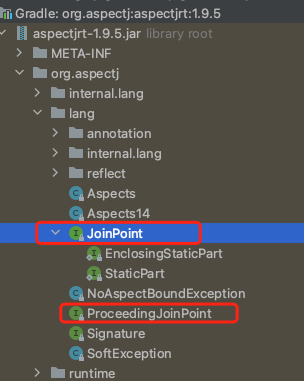
我们看一个demo
/**
* @Author xiaoyuanzai
* @Date 2023/6/5 20:09
* @description:
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspectV3 {
//定义一个切入点:指定哪些方法可以被切入(如果是别的类需要使用 请用该方法的全类名)
@Pointcut( "execution(public void com.xiaoyuanzai.service.UserService.test())" )
public void pointCut() {
}
@Before( "pointCut()" )
public void beforeAdvice( JoinPoint joinPoint ) {
System.out.println("目标方法名为:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("目标方法所属类的简单类名:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("目标方法所属类的类名:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName());
System.out.println("目标方法声明类型:" + Modifier.toString(joinPoint.getSignature().getModifiers()));
//获取传入目标方法的参数
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
System.out.println("第" + (i+1) + "个参数为:" + args[i]);
}
System.out.println("被代理的对象:" + joinPoint.getTarget());
System.out.println("代理对象自己:" + joinPoint.getThis());
}
}
输出:
目标方法名为:test
目标方法所属类的简单类名:UserService
目标方法所属类的类名:com.xiaoyuanzai.service.UserService
目标方法声明类型:public
被代理的对象:com.xiaoyuanzai.service.UserService@45820e51
代理对象自己:com.xiaoyuanzai.service.UserService@45820e51
advice test!!!从上面例子可以看出,这个joinpoint里面封装了SpringAop连接点的切面方法的信息。
public interface JoinPoint {
/**
* 代理对象
*/
Object getThis();
/**
* 目标对象
*/
Object getTarget();
/**
* 目标方法参数们
*/
Object[] getArgs();
/**
* 该对象可以获取目标方法名、所属class等内容信息
*/
Signature getSignature();
在上面还看到了ProccedingJoinPoint接口,它是JoinPoint的子接口,用于@Around的切面方法中
public interface ProceedingJoinPoint extends JoinPoint {
//执行目标方法
public Object proceed() throws Throwable;
//传入的新的参数去执行目标方法
public Object proceed(Object[] args) throws Throwable;
}demo如下
@Pointcut( "execution(public void com.xiaoyuanzai.service.UserService.test())" )
public void pointCut() {
}
@Around("pointCut()")
public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjd){
Object result = null;
try {
//前置通知
System.out.println("目标方法执行前...");
//执行目标方法
//result = pjd.proeed();
//用新的参数值执行目标方法
result = pjd.proceed(new Object[]{"args"});
//返回通知
System.out.println("目标方法返回结果后...");
} catch (Throwable e) {
//异常通知
System.out.println("执行目标方法异常后...");
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//后置通知
System.out.println("目标方法执行后...");
return result;
}2.1.2. org.aopalliance.intercept.JoinPoint
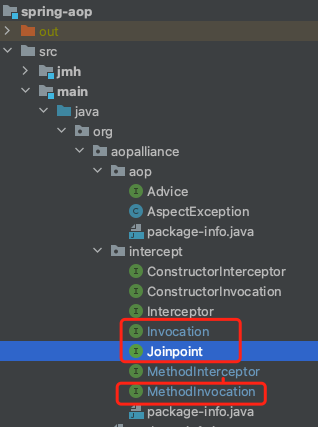
从红色圈出来的部分可知,这几个都将是下面要讲的重点,而且是org.aopalliance.intercept路径下的
package org.aopalliance.intercept;
import java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject;
public interface Joinpoint {
/**
* 执行当前拦截点(执行当前advice通知),并递归进入和执行下一个连接点(执行下一个advice通知)
* 核心方法!!!!
*/
@Nullable
Object proceed() throws Throwable;
/**
* 返回当前target模板对象
*/
@Nullable
Object getThis();
/**
* 返回此静态连接点 一般就为当前的Method(至少目前的唯一实现是MethodInvocation,所以连接点得静态部分肯定就是本方法)
*/
@Nonnull
AccessibleObject getStaticPart();
}org.aopalliance.intercept.JoinPoint是本文重点,下面讲的都是他的子接口/子类
2.2. Invocation
他是org.aopalliance.intercept.Invocation路径下的
public interface Invocation extends Joinpoint {
// 获得方法的入参
@Nonnull
Object[] getArguments();
}这里面只有一个方法,用于获取目标方法的参数
2.3. MethodInvocation
他是org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation路径下的,顾名思义,他是方法执行器,很显然跟方法相关,接口到这一层就很具象化了。
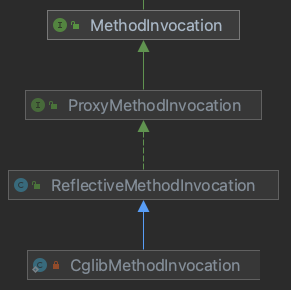
2.4. ProxyMethodInvocation
ProxyMethodInvocation是MethodInvocation的继承扩展接口,路径是org.springframework.aop.ProxyMethodInvocation
package org.springframework.aop;
/**
* 它允许访问 方法被调用的代理对象以及其它相关信息
*/
public interface ProxyMethodInvocation extends MethodInvocation {
/**
* 返回代理对象
*/
Object getProxy();
/**
* 克隆一个,使用的Object得clone方法
*/
MethodInvocation invocableClone();
MethodInvocation invocableClone(Object... arguments);
/**
* 设置参数 增强器、通知们执行的时候可能会用到
*/
void setArguments(Object... arguments);
/**
* 添加一些属性kv。这些kv并不会用于AOP框架内,而是保存下来给特殊的一些拦截器实用
*/
void setUserAttribute(String key, @Nullable Object value);
/**
* Return the value of the specified user attribute.
* @param key the name of the attribute
* @return the value of the attribute, or {@code null} if not set
* @see #setUserAttribute
*/
@Nullable
Object getUserAttribute(String key);
}2.5. ReflectiveMethodInvocation
代理对象方法被执行的时候,spring需要拦截该方法并递归执行我们定义的所有的advice通知(让所有advice通知执行起来),以及调用目标方法。而ReflectiveMethodInvocation就是干这个的,它可以理解为一个方法拦截,专门拦截方法并执行那些advice通知和目标方法。不过它处理的是jdk动态代理,如果是cglib代理的话,需要CglibMethodInvocation类,下面会讲到。
先给个demo,以便于等下理解源码
package com.xiaoyuanzai.aspect;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @Author xiaoyuanzai
* @Date 2023/6/5 22:02
* @description:
*/
public class ProxyMain {
//订单接口
public interface IOrder {
//查询功能的接口
Integer query( String type );
}
//订单服务实现类
public static class OrderService implements IOrder {
@Override
public Integer query( String type ) {
System.out.println( "查询类型为" + type + "订单数量" );
return 1;
}
}
static class MyMethodBeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
@Override
public void before( Method method, Object[] args, Object target ) throws Throwable {
if( method.getName().equals( "query" ) ) {
System.out.println( "MyMethodBeforeAdvice" );
}
}
}
static class MyAfterReturningAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice {
@Override
public void afterReturning( Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target ) throws Throwable {
if( method.getName().equals( "query" ) ) {
System.out.println( "MyAfterReturningAdvice" );
}
}
}
static class MyMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke( MethodInvocation invocation ) throws Throwable {
System.out.println( "MyMethodInterceptor" );
Object retVal = invocation.proceed();
return retVal;
}
}
public static void main( String[] args ) {
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.addAdvice( new MyMethodInterceptor() );
proxyFactory.addAdvice( new MyAfterReturningAdvice() );
proxyFactory.addAdvice( new MyMethodBeforeAdvice() );
proxyFactory.setTarget( new OrderService() );
proxyFactory.setInterfaces( OrderService.class.getInterfaces() );
IOrder proxy = ( IOrder )proxyFactory.getProxy();
proxy.query( "安踏" );
}
}
输出:
MyMethodInterceptor
MyMethodBeforeAdvice
查询类型为安踏订单数量
MyAfterReturningAdvice源码如下
public class ReflectiveMethodInvocation implements ProxyMethodInvocation, Cloneable {
// 代理对象
protected final Object proxy;
// 目标对象
@Nullable
protected final Object target;
// 目标对象被拦截的方法
protected final Method method;
protected Object[] arguments;
@Nullable
private final Class<?> targetClass;
@Nullable
private Map<String, Object> userAttributes;
/**
* List<MethodInterceptor and InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher>
*/
protected final List<?> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers;
private int currentInterceptorIndex = -1;
/**
* 创建一个方法调用对象(protected类型说明是本包和子包才能调用,Spring内部才能使用的类)
* @param proxy 代理对象
* @param target 目标对象
* @param method 执行的目标方法
* @param arguments 执行目标方法的参数
* @param targetClass 目标对象的class
* @param interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers 我们的方法拦截器 this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass)这个方法找出来的
*/
protected ReflectiveMethodInvocation(
Object proxy, @Nullable Object target, Method method, @Nullable Object[] arguments,
@Nullable Class<?> targetClass, List<Object> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers) {
this.proxy = proxy;
this.target = target;
this.targetClass = targetClass;
// 桥接方法
this.method = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
// 对参数进行适配
this.arguments = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, arguments);
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers = interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers;
}
@Override
public final Object getProxy() {
return this.proxy;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public final Object getThis() {
return this.target;
}
// 返回的就是当前得method
@Override
public final AccessibleObject getStaticPart() {
return this.method;
}
/**
* Return the method invoked on the proxied interface.
* May or may not correspond with a method invoked on an underlying
* implementation of that interface.
*/
// 这里返回的可能是桥接方法
@Override
public final Method getMethod() {
return this.method;
}
@Override
public final Object[] getArguments() {
return this.arguments;
}
@Override
public void setArguments(Object... arguments) {
this.arguments = arguments;
}
/**
* 递归调用proceed,执行所有通知
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// currentInterceptorIndex初始值为-1,如果执行到链条的末尾 则直接调用连接点方法 即 直接调用目标方法
// 当调用完了最后一个interceptor后就会执行被代理方法
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
// 调用了目标方法
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
// currentInterceptorIndex +1,且获取集合元素MethodInterceptor
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
//这里是处理动态匹配的逻辑
//把MethodInterceptor实例和MethodMatcher放在了一起。看看在advisor chain里面是否能够匹配上
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
// 动态匹配,根据方法参数匹配这个拦截器是否适用于这个目标方法
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// 递归调用
return proceed();
}
}
else {
//在这个地方需要注意,传入的this 则当前的方法拦截器对象
// 如果执行到链条的末尾 则直接调用连接点方法 即 直接调用目标方法
//非动态匹配的逻辑,执行拦截器
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
// 底层调用 method.invoke(target, args);
// 子类可以复写此方法。比如它的唯一子类CglibAopProxy内部类 CglibMethodInvocation就复写了这个方法 它对public的方法做了一个处理(public方法调用MethodProxy.invoke)
@Nullable
protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable {
// 此处传入的是target,而不能是proxy,否则进入死循环
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.target, this.method, this.arguments);
}
@Override
public MethodInvocation invocableClone() {
Object[] cloneArguments = this.arguments;
if (this.arguments.length > 0) {
// Build an independent copy of the arguments array.
cloneArguments = this.arguments.clone();
}
return invocableClone(cloneArguments);
}
@Override
public MethodInvocation invocableClone(Object... arguments) {
// Force initialization of the user attributes Map,
// for having a shared Map reference in the clone.
if (this.userAttributes == null) {
this.userAttributes = new HashMap<>();
}
// Create the MethodInvocation clone.
try {
ReflectiveMethodInvocation clone = (ReflectiveMethodInvocation) clone();
clone.arguments = arguments;
return clone;
}
catch (CloneNotSupportedException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Should be able to clone object of type [" + getClass() + "]: " + ex);
}
}
@Override
public void setUserAttribute(String key, @Nullable Object value) {
if (value != null) {
if (this.userAttributes == null) {
this.userAttributes = new HashMap<>();
}
this.userAttributes.put(key, value);
}
else {
if (this.userAttributes != null) {
this.userAttributes.remove(key);
}
}
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getUserAttribute(String key) {
return (this.userAttributes != null ? this.userAttributes.get(key) : null);
}
public Map<String, Object> getUserAttributes() {
if (this.userAttributes == null) {
this.userAttributes = new HashMap<>();
}
return this.userAttributes;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// Don't do toString on target, it may be proxied.
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("ReflectiveMethodInvocation: ");
sb.append(this.method).append("; ");
if (this.target == null) {
sb.append("target is null");
}
else {
sb.append("target is of class [").append(this.target.getClass().getName()).append(']');
}
return sb.toString();
}
}我们看一下上面三个advice通知器,proceed()递归调用顺序是什么样的
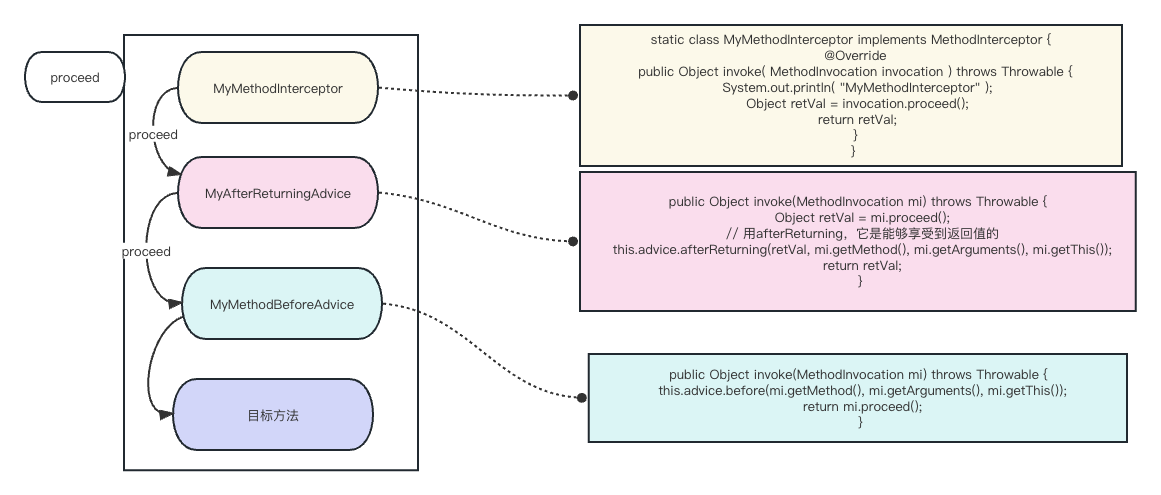
当调用ReflectiveMethodInvocation#proceed()方法时,他会调用((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this)方法,会先执行MyMethodInterceptor拦截器,他是MethodInterceptor类型。然后来到了MethodInterceptor的invoke方法。注意:invoke(this)的this是透传的,这也是递归调用的核心!
static class MyMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke( MethodInvocation invocation ) throws Throwable {
System.out.println( "MyMethodInterceptor" );
Object retVal = invocation.proceed();
return retVal;
}
}当调用到invocation.proceed()方法时,会递归回到我们上面分析的proceed()方法。如果还有拦截器的话会继续上面的流程。
同理,当调用到MyMethodBeforeAdvice的增强器时,会进入AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor#invoke()方法。当调用到mi.proceed()方法时,会回到上面proceed()方法
public class AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {
private final AfterReturningAdvice advice;
public AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor(AfterReturningAdvice advice) {
Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");
this.advice = advice;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
//递归调用
Object retVal = mi.proceed();
// 用afterReturning,它是能够享受到返回值的
//它执行的是下面MyAfterReturningAdvice#afterReturning()方法
this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
return retVal;
}
}
static class MyAfterReturningAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice {
@Override
public void afterReturning( Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target ) throws Throwable {
if( method.getName().equals( "query" ) ) {
System.out.println( "MyAfterReturningAdvice" );
}
}
}最后看一下MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor,跟上面同理
public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, BeforeAdvice, Serializable {
private final MethodBeforeAdvice advice;
public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) {
Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");
this.advice = advice;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
//调用下面的MyMethodBeforeAdvice#before()方法
this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
//递归调用
return mi.proceed();
}
}
static class MyMethodBeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
@Override
public void before( Method method, Object[] args, Object target ) throws Throwable {
if( method.getName().equals( "query" ) ) {
System.out.println( "MyMethodBeforeAdvice" );
}
}
}至此。proceed()方法的用法就讲完了。大家留意一下上面的代码,MethodInterceptor里面是包着一个Advice对象的,也就是说MethodInterceptor相当于适配器一样去适配各种Advice,然后统一提供一个invoke()方法,供递归调用
2.6. CglibMethodInvocation
/**
* 继承AOP联盟的MethodInvocation,CglibAopProxy自己使用的执行器。
*/
private static class CglibMethodInvocation extends ReflectiveMethodInvocation {
//生成 对方法的代理 的代理类。cglib用来生成代替Method对象的一个对象,使用MethodProxy比调用JDK自身的Method直接执行方法效率会有提升
// 它有两个重要的方法:invoke和invokeSuper
@Nullable
private final MethodProxy methodProxy;
public CglibMethodInvocation(Object proxy, @Nullable Object target, Method method,
Object[] arguments, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
List<Object> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers, MethodProxy methodProxy) {
// 调用父类的构造 完成参数的初始化
super(proxy, target, method, arguments, targetClass, interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers);
this.methodProxy = (Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers()) &&
method.getDeclaringClass() != Object.class && !AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method) &&
!AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method) && !AopUtils.isToStringMethod(method) ?
methodProxy : null);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
try {
// 调用父类ReflectiveMethodInvocation #proceed()
return super.proceed();
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (ReflectionUtils.declaresException(getMethod(), ex.getClass()) ||
KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(getMethod().getDeclaringClass())) {
throw ex;
}
else {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(ex);
}
}
}
@Override
protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable {
// 如果是public的方法,调用methodProxy去执行目标方法
// 否则直接执行method即可
if (this.methodProxy != null) {
// 此处务必注意的是,传入的是target,而不能是proxy,否则进入死循环
return this.methodProxy.invoke(this.target, this.arguments);
}
else {
return super.invokeJoinpoint();
}
}
}3. MethodInterceptor
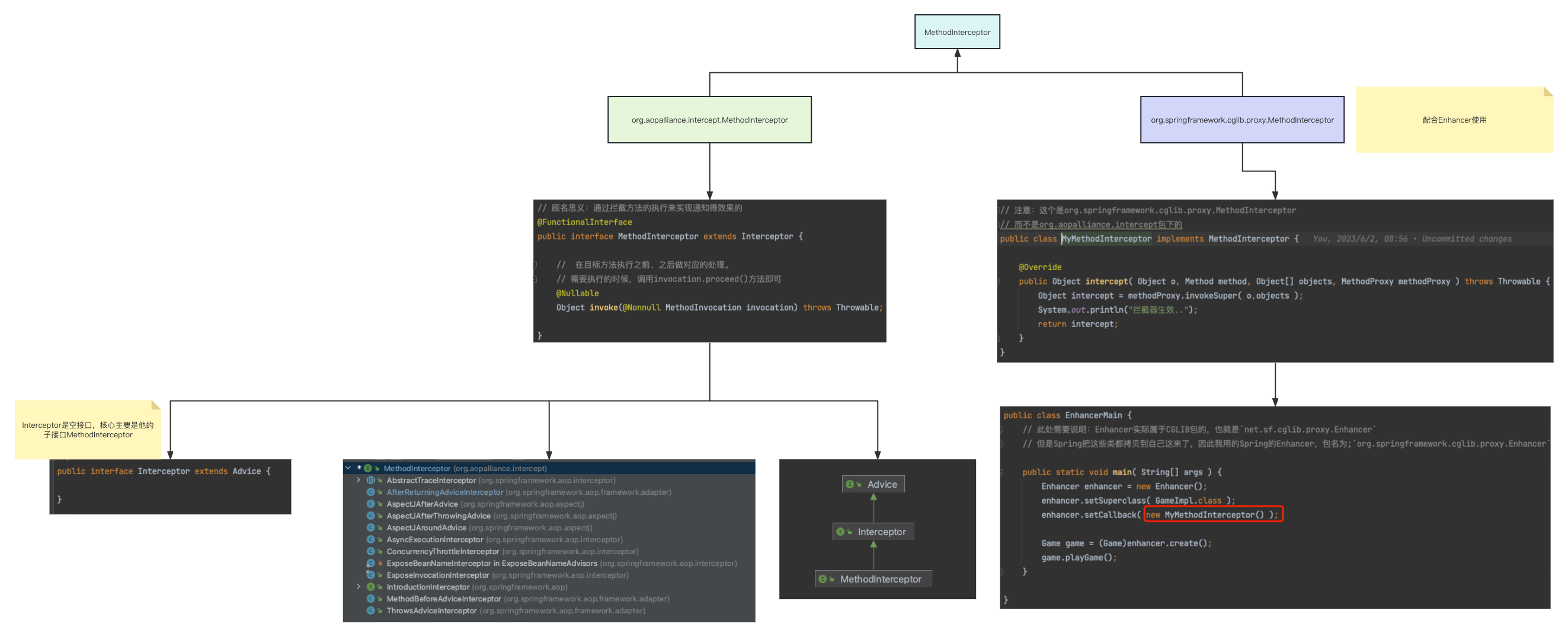
1、MethodInterceptor有两个路径,一个是存在cglib包下的org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor,一般配合Enhancer来创建动态代理对象
2、另一个就是我们今天的重点org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor,那些@AspectJ定义的通知们(增强器们),或者是自己实现的MethodBeforeAdvice、AfterReturningAdvice、ThrowsAdvice(都是继承org.aopalliance.aop.Advice),最终都会被包装成一个org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor,最终交给MethodInvocation(其子类ReflectiveMethodInvocation)去执行,它会把你所有的增强器都给执行了,这就是我们面向切面编程的核心思路过程。
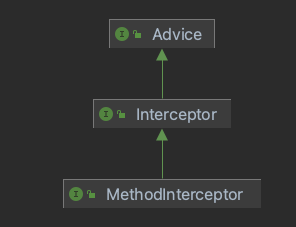
Advice:作为顶层接口,没有具体实现
Interceptor:继承于Advice接口,是中间接口,也没有具体实现
这两个接口都是标记接口
MethodInterceptor:是Interceptor的子接口
// 顾名思义:通过拦截方法的执行来实现通知得效果的
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MethodInterceptor extends Interceptor {
// 在目标方法执行之前、之后做对应的处理。
// 需要执行的时候,调用invocation.proceed()方法即可
@Nullable
Object invoke(@Nonnull MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable;
}MethodInterceptor有很多具体实现类
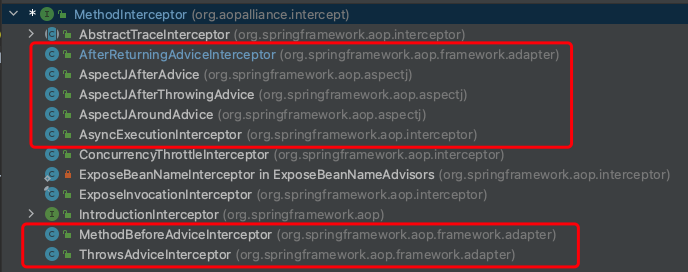
3.1. AspectJ切面相关的advice
@Aspect切面有五个注解,@Before、@After、@Around、@AfterReturning、@AfterThrowing,每个注解最终都会分别被包装成下面的Advice类
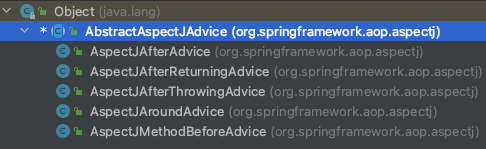
3.1.1. AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice
public class AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice, Serializable {
/**
*
* @param aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod @Before所注解的Method对象
* @param pointcut @Before所对应的Pointcut,表示当前Advice所对应的切点
* @param aif
*/
public AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
Method aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut, AspectInstanceFactory aif) {
super(aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, pointcut, aif);
}
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, @Nullable Object target) throws Throwable {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);
}
@Override
public boolean isBeforeAdvice() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAfterAdvice() {
return false;
}
}3.1.2. AspectJAfterAdvice
public class AspectJAfterAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice
implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {
public AspectJAfterAdvice(
Method aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut, AspectInstanceFactory aif) {
super(aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, pointcut, aif);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);
}
}
@Override
public boolean isBeforeAdvice() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isAfterAdvice() {
return true;
}
}3.1.3. AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice
public class AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice
implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {
public AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
Method aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut, AspectInstanceFactory aif) {
super(aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, pointcut, aif);
}
@Override
public boolean isBeforeAdvice() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isAfterAdvice() {
return true;
}
@Override
public void setThrowingName(String name) {
setThrowingNameNoCheck(name);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (shouldInvokeOnThrowing(ex)) {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
/**
* In AspectJ semantics, after throwing advice that specifies a throwing clause
* is only invoked if the thrown exception is a subtype of the given throwing type.
*/
private boolean shouldInvokeOnThrowing(Throwable ex) {
return getDiscoveredThrowingType().isAssignableFrom(ex.getClass());
}
}3.1.4. AspectJAroundAdvice
public class AspectJAroundAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
public AspectJAroundAdvice(
Method aspectJAroundAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut, AspectInstanceFactory aif) {
super(aspectJAroundAdviceMethod, pointcut, aif);
}
@Override
public boolean isBeforeAdvice() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isAfterAdvice() {
return false;
}
@Override
protected boolean supportsProceedingJoinPoint() {
return true;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
if (!(mi instanceof ProxyMethodInvocation)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MethodInvocation is not a Spring ProxyMethodInvocation: " + mi);
}
ProxyMethodInvocation pmi = (ProxyMethodInvocation) mi;
ProceedingJoinPoint pjp = lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(pmi);
JoinPointMatch jpm = getJoinPointMatch(pmi);
return invokeAdviceMethod(pjp, jpm, null, null);
}
protected ProceedingJoinPoint lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(ProxyMethodInvocation rmi) {
return new MethodInvocationProceedingJoinPoint(rmi);
}
}3.1.5. AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice
public class AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice
implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {
public AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
Method aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut, AspectInstanceFactory aif) {
super(aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, pointcut, aif);
}
@Override
public boolean isBeforeAdvice() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isAfterAdvice() {
return true;
}
@Override
public void setThrowingName(String name) {
setThrowingNameNoCheck(name);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (shouldInvokeOnThrowing(ex)) {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
/**
* In AspectJ semantics, after throwing advice that specifies a throwing clause
* is only invoked if the thrown exception is a subtype of the given throwing type.
*/
private boolean shouldInvokeOnThrowing(Throwable ex) {
return getDiscoveredThrowingType().isAssignableFrom(ex.getClass());
}
}3.2. DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry
在DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry 适配器中,支持三种适配器,分别是MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter,AfterReturningAdviceAdapter,ThrowsAdviceAdapter,这些适配器是把advice适配成MethodInterceptor,所以我们得分别看下这些MethodInterceptor
public class DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry implements AdvisorAdapterRegistry, Serializable {
//通知器适配器集合
private final List<AdvisorAdapter> adapters = new ArrayList<>(3);
/**
* 默认就支持这几种类型的适配器
*/
public DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry() {
registerAdvisorAdapter(new MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter());
registerAdvisorAdapter(new AfterReturningAdviceAdapter());
registerAdvisorAdapter(new ThrowsAdviceAdapter());
}
// 将通知advice封装为通知器advisor
@Override
public Advisor wrap(Object adviceObject) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
if (adviceObject instanceof Advisor) {
return (Advisor) adviceObject;
}
if (!(adviceObject instanceof Advice)) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(adviceObject);
}
Advice advice = (Advice) adviceObject;
// 如果是MethodInterceptor类型,就根本不用适配器。DefaultPointcutAdvisor是天生处理这种有连接点得通知器的
if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {
// So well-known it doesn't even need an adapter.
return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(advice);
}
// 这一步很显然了,就是校验看看这个advice是否是我们支持的这些类型(系统默认给出,但是我们也可以自己往里添加注册的)
for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) {
// Check that it is supported.
if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {
// 如果是支持的,也是被包装成了一个通用类型的DefaultPointcutAdvisor
return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(advice);
}
}
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advice);
}
// 获得通知器advisor的通知器MethodInterceptor
@Override
public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>(3);
Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();
//当类型为MethodInterceptor,会直接放入interceptors中返回
if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {
interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice);
}
// 将Advice适配成MethodInterceptor
for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) {
if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {
// 这一步需要注意:一定要把从适配器中拿到MethodInterceptor类型的通知器
interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));
}
}
if (interceptors.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice());
}
return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[0]);
}
//注册 通知适配器(AdvisorAdapter)
@Override
public void registerAdvisorAdapter(AdvisorAdapter adapter) {
this.adapters.add(adapter);
}
}3.2.1. MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, BeforeAdvice, Serializable {
private final MethodBeforeAdvice advice;
/**
* Create a new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor for the given advice.
* @param advice the MethodBeforeAdvice to wrap
*/
public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) {
Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");
this.advice = advice;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
return mi.proceed();
}
}3.2.2. AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor
public class AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {
private final AfterReturningAdvice advice;
/**
* Create a new AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor for the given advice.
* @param advice the AfterReturningAdvice to wrap
*/
public AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor(AfterReturningAdvice advice) {
Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");
this.advice = advice;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
Object retVal = mi.proceed();
// 用afterReturning,它是能够享受到返回值的
this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
return retVal;
}
}
3.2.3. ThrowsAdviceInterceptor
包装的ThrowsAdvice,比较复杂,不做展示
4. 总结
看截图可知,aioalliance全都是接口,负责定义一些规范标准
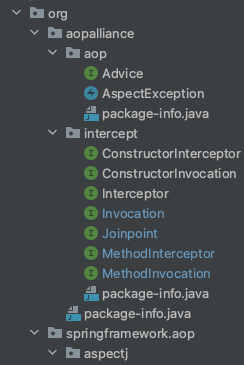
org.aoplliance.aop包
- Advice:通知的标记接口,也是顶层接口
- AspectException:所有AOP框架异常的父类,是个RuntimeException
org.aoplliance.intercept包
- Interceptor:继承Advice,通过拦截器的方式实现通知效果(标记接口,空实现)
- MethodInterceptor:具体接口,拦截方法(很多具体实现类)
- ConstructorInterceptor:具体接口。拦截构造器 (Spring并没有提供实现类)
- Joinpoint:AOP运行时连接点(顶层接口)
- invocation:继承于Joinpoint,提供了Object[] getArguments()来获取执行所需的参数
- MethodInvocation:(和MethodInterceptor对应,它的invoke方法入参就是它)表示一个和方法有关的执行器。提供方法Method getMethod()
- ConstructorInvocation:和构造器有关。Constructor<?> getConstructor(); (Spring没有提供任何实现类)
在当前注解驱动的流行下,基于POJO(xml方式)以及编程的方式去书写AOP代理,显得非常的繁琐。因此Spring提供了另外一种实现:基于AspectJ,到这才使用到了AspectJ的相关注解、以及类。不过哪怕使用到了AspectJ的相关注解和类,但核心的AOP织入的逻辑,还都是Spring自己用动态代理去实现的,没用AspectJ它那种特殊的语法和特有的编译器。
最后说一句,若在Spring AOP中想使用AspectJ的方式去实现(也是当下最流行的方式),必须导入Jar包:aspectjweaver-1.9.5.jar,这个包里面有@Before等注解可以被使用,而Spring的这个包org.springframework.aop.aspectj下面的所有类,都是专门为了使用@Aspect的方式去服务的,毕竟AOP功能是Spring自己实现的,而不是依赖于AspectJ这个组件的
aspectjweaver-1.9.5.jar如下:有各种注解
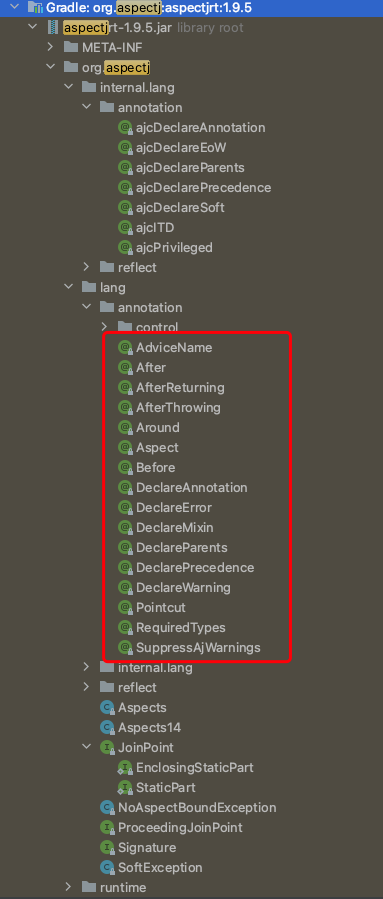
为上面注解提供服务的是org.springframework.aop.aspectj包下的类

























 8545
8545











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










