〇、常见示例
[root@VM_16_37_centos ~]# groupadd log # 添加组log
[root@VM_16_37_centos ~]# useradd -m -g "log" -s "/bin/bash" "wuweixiang" # 添加用户wuweixiang
[root@VM_16_37_centos ~]# passwd wuweixiang # 设置用户密码
Changing password for user wuweixiang.
New password:
BAD PASSWORD: The password fails the dictionary check - it is too simplistic/systematic
Retype new password:
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
# useradd -m -g "初始组" -G "附加组" -s "登陆shell" "用户"
[root@VM_16_37_centos tomcat]# useradd --help
Usage: useradd [options] LOGIN
useradd -D
useradd -D [options]
Options:
-b, --base-dir BASE_DIR base directory for the home directory of the new account
-c, --comment COMMENT GECOS field of the new account
-d, --home-dir HOME_DIR home directory of the new account
-D, --defaults print or change default useradd configuration
-e, --expiredate EXPIRE_DATE expiration date of the new account
-f, --inactive INACTIVE password inactivity period of the new account
-g, --gid GROUP name or ID of the primary group of the new account
-G, --groups GROUPS list of supplementary groups of the new account
-h, --help display this help message and exit
-k, --skel SKEL_DIR use this alternative skeleton directory
-K, --key KEY=VALUE override /etc/login.defs defaults
-l, --no-log-init do not add the user to the lastlog and faillog databases
-m, --create-home create the user's home directory
-M, --no-create-home do not create the user's home directory
-N, --no-user-group do not create a group with the same name as the user
-o, --non-unique allow to create users with duplicate (non-unique) UID
-p, --password PASSWORD encrypted password of the new account
-r, --system create a system account
-R, --root CHROOT_DIR directory to chroot into
-s, --shell SHELL login shell of the new account # 默认是 Bash
-u, --uid UID user ID of the new account
-U, --user-group create a group with the same name as the user
-Z, --selinux-user SEUSER use a specific SEUSER for the SELinux user mapping
su
直接切换为超级用户
sudo
直接使用 sudo 命令前缀执行系统管理命令。执行系统管理命令时无需知道超级用户的口令,使用普通用户自己的口令即可
# 给普通用户加sudo权限
[root@VM_16_37_centos logs]# cd ~
[root@VM_16_37_centos ~]# pwd
/root
[root@VM_16_37_centos ~]# visudo
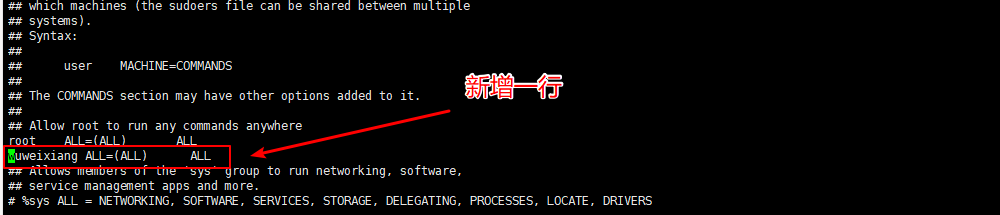
[root@VM_16_37_centos ~]# groups wuweixiang
wuweixiang : log
[root@VM_16_37_centos ~]# id wuweixiang
uid=1000(wuweixiang) gid=1000(log) groups=1000(log)
[root@VM_16_37_centos ~]# w
10:17:14 up 1 day, 35 min, 2 users, load average: 0.02, 0.02, 0.05
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
root pts/0 118.25.55.134 09:21 53:54 0.02s 0.02s -bash
root pts/1 27.154.26.173 Mon18 2.00s 0.06s 0.06s -bash
一 、组操作
1,创建组
groupadd test
增加一个test组
2,修改组
groupmod -n test2 test
将test组的名子改成test2
3,删除组
groupdel test2
删除 组test2
4,查看组
a),查看当前登录用户所在的组 groups,查看apacheuser所在组groups apacheuser
b),查看所有组cat /etc/group
c),有的linux系统没有/etc/group文件的,这个时候看下面的这个方法
cat /etc/passwd |awk -F [:] '{print $4}' |sort|uniq | getent group |awk -F [:] '{print $1}'
这里用到一个命令是getent,可以通过组ID来查找组信息,如果这个命令没有的话,那就很难查找,系统中所有的组了.
二、用户操作
1,增加用户
useradd test
passwd test
增加用户test,有一点要注意的,useradd增加一个用户后,不要忘了给他设置密码,不然不能登录的。
2,修改用户
usermod -d /home/test -G test2 test
将test用户的登录目录改成/home/test,并加入test2组,注意这里是大G。
gpasswd -a test test2将用户test加入到test2组
gpasswd -d test test2 将用户test从test2组中移出
3,删除用户
userdel test
将test用户删除
4,查看用户
a),查看当前登录用户
[root@krlcgcms01 ~]#w
[root@krlcgcms01 ~]# who
b),查看自己的用户名
[root@krlcgcms01 ~]# whoami
c),查看单个用户信息
[root@krlcgcms01 ~]# finger apacheuser
[root@krlcgcms01 ~]#id apacheuser
d),查看用户登录记录
[root@krlcgcms01 ~]# last查看登录成功的用户记录
[root@krlcgcms01 ~]#lastb查看登录不成功的用户记录
e),查看所有用户
[root@krlcgcms01 ~]# cut -d : -f 1 /etc/passwd
[root@krlcgcms01 ~]# cat /etc/passwd |awk -F \: '{print $1}'
文件
作用
/etc/shadow
保存用户安全信息
/etc/passwd
用户账户信息
/etc/gshadow
保存组账号的安全信息
/etc/group
定义用户所属的组
/etc/sudoers
可以运行 sudo 的用户
/home/*
主目录
用户组
组
影响文件
作用
adm
类似 wheel 的管理器群组.
ftp
/srv/ftp/
访问 FTP 服务器.
games
/var/games
访问一些游戏。
log
访问 syslog-ng 创建的 /var/log/ 日志文件.
http
/srv/http/
访问 HTTP 服务器文件.
rfkill
不再使用! 控制无线设备的电源 (被 rfkill 使用).
sys
Right to administer printers in CUPS.
systemd-journal
/var/log/journal/*
以只读方式访问系统日志,和 adm 和 wheel 不同 [1]. 不在此组中的用户仅能访问自己生成的信息。
users
标准用户组.
uucp
/dev/ttyS[0-9]+, /dev/tts/[0-9]+, /dev/ttyUSB[0-9]+, /dev/ttyACM[0-9]+
串口和 USB 设备,例如猫、手柄 RS-232/串口。
wheel
管理组,通常用于 sudo 和 su 命令权限。systemd 会允许非 root 的 wheel 组用户启动服务。[2]





















 192
192











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








