1、首先我在Mysql中准备了一条数据
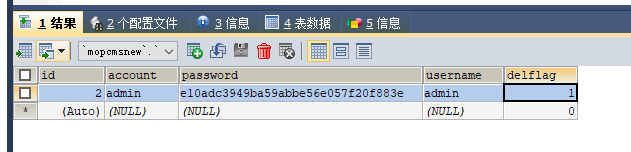
2、简单粗暴的开始测试了
1、我们的目的是需要把delflag修改为0 简单的准备一下sql
<update id="test">
UPDATE tbl_users set delflag='0' where account='admin'
</update>2、我们先来测试一下@Transactional 代码如下 大家都知道2/0必会抛出异常
@Override
@Transactional
public Ret test(){
int i = articleMapper.test();
int a = 2/0;
if(i > 0){
ResultUtil.success();
}
return ResultUtil.error();
}3、执行测试 i=1说明更新成功 别着急咱们继续断点往下面走

4、果然不出所料 执行到第54行的时候报错了 出现了java.lang.ArithmeticException: /by zero

5、细心的同学会发现ArithmeticException这个异常类是继承了RuntimeException的
而@Transactional默认回滚的的异常就是RuntimeException

6、我们在点进去RuntimeException这个类里面一探究竟 我们发现RuntimeException又是继承Exception的
而所有的异常类基本都是继承RuntimeException包括刚才上面的java.lang.ArithmeticException异常
所以只要是RuntimeException和RuntimeException下面的子类抛出的异常 @Transactional都可以回滚的

7、这个时候我们去看一下数据库的值到底有没有修改成功 很显然数据是被回滚了 并没有修改成0

1、下面我们在试试@Transactional不能过滚的异常 代码如下
我们直接先用try catch来捕获异常 然后在catch里面自定义抛出Exception异常
@Override
@Transactional
public Ret test() throws Exception {
int i = articleMapper.test();
try {
int a = 2 / 0;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Exception();
}
if (i > 0) {
ResultUtil.success();
}
return ResultUtil.error();
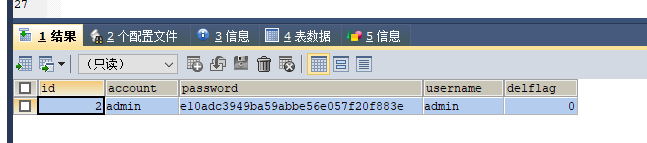
}2、ok直接 抛出的异常是我们指定的java.lang.Exception异常 我们去看看数据库

3、数据库被更新成0了 说明@Transactional并不能回滚Exception异常
总结一下:@Transactional只能回滚RuntimeException和RuntimeException下面的子类抛出的异常 不能回滚Exception异常
如果需要支持回滚Exception异常请用@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
这里如果是增删改的时候我建议大家都使用@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
补充一下@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)一些失效的场景
1、不是用public修饰
2、try catch捕获了异常(没有在catch里面手动抛出异常)
3、没有加@Service(也就是没有被 Spring 管理)
具体的补充可以看一下这位博主






















 211
211











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








