第一题 Leetcode 395
Loading...leetcode.com
Find the length of the longest substring T of a given string (consists of lowercase letters only) such that every character in T appears no less than k times.
Example 1:
Input:
s = "aaabb", k = 3
Output:
3
The longest substring is "aaa", as 'a' is repeated 3 times.
暴力解法应该是
讨论区有这样一种解法,把复杂度降到了

思路是这样的。对于整个string来说,如果有字母的出现次数小于K,那么这个字母不可能被包含在答案里面。于是我们可以用这些不达标的字母作为分割,把整个string分割成若干截,每一截都有可能包含正确答案,但是不一定。
为什么说有可能呢,因为本来符合出现次数要求的字母,可能被分割到了不止一段小截中,每一截中出现的次数又不够K了。比如aba, K=2这个例子,b一开始出现的次数不足2,所以用来做分割,我们只考虑a和a(左右两个子字符串)。但是这时候每一个小截中包含的a的个数也不足2了。
所以对于分割开来的每一个小截,我们都可以当成一个新的问题,然后递归来处理。代码实现如下:
int longestSubstring(string s, int k) {
return longestSubstring_recur(s, k, 0, s.size());
}
int longestSubstring_recur(const string& s, int k, int first, int last) {
int count[26] = {0};
for (int j = first; j < last; ++j) ++count[s[j] - 'a'];
int max_len = 0;
for (int j = first; j < last;) {
while (j < last && count[s[j]-'a']<k) ++j;
if (j == last) break;
int l = j;
while (l < last && count[s[l]-'a']>=k) ++l;
//all chars appear more than k times
if (j == first && l == last) return last-first;
max_len = max(max_len, longestSubstring_recur(s, k, j, l));
j = l;
}
return max_len;
}
有意思的部分来了。作者说复杂度是O(N)因为递归的层数最多是26层。这个结论乍一看有点懵,于是我又看了看底下的讨论,发现是这样的。我们已经看到每一次递归,我们都会把不符合要求(出现次数小于K)的字母给去掉,因此最多只有26个字母可以去,一个字母没有机会被去除两次。(比如在某一次递归中字母a出现的次数小于K,那么它在recursion tree中的所有children中都不会出现字母a了。)每一层递归所做的工作的总和又是线性的,所以总体的实现复杂度也是线性的。
第二题 Leetcode 749
Loading...leetcode.com
A virus is spreading rapidly, and your task is to quarantine the infected area by installing walls.
The world is modeled as a 2-D array of cells, where 0 represents uninfected cells, and 1 represents cells contaminated with the virus. A wall (and only one wall) can be installed between any two 4-directionally adjacent cells, on the shared boundary.
Every night, the virus spreads to all neighboring cells in all four directions unless blocked by a wall. Resources are limited. Each day, you can install walls around only one region -- the affected area (continuous block of infected cells) that threatens the most uninfected cells the following night. There will never be a tie.
Can you save the day? If so, what is the number of walls required? If not, and the world becomes fully infected, return the number of walls used.
Example 1:
Input: grid =
[[0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1],
[0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]]
Output: 10
Explanation:
There are 2 contaminated regions.
On the first day, add 5 walls to quarantine the viral region on the left. The board after the virus spreads is:
[[0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1],
[0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1]]
On the second day, add 5 walls to quarantine the viral region on the right. The virus is fully contained.直接放官网的solution:
Approach #1: Simulation [Accepted]
Intuition
Let's work on simulating one turn of the process. We can repeat this as necessary while there are still infected regions.
Algorithm
Though the implementation is long, the algorithm is straightforward. We perform the following steps:
- Find all viral regions (connected components), additionally for each region keeping track of the frontier (neighboring uncontaminated cells), and the perimeter of the region.
- Disinfect the most viral region, adding it's perimeter to the answer.
- Spread the virus in the remaining regions outward by 1 square.
class Solution {
Set<Integer> seen;
List<Set<Integer>> regions;
List<Set<Integer>> frontiers;
List<Integer> perimeters;
int[][] grid;
int R, C;
int[] dr = new int[]{-1, 1, 0, 0};
int[] dc = new int[]{0, 0, -1, 1};
public int containVirus(int[][] grid) {
this.grid = grid;
R = grid.length;
C = grid[0].length;
int ans = 0;
while (true) {
seen = new HashSet();
regions = new ArrayList();
frontiers = new ArrayList();
perimeters = new ArrayList();
for (int r = 0; r < R; ++r) {
for (int c = 0; c < C; ++c) {
if (grid[r][c] == 1 && !seen.contains(r*C + c)) {
regions.add(new HashSet());
frontiers.add(new HashSet());
perimeters.add(0);
dfs(r, c);
}
}
}
if (regions.isEmpty()) break;
int triageIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < frontiers.size(); ++i) {
if (frontiers.get(triageIndex).size() < frontiers.get(i).size())
triageIndex = i;
}
ans += perimeters.get(triageIndex);
for (int i = 0; i < regions.size(); ++i) {
if (i == triageIndex) {
for (int code: regions.get(i))
grid[code / C][code % C] = -1;
} else {
for (int code: regions.get(i)) {
int r = code / C, c = code % C;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int nr = r + dr[k], nc = c + dc[k];
if (nr >= 0 && nr < R && nc >= 0 && nc < C && grid[nr][nc] == 0)
grid[nr][nc] = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
public void dfs(int r, int c) {
if (!seen.contains(r*C + c)) {
seen.add(r*C + c);
int N = regions.size()
regions.get(N - 1).add(r*C + c);
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int nr = r + dr[k], nc = c + dc[k];
if (nr >= 0 && nr < R && nc >= 0 && nc < C) {
if (grid[nr][nc] == 1) {
dfs(nr, nc);
} else if (grid[nr][nc] == 0){
frontiers.get(N - 1).add(nr*C + nc);
perimeters.set(N - 1, perimeters.get(N - 1) + 1);
}
}
}
}
}
}讲解还是比较清楚的,就是一般的simulation步骤。我一开始想keep track of所有的受感染的region,然后每次更新受感染的region,而不是遍历整个board。后来发现并不可行,因为在更新的过程中,多个受感染的region有可能会融合成一个新的更大的region,这一部分很难追踪。
比较有意思的是答案里的时间复杂度:
Time Complexity:
首先我们知道,每一次iteration中,我们都要遍历整个board,因此每个iteration都是
假设我们没有进行任何的quarantine,每一个受感染的区域面积随时间t的变化为
因此总感染面积随时间t的变化为立方关系(最高次幂为3).当总感染面积达到了整个board的大小的时候,也就是iteration停止的时间。
在给 @Chao Xu review了我的思路之后,他指出平方增长并不严谨。然后给了我这一样一个图。
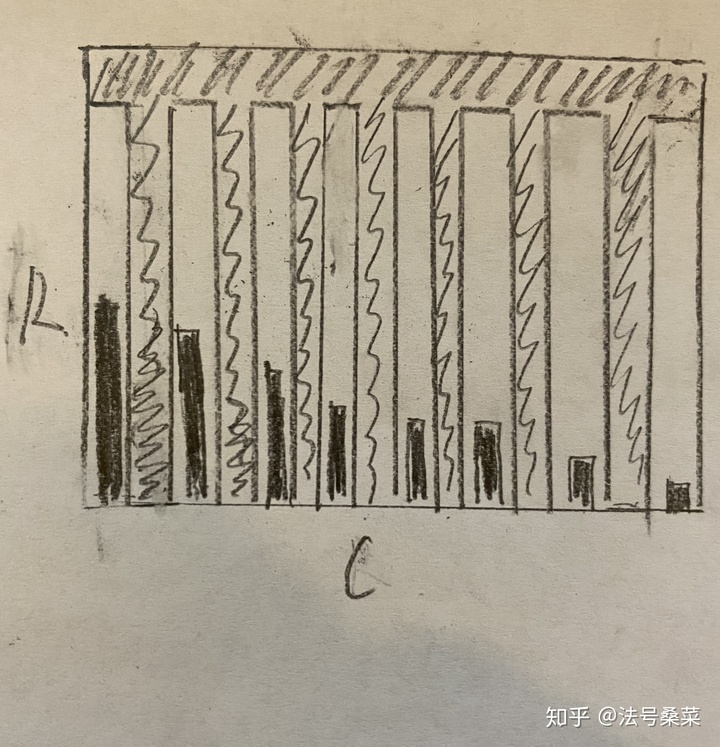
图中阴影和纯黑都为病毒。阴影的是一个非常大的像梳子状的病毒区域。第一次时间一定会把阴影部分的区域给隔离起来(因为是是危害最大的)。从此之后,纯黑部分的病毒区域增长为线性,也就是需要





















 1200
1200











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








