852. Peak Index in a Mountain Array(e-201)
Let's call an array A a mountain if the following properties hold:
A.length >= 3- There exists some
0 < i < A.length - 1such thatA[0] < A[1] < ... A[i-1] < A[i] > A[i+1] > ... > A[A.length - 1]
Given an array that is definitely a mountain, return any i such that A[0] < A[1] < ... A[i-1] < A[i] > A[i+1] > ... > A[A.length - 1].
class Solution(object):
def peakIndexInMountainArray(self, A):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
a=max(A)
for i in range(len(A)):
if A[i]==a:
return i859. Buddy Strings(e-202)
Given two strings A and B of lowercase letters, return true if and only if we can swap two letters in A so that the result equals B.
class Solution:
def buddyStrings(self, A, B):
"""
:type A: str
:type B: str
:rtype: bool
"""
if len(A) != len(B):
return False
diff = 0
idxs = []
for i, a in enumerate(A):
if B[i] != a:
diff += 1
idxs.append(i)
counter = dict()
if diff == 0:
for a in A:
if a in counter and counter[a]:
return True
else:
counter[a] = True
if diff != 2:
return False
return A[idxs[0]] == B[idxs[1]] and A[idxs[1]] == B[idxs[0]]
860. Lemonade Change(e-203)
At a lemonade stand, each lemonade costs $5.
Customers are standing in a queue to buy from you, and order one at a time (in the order specified by bills).
Each customer will only buy one lemonade and pay with either a $5, $10, or $20 bill. You must provide the correct change to each customer, so that the net transaction is that the customer pays $5.
Note that you don't have any change in hand at first.
Return true if and only if you can provide every customer with correct change.
class Solution(object):
def lemonadeChange(self, bills):
"""
:type bills: List[int]
:rtype: bool
"""
changes={5:0, 10:0}
for bill in bills:
if bill==5:
changes[5]+=1
elif bill==10:
if changes[5]==0:
return False
else:
changes[10]+=1
changes[5]-=1
elif bill==20:
if changes[10]!=0:
if changes[5]==0:
return False
else:
changes[10]-=1
changes[5]-=1
else:
if changes[5]<3:
return False
else:
changes[5]-=3
return True867. Transpose Matrix(e-204)
Given a matrix A, return the transpose of A.
The transpose of a matrix is the matrix flipped over it's main diagonal, switching the row and column indices of the matrix.
class Solution(object):
def transpose(self, A):
"""
:type A: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
rows=len(A)
cols=len(A[0])
res=[[0]*rows for _ in range(cols)]
for row in range(rows):
for col in range(cols):
res[col][row]=A[row][col]
return res868. Binary Gap(e-205)
Given a positive integer N, find and return the longest distance between two consecutive 1's in the binary representation of N.
If there aren't two consecutive 1's, return 0.
class Solution(object):
def binaryGap(self, N):
"""
:type N: int
:rtype: int
"""
binary=bin(N)[2:]
dist=[0]*len(binary)
left=0
for i, b in enumerate(binary):
if b=='1':
dist[i]=i-left
left=i
return max(dist)872. Leaf-Similar Trees(e-206)-----------------
Consider all the leaves of a binary tree. From left to right order, the values of those leaves form a leaf value sequence.
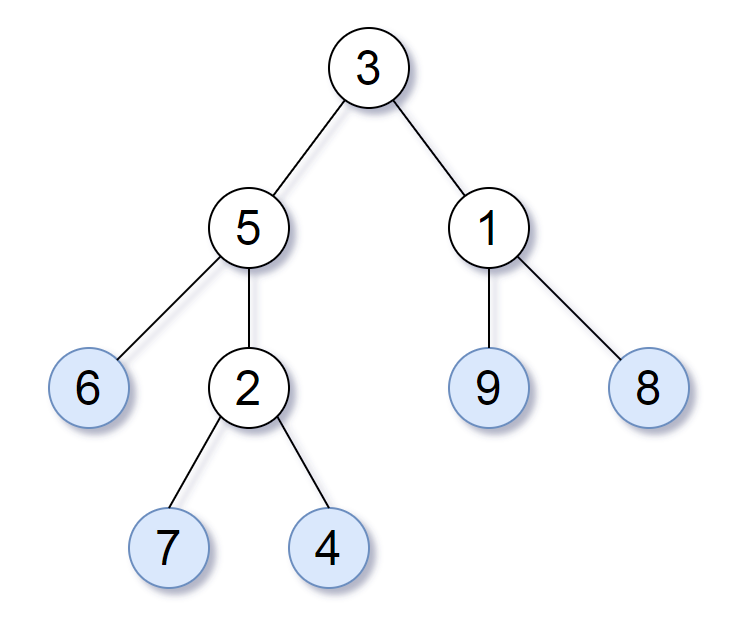
For example, in the given tree above, the leaf value sequence is (6, 7, 4, 9, 8).
Two binary trees are considered leaf-similar if their leaf value sequence is the same.
Return true if and only if the two given trees with head nodes root1 and root2 are leaf-similar.
874. Walking Robot Simulation(e-207)-------------------
A robot on an infinite grid starts at point (0, 0) and faces north. The robot can receive one of three possible types of commands:
-2: turn left 90 degrees-1: turn right 90 degrees1 <= x <= 9: move forwardxunits
Some of the grid squares are obstacles.
The i-th obstacle is at grid point (obstacles[i][0], obstacles[i][1])
If the robot would try to move onto them, the robot stays on the previous grid square instead (but still continues following the rest of the route.)
Return the square of the maximum Euclidean distance that the robot will be from the origin.
884. Uncommon Words from Two Sentences(e-208)
We are given two sentences A and B. (A sentence is a string of space separated words. Each word consists only of lowercase letters.)
A word is uncommon if it appears exactly once in one of the sentences, and does not appear in the other sentence.
Return a list of all uncommon words.
You may return the list in any order.
class Solution:
def uncommonFromSentences(self, A, B):
"""
:type A: str
:type B: str
:rtype: List[str]
"""
count_A = collections.Counter(A.split(' '))
count_B = collections.Counter(B.split(' '))
words=list((count_A.keys() | count_B.keys()) - (count_A.keys() & count_B.keys()))
ans = []
for word in words:
if count_A[word] == 1 or count_B[word] == 1:
ans.append(word)
return ans
888. Fair Candy Swap(e-209)
Alice and Bob have candy bars of different sizes: A[i] is the size of the i-th bar of candy that Alice has, and B[j] is the size of the j-th bar of candy that Bob has.
Since they are friends, they would like to exchange one candy bar each so that after the exchange, they both have the same total amount of candy. (The total amount of candy a person has is the sum of the sizes of candy bars they have.)
Return an integer array ans where ans[0] is the size of the candy bar that Alice must exchange, and ans[1] is the size of the candy bar that Bob must exchange.
If there are multiple answers, you may return any one of them. It is guaranteed an answer exists.
class Solution(object):
def fairCandySwap(self, A, B):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:type B: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
sum_A, sum_B, set_B=sum(A), sum(B), set(B)
target=(sum_A+sum_B)/2
for a in A:
b=target-sum_A+a
if b>=1 and b<=100000 and b in set_B:
return [a,b]
892. Surface Area of 3D Shapes(e-210)
On a N * N grid, we place some 1 * 1 * 1 cubes.
Each value v = grid[i][j] represents a tower of v cubes placed on top of grid cell (i, j).
Return the total surface area of the resulting shapes.
class Solution(object):
def surfaceArea(self, grid):
"""
:type grid: List[List[int]]
:rtype: int
"""
area = 0
n = len(grid)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j]: area += grid[i][j] * 4 + 2
if i: area -= min(grid[i][j], grid[i-1][j]) * 2
if j: area -= min(grid[i][j], grid[i][j-1]) * 2
return area
893. Groups of Special-Equivalent Strings(e-211)
You are given an array A of strings.
Two strings S and T are special-equivalent if after any number of moves, S == T.
A move consists of choosing two indices i and j with i % 2 == j % 2, and swapping S[i] with S[j].
Now, a group of special-equivalent strings from A is a non-empty subset S of A such that any string not in S is not special-equivalent with any string in S.
Return the number of groups of special-equivalent strings from A.
class Solution(object):
def numSpecialEquivGroups(self, A):
"""
:type A: List[str]
:rtype: int
"""
B=set()
for a in A:
B.add(''.join(sorted(a[0::2]))+''.join(sorted(a[1::2])))
return len(B)
896. Monotonic Array(e-212)
An array is monotonic if it is either monotone increasing or monotone decreasing.
An array A is monotone increasing if for all i <= j, A[i] <= A[j]. An array A is monotone decreasing if for all i <= j, A[i] >= A[j].
Return true if and only if the given array A is monotonic.
class Solution(object):
def isMonotonic(self, A):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:rtype: bool
"""
B=sorted(A)
C=B[::-1]
if A==B or A==C:
return True
else:
return False897. Increasing Order Search Tree(e-213)-----------------
Given a tree, rearrange the tree in in-order so that the leftmost node in the tree is now the root of the tree, and every node has no left child and only 1 right child.
905. Sort Array By Parity(e-214)
Given an array A of non-negative integers, return an array consisting of all the even elements of A, followed by all the odd elements of A.
You may return any answer array that satisfies this condition.
class Solution(object):
def sortArrayByParity(self, A):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
return sorted(A, key=lambda x: x%2)908. Smallest Range I(e-215)
Given an array A of integers, for each integer A[i] we may choose any x with -K <= x <= K, and add x to A[i].
After this process, we have some array B.
Return the smallest possible difference between the maximum value of B and the minimum value of B.
class Solution(object):
def smallestRangeI(self, A, K):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:type K: int
:rtype: int
"""
return max(max(A)-min(A)-2*K, 0)914. X of a Kind in a Deck of Cards(e-216)
In a deck of cards, each card has an integer written on it.
Return true if and only if you can choose X >= 2 such that it is possible to split the entire deck into 1 or more groups of cards, where:
- Each group has exactly
Xcards. - All the cards in each group have the same integer.
class Solution(object):
def hasGroupsSizeX(self, deck):
"""
:type deck: List[int]
:rtype: bool
"""
count=collections.Counter(deck)
X=min(count.values())
for x in range(2, X+1):
if all(v%x==0 for v in count.values()):
return True
return False917. Reverse Only Letters(e-217)
Given a string S, return the "reversed" string where all characters that are not a letter stay in the same place, and all letters reverse their positions.
class Solution(object):
def reverseOnlyLetters(self, S):
"""
:type S: str
:rtype: str
"""
letters=[]
for i, s in enumerate(S):
if s.isalpha():
letters.append(s)
res=""
for i, s in enumerate(S):
if s.isalpha():
res+=letters.pop()
else:
res+=s
return res922. Sort Array By Parity II(e-218)
Given an array A of non-negative integers, half of the integers in A are odd, and half of the integers are even.
Sort the array so that whenever A[i] is odd, i is odd; and whenever A[i] is even, i is even.
You may return any answer array that satisfies this condition.
class Solution(object):
def sortArrayByParityII(self, A):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
odd=[x for x in A if x%2==0]
even=[x for x in A if x%2==1]
res=[]
isnum=True
while odd or even:
if isnum:
res.append(odd.pop())
else:
res.append(even.pop())
isnum=not isnum
return res925. Long Pressed Name(e-219)
Your friend is typing his name into a keyboard. Sometimes, when typing a character c, the key might get long pressed, and the character will be typed 1 or more times.
You examine the typed characters of the keyboard. Return True if it is possible that it was your friends name, with some characters (possibly none) being long pressed.
class Solution(object):
def isLongPressedName(self, name, typed):
"""
:type name: str
:type typed: str
:rtype: bool
"""
M = len(name)
N = len(typed)
i, j = 0, 0
while i < M:
c_i = name[i]
count_i = 0
count_j = 0
while i < M and name[i] == c_i:
i += 1
count_i += 1
while j < N and typed[j] == c_i:
j += 1
count_j += 1
if count_j < count_i:
return False
return True
























 1044
1044

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








