Java中任何实现了Cloneable接口的类都可以通过调用clone()方法来复制一份自身然后传给调用者。一般而言,clone()方法满足:
(1) 对任何的对象x,都有x.clone() !=x,即克隆对象与原对象不是同一个对象。
(2) 对任何的对象x,都有x.clone().getClass()==x.getClass(),即克隆对象与原对象的类型一样。
(3) 如果对象x的equals()方法定义恰当,那么x.clone().equals(x)应该成立。
/*** Creates and returns a copy of this object. The precise meaning
* of "copy" may depend on the class of the object. The general
* intent is that, for any object {@codex}, the expression:
*
*
* x.clone() != x
* will be true, and that the expression:
*
*
* x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()
* will be {@codetrue}, but these are not absolute requirements.
* While it is typically the case that:
*
*
* x.clone().equals(x)
* will be {@codetrue}, this is not an absolute requirement.
*
* By convention, the returned object should be obtained by calling
* {@codesuper.clone}. If a class and all of its superclasses (except
* {@codeObject}) obey this convention, it will be the case that
* {@codex.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()}.
*
* By convention, the object returned by this method should be independent
* of this object (which is being cloned). To achieve this independence,
* it may be necessary to modify one or more fields of the object returned
* by {@codesuper.clone} before returning it. Typically, this means
* copying any mutable objects that comprise the internal "deep structure"
* of the object being cloned and replacing the references to these
* objects with references to the copies. If a class contains only
* primitive fields or references to immutable objects, then it is usually
* the case that no fields in the object returned by {@codesuper.clone}
* need to be modified.
*
* The method {@codeclone} for class {@codeObject} performs a
* specific cloning operation. First, if the class of this object does
* not implement the interface {@codeCloneable}, then a
* {@codeCloneNotSupportedException} is thrown. Note that all arrays
* are considered to implement the interface {@codeCloneable} and that
* the return type of the {@codeclone} method of an array type {@codeT[]}
* is {@codeT[]} where T is any reference or primitive type.
* Otherwise, this method creates a new instance of the class of this
* object and initializes all its fields with exactly the contents of
* the corresponding fields of this object, as if by assignment; the
* contents of the fields are not themselves cloned. Thus, this method
* performs a "shallow copy" of this object, not a "deep copy" operation.
*
* The class {@codeObject} does not itself implement the interface
* {@codeCloneable}, so calling the {@codeclone} method on an object
* whose class is {@codeObject} will result in throwing an
* exception at run time.
*
*@returna clone of this instance.
*@throwsCloneNotSupportedException if the object's class does not
* support the {@codeCloneable} interface. Subclasses
* that override the {@codeclone} method can also
* throw this exception to indicate that an instance cannot
* be cloned.
*@seejava.lang.Cloneable*/
protected nativeObject clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
首先来看看浅拷贝和深拷贝的定义:
浅拷贝:使用一个已知实例对新创建实例的成员变量逐个赋值,这个方式被称为浅拷贝。
深拷贝:当一个类的拷贝构造方法,不仅要复制对象的所有非引用成员变量值,还要为引用类型的成员变量创建新的实例,并且初始化为形式参数实例值。这个方式称为深拷贝
也就是说浅拷贝只复制一个对象,传递引用,不能复制实例。而深拷贝对对象内部的引用均复制,它是创建一个新的实例,并且复制实例。
对于浅拷贝当对象的成员变量是基本数据类型时,两个对象的成员变量已有存储空间,赋值运算传递值,所以浅拷贝能够复制实例。但是当对象的成员变量是引用数据类型时,就不能实现对象的复制了。
存在一个对象Person,代码如下:

public class Person {
private String name;
private String sex;
private int age;
public Person(String name,String sex,int age){
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
}
public Person(Person p){ //拷贝构造方法,复制对象
this.name = p.name;
this.sex = p.sex;
this.age = p.age;
}
}

上面的对象Person有三个成员变量。name、sex、age。两个构造方法。第二个的参数为该对象,它称为拷贝构造方法,它将创建的新对象初始化为形式参数的实例值,通过它可以实现对象复制功能。
又有一个对象Asian,如下:

public class Asian {
private String skin;
Person person;
public Asian(String skin,Person person){
this.skin = skin;
this.person = person; //引用赋值
}
public Asian(Asian asian){ //拷贝构造方法,复制对象
this(asian.skin,asian.person);
}
}

上面对象也存在着两个成员变量,skin 和Person对象
对于person对象有如下:
Person p1 = new Person("李四","mam",23);
Person p2 = new Person(P1);
当调用上面的语句时。P2对象将会对P1进行复制。执行情况如下如下图:

对于Asian对象有:
Asian a1 = new Asian("yellow",new Person("李四","mam",23));
Asian a2 = new Asian(a1);
New Asian(a1)执行Asian类的拷贝构造方法,由于对象赋值是引用赋值。使得a1和a2引用同一个对象
如下图:
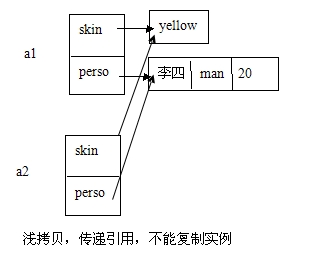
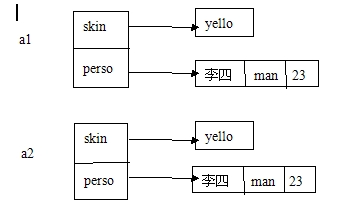
当a1执行某条可以改变该值的语句时,那么a1将会通过这个语句也可以改变a2对象的成员变量
如果执行以下语句:a2.name = new Person(a1.name)
这时将会创建一个新的Person对象
如下图:
http://www.cnblogs.com/chenssy/p/3308489.html





















 135
135

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








