目前线上的机器都是08年的老机器了,很多硬盘都用快6年了,为防止硬盘那天突然崩掉了,整个应用也就挂了,所以全网检测了下服务器硬盘,有如下方法:
硬盘状态测试工具:smartctl、Badblocks、hdparm
感觉用smartctl挺快的,也能快速看到硬盘是否健康,命令如下:
[root@qy ~]#yum install smartmontools -y
启动SMART
# smartctl --smart=on --offlineauto=on --saveauto=on /dev/sda
[root@qy ~]# smartctl -a /dev/sda
smartctl 5.42 2011-10-20 r3458[i686-linux-2.6.18-194.el5PAE] (local build)
Copyright (C) 2002-11 by Bruce Allen,http://smartmontools.sourceforge.net
Vendor: SEAGATE
Product: ST3146356SS
Revision: HS09
User Capacity: 146,815,733,760 bytes [146 GB]
Logical block size: 512 bytes
Logical Unit id: 0x5000c50004fa837f
Serial number: 3QN0EL91
Device type: disk
Transport protocol: SAS
Local Time is: Fri Oct 31 10:45:58 2014 CST
Device supports SMART and is Enabled
Temperature Warning Disabled or NotSupported
SMART Health Status: OK #版本的不通这里显示的也不一样。
Current Drive Temperature: 30 C
Drive Trip Temperature: 68 C
Elements in grown defect list: 0 #才是出坏道,俗称成长坏道。
Vendor (Seagate) cache information
Blocks sent to initiator = 3752023409
Blocks received from initiator = 3916316860
Blocks read from cache and sent to initiator = 4025399956
Number of read and write commands whose size <= segment size =3339079605
Number of read and write commands whose size > segment size = 2746
Vendor (Seagate/Hitachi) factoryinformation
number of hours powered up = 34120.02
number of minutes until next internal SMART test = 1
Error counter log:
Errors Corrected by Total Correction Gigabytes Total
ECC rereads/ errors algorithm processed uncorrected
fast | delayed rewrites corrected invocations [10^9 bytes] errors
read: 248894024 0 0 248894024 248894024 85241.186 0
write: 0 0 0 0 0 30998.996 0
verify: 340001 0 0 340001 340001 141.757 0
Non-medium errorcount:51 #非介质错误。意思是说不是盘的问题,一般是电缆、传输、校验问题,可以忽略的。
No self-tests have been logged
Long (extended) Self Test duration: 1740seconds [29.0 minutes]
可以用命令直接查看硬盘的好坏:
[root@qy ~]# smartctl -H /dev/sda
smartctl 5.42 2011-10-20 r3458[i686-linux-2.6.18-194.el5PAE] (local build)
Copyright (C) 2002-11 by Bruce Allen,http://smartmontools.sourceforge.net
SMART Health Status: OK
[root@localhost ~]# smartctl -H /dev/sda
smartctl 5.43 2012-06-30 r3573 [x86_64-linux-2.6.32-358.el6.x86_64] (local build)
Copyright (C) 2002-12 by Bruce Allen, http://smartmontools.sourceforge.net
=== START OF READ SMART DATA SECTION ===
SMART STATUS RETURN: incomplete response, ATA output registers missing
SMART overall-health self-assessment test result: PASSED
Warning: This result is based on an Attribute check.
OK和PASSED都属于磁盘是正常的。
Badblocks工具测试正常,无坏道信息:
badblocks命令可以检查磁盘装置中损坏的区块。执行该指令时须指定所要检查的磁盘装置,及此装置的磁盘区块数。
badblocks -s//显示进度 -v//显示执行详细情况 /dev/sda1
badblocks -s//显示进度 -w//以写去检测 -v//显示执行详细情况 /dev/sda2
注意,不能以写的方式检测已经挂载的硬盘
[root@qy ~]# badblocks -s -v /dev/sda
Checking blocks 0 to 143374740
Checking for bad blocks (read-only test):done
Passcompleted, 0 bad blocks found.
此磁盘通过测试,没有坏道(坏块)。您可以放心使用。
磁盘有坏道了……
但是,如果您检测过程中再某一个区块停滞不前,而后报告中提示有坏块,那么杯具了……您的磁盘有坏道了。
不论是什么类型的坏道,均建议您首先进行数据备份!把重要数据进行备份然后再尝试修复。如果您有重要数据却无法读取(磁盘出现异常),那么请立即停止使用此磁盘并找专业人员进行修复。
使用hdparm测试
测试硬盘读写速度
# hdparm -Tt /dev/sda
/dev/sda:
Timing cached reads:
1918 MB in 2.00 seconds = 959.62 MB/sec
Timing buffered disk reads: 184 MB in 3.00 seconds = 61.26 MB/sec
hdparm可检测,显示与设定IDE或SCSI硬盘的参数。
语法:
hdparm [-CfghiIqtTvyYZ][-a ][-A <0或1>][-c ][-d <0或1>][-k <0或1>][-K <0或1>][-m ][-n <0或1>][-p ][-P ][-r <0或1>][-S ][-u <0或1>][-W <0或1>][-X ] [设备]
-a 设定读取文件时,预先存入块区的分区数,若不加上选项,则显示目前的设定。 -A<0或1> 启动或关闭读取文件时的快取功能。-c 设定IDE32位I/O模式。 -C 检测IDE硬盘的电源管理模式。-d<0或1> 设定磁盘的DMA模式。-f 将内存缓冲区的数据写入硬盘,并清楚缓冲区。 -g 显示硬盘的磁轨,磁头,磁区等参数。-h 显示帮助。-i 显示硬盘的硬件规格信息,这些信息是在开机时由硬盘本身所提供。 -I 直接读取硬盘所提供的硬件规格信息。-k<0或1> 重设硬盘时,保留-dmu参数的设定。 -K<0或1> 重设硬盘时,保留-APSWXZ参数的设定。-m 设定硬盘多重分区存取的分区数。 -n<0或1> 忽略硬盘写入时所发生的错误。-p 设定硬盘的PIO模式。 -P 设定硬盘内部快取的分区数。-q 在执行后续的参数时,不在屏幕上显示任何信息。 -r<0或1> 设定硬盘的读写模式。-S 设定硬盘进入省电模式前的等待时间。-t 评估硬盘的读取效率。 -T 平谷硬盘快取的读取效率。-u<0或1> 在硬盘存取时,允许其他中断要求同时执行。-v 显示硬盘的相关设定。 -W<0或1> 设定硬盘的写入快取。-X 设定硬盘的传输模式。-y 使IDE硬盘进入省电模式。 -Y 使IDE硬盘进入睡眠模式。-Z 关闭某些Seagate硬盘的自动省电功能。
可以使用sg_vpd命令查看硬盘转速,sg_vpd命令是sg3_utils其中一个工具.
下载地址:http://sg.danny.cz/sg/sg3_utils.html
VPD:Vital Product Data
[root@qy sg3_utils-1.39]# sg_vpd /dev/sda
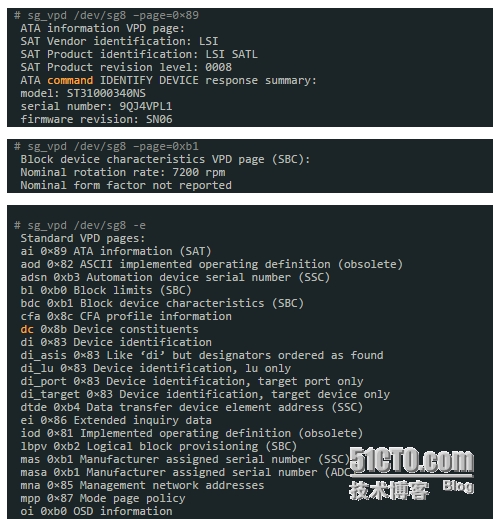
关于smart检测硬盘命令补充:
smartctl -a 检查该设备是否已经打开SMART技术。 smartctl -s on 如果没有打开SMART技术,使用该命令打开SMART技术。 smartctl -t short 后台检测硬盘,消耗时间短; smartctl -t long 后台检测硬盘,消耗时间长; smartctl -C -t short 前台检测硬盘,消耗时间短; smartctl -C -t long 前台检测硬盘,消耗时间长。其实就是利用硬盘SMART的自检程序。 smartctl -X 中断后台检测硬盘。 smartctl -l selftest 显示硬盘检测日志。 smartctl -l error 显示硬盘错误汇总。
首先通过dmesg工具,确认一下硬盘的设备符号。例如一个IDE硬盘连接到Primary IDE 总线上的Slave位置,硬盘设备符号是/dev/hdb,hdb中的h代表IDE,如果显示为sdb,则代表SATA和SCSI,最后一个字幕b代表Primary总线,第二块硬盘即Slave位置,确认硬盘是否打开了SMART支持:
# smartctl -i /dev/sda
smartctl 5.40 2010-10-16 r3189 [i386-redhat-linux-gnu] (local build)
Copyright (C) 2002-10 by Bruce Allen,http://smartmontools.sourceforge.net
=== START OF INFORMATION SECTION ===
Device Model: HITACHI HTS543225L9SA00
Serial Number: 090131FB2F32YLG28JEA
Firmware Version: FBEZC48C
User Capacity: 250,059,350,016 bytes
Device is: Not in smartctl database [for details use: -P showall]
ATA Version is: 8
ATA Standard is: ATA-8-ACS revision 3f
Local Time is: Wed May 25 10:10:39 2011 CST
SMART support is: Available - device has SMART capability.
SMART support is: Enabled //表示启用了smart支持
如果看到SMART support is: Disabled表示SMART未启用,执行如下命令,启动SMART
# smartctl --smart=on --offlineauto=on --saveauto=on /dev/sda
smartctl 5.40 2010-10-16 r3189 [i386-redhat-linux-gnu] (local build)
Copyright (C) 2002-10 by Bruce Allen,http://smartmontools.sourceforge.net
=== START OF ENABLE/DISABLE COMMANDS SECTION ===
SMART Enabled.
SMART Attribute Autosave Enabled.
SMART Automatic Offline Testing Enabled every four hours.
现在硬盘的SMART功能已经被打开,执行如下命令查看硬盘的健康状况
# smartctl -H /dev/sda
smartctl 5.40 2010-10-16 r3189 [i386-redhat-linux-gnu] (local build)
Copyright (C) 2002-10 by Bruce Allen,http://smartmontools.sourceforge.net
=== START OF READ SMART DATA SECTION ===
SMART overall-health self-assessment test result: PASSED
请注意result后边的结果:PASSED,这表示硬盘健康状态良好;如果这里显示Failure,那么最好立刻给服务器更换硬盘。SMART只能报告磁盘已经不再健康,但是报警后还能继续运行多久是不确定的。通常,SMART报警参数是有预留的,磁盘报警后,不会当场坏掉,一般能坚持一段时间,有的硬盘SMART报警后还继续跑了好几年,有的硬盘SMART报错后几天就坏了。但是一旦出现报警,侥幸心里是万万不能的……
#smartctl -A /dev/sda 查看硬盘的详细信息
#smartctl -s on /dev/sda 如果没有打开SMART技术,使用该命令打开SMART技术。
#smartctl -t short /dev/sda 后台检测硬盘,消耗时间短;
#smartctl -t long /dev/sda 后台检测硬盘,消耗时间长;
#smartctl -C -t /dev/sda short前台检测硬盘,消耗时间短;
#smartctl -C -t /dev/sda long前台检测硬盘,消耗时间长。其实就是利用硬盘SMART的自检程序。
#smartctl -X /dev/sda 中断后台检测硬盘。
#smartctl -l selftest /dev/sda 显示硬盘检测日志。
#smartctl -l error /dev/sda 显示硬盘错误汇总。
如果需要定期登录到服务器上运行smartctl比较麻烦时,linux还提供了系统进程smartd,编辑配置文件:1 vi /etc/smartd.conf
这个配置文件中大部分可能是注释掉的说明,只需要写入和当前硬盘相关的配置即可:
/dev/sda -H -m test@test123123.com //监控磁盘的健康状态,当SMART中报告PASSED的时候不理睬。一旦出现Failure,立刻用邮件通知用户指定的邮箱
/dev/sda -a -m admin@example.com,root@localhost //监控磁盘的所有属性,当SMART中报告PASSED的时候不理睬。一旦出现Failure,立刻用邮件通知用户指定的邮箱
/dev/twa0 -d 3ware,0 -a -s L/../../7/00 //监控3ware 9000控制器上的第一个ATA磁盘的所有属性,在每个礼拜天的00:00--01:00进行长格式的自我检测
/dev/sg2 -d areca,1 -a -s L/../(01|15)/./22 //监控Areca Raid控制器上的第一个SATA磁盘的所有属性,在每个礼拜月的第1天和第15天的22:00--23:00进行长格式的自我检测
-s (O/../.././(00|06|12|18)|S/../.././01|L/../../6/03) //在每天的00:00,06:00,12:00,18:00进行离线的自检,并在每天的01:00-02:00进行短格式的自检,并在每个礼拜6的03:00-04:00进行长格式的自检
配置好smartd.conf后需执行
/etc/init.d/smartd restart 即可生效
其他和smartd.conf相关的配置可参见:




















 938
938











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








