随着数据分析需求的不断增长,高效查询和分析大数据集变得越来越重要。Easysearch 作为一种强大的国产化搜索和分析引擎,同时作为 Elasticsearch 国产替代方案,支持原生 DSL 查询语法和 SQL 查询,确保原业务代码无需调整即可无缝迁移。Easysearch 兼容 ES 7.x 现有的 SDK 和索引存储格式,支持冷热架构和索引生命周期管理,为用户提供了全面的数据处理解决方案。本文将详细介绍如何使用 ES 7.x Python SDK 与 Easysearch 进行交互,包括安装、连接、数据操作和查询等方面。
1. 安装 Elasticsearch Python 客户端
要使用 Elasticsearch Python 客户端,首先需要通过pip进行安装。打开终端或命令提示符,并运行以下命令:
如果使用默认版本安装,会安装 8.x 的依赖,可能会报错 elasticsearch.UnsupportedProductError: The client noticed that the server is not Elasticsearch and we do not support this unknown product.
由于 Elasticsearch 7.10.2 以后变更了许可模式,引入了 Server Side Public License (SSPL) 和 Elastic License,很多基于 Elasticsearch 7.10.2 分支出来的搜索引擎需要使用 7.x 版本的 SDK 和 agent,比如 Beats 全家桶。
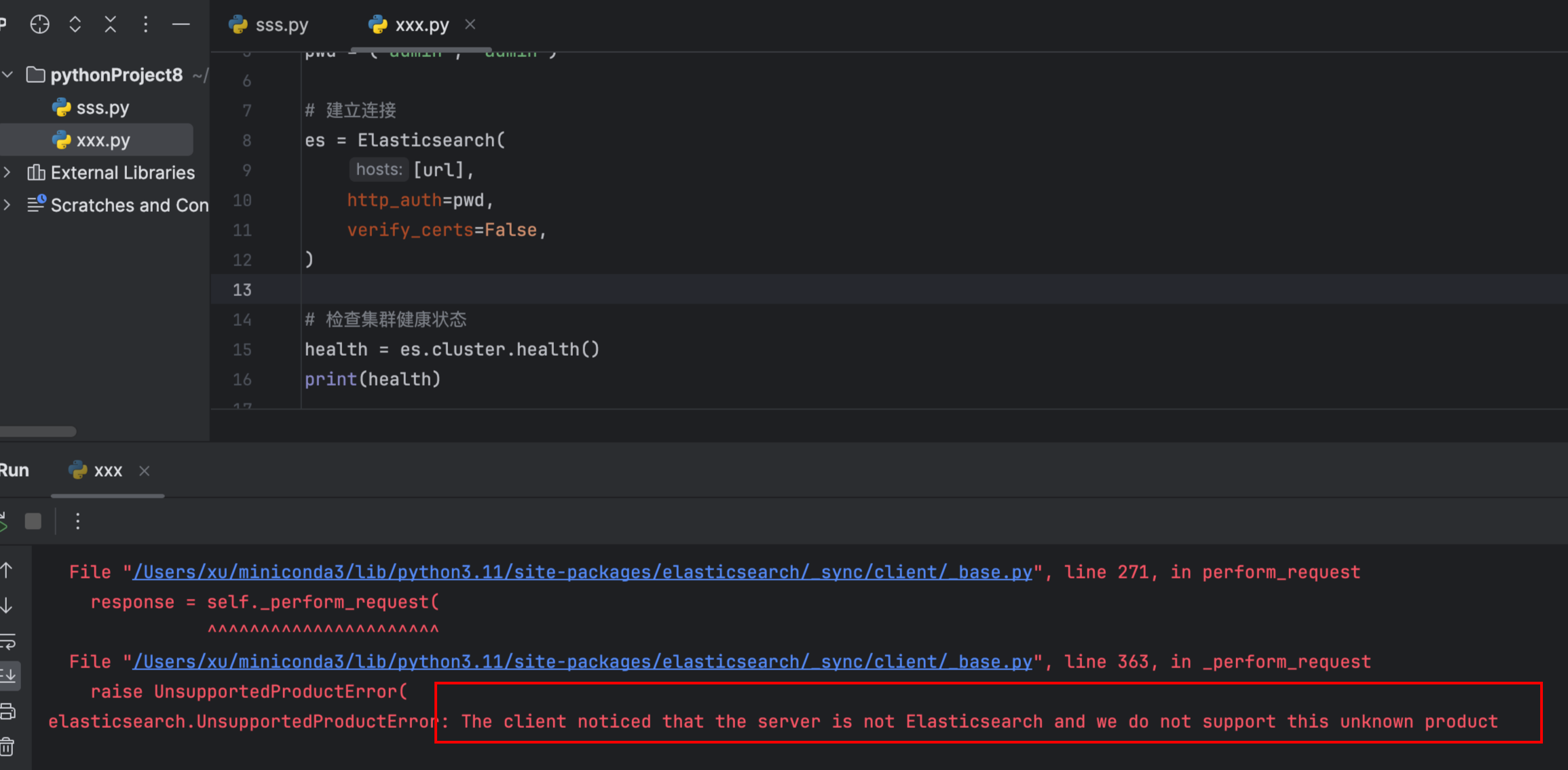
这是一个获取集群信息的 demo,使用es.cluster.health() 调用 Elasticsearch 集群的健康检查 API,返回集群的健康状态。
由于使用了自签名证书,所以在初始化时加上 verify_certs=False 参数,同时使用 warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") 设置 Python 的警告系统,忽略所有发出的警告。这在生产代码中通常不推荐,因为它会隐藏潜在的问题,但在开发或测试环境中,如果警告信息太多干扰调试,可能会暂时使用。
2. 准备示例数据
在进行查询之前,我们需要在 Easysearch 中创建一些示例数据。
3. 使用 REST API 进行查询
REST API 是与 Easysearch 进行通信的常用方式。通过 REST API,开发者可以发送 HTTP 请求来执行各种操作,包括索引文档、搜索数据等。以下示例展示了如何在 Python 中执行 REST 查询。
由于是 REST API,我们可以先使用 Postman 进行测试。
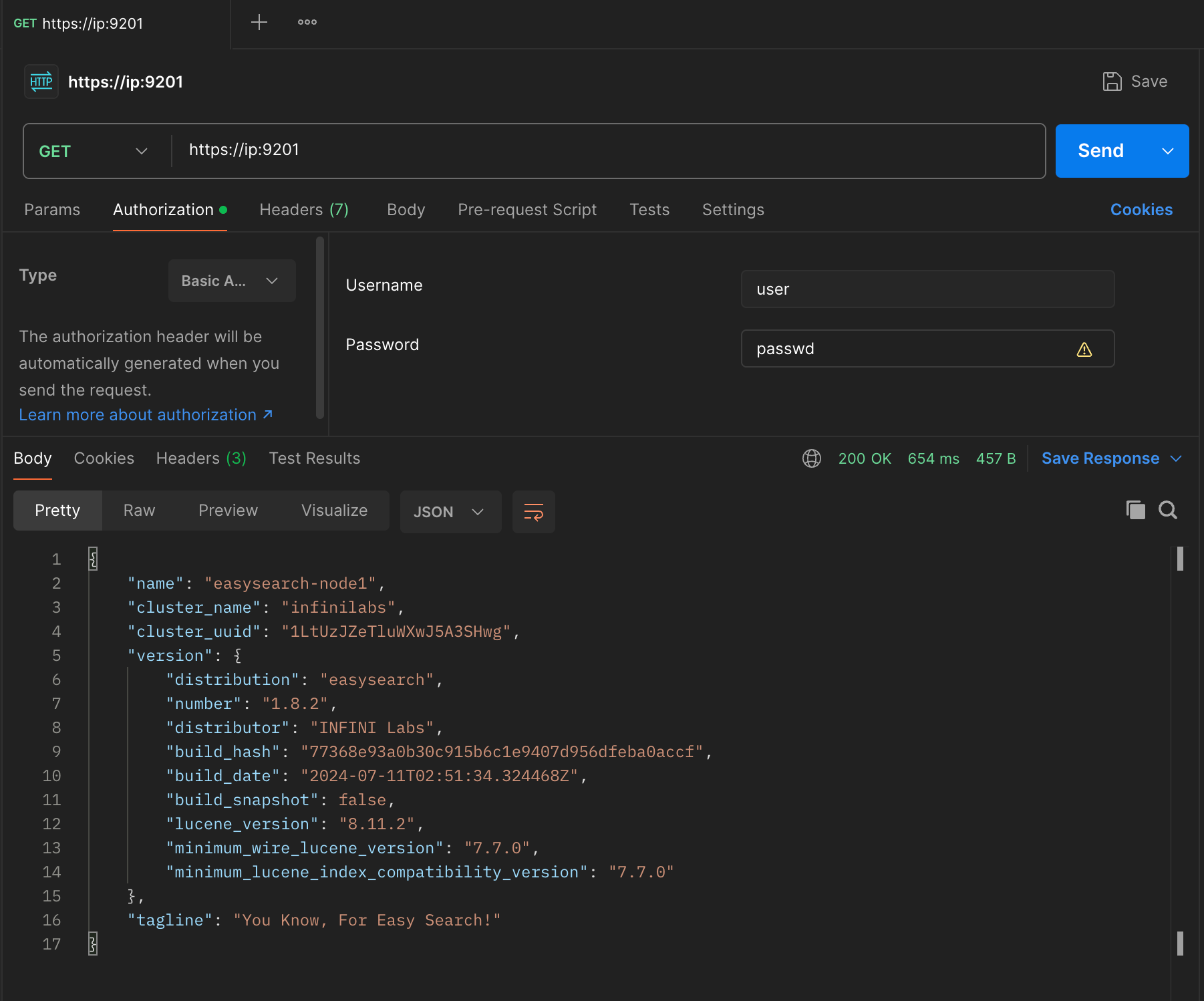
我们可以看到 HTTP 端点可以正常返回,然后就可以使用编程方式进行访问了:
4. 通过 DSL 对索引数据进行增删改查
DSL(Domain-Specific Language)是 Easysearch 的原生查询语言,允许用户构建复杂的查询。以下是一些示例:
插入数据
如果不指定 document ID,那么随机生成一个 ID 并写入。
更新数据
指定 ID 为 1 来手动更新索引:
更新单条数据
删除数据
5. 索引数据 SQL 查询
创建客户端实例后,我们可以使用 sql 方法执行 SQL 查询。以下示例展示了如何执行一个简单的 SELECT 查询。
6. 索引数据批量操作
Bulk API 允许用户一次性对多个文档进行创建、更新或删除操作,极大提高了操作效率。以下是一些示例:
批量插入数据
批量更新数据
批量删除数据
7. 索引级别的操作
接下来,介绍索引创建、删除和检查索引是否存在操作。以下是一些示例:
创建索引
删除索引
检查索引是否存在
8. 总结
Easysearch 虽然没有专门的 Python SDK,但完全兼容 ES 7.x 的 Python SDK 客户端,这为开发者提供了极大的便利。通过使用 ES 7.x Python SDK,开发者可以轻松地使用 DSL 和 SQL 语法对 Easysearch 进行查询和数据操作。Easysearch 主要优势包括:
- 兼容性强:无需修改现有代码,即可从 ES 迁移到 Easysearch。
- 功能全面:支持 DSL 查询、SQL 查询、批量操作等高级功能。
- 易于使用:提供简洁明了的 API,降低学习成本。
- 高效性能:批量操作 API 大幅提高数据处理效率。
Easysearch 结合 ES 7.x Python SDK 的强大功能,为开发者提供了一个高效、灵活的大数据处理平台。无论是执行简单的 SQL 查询,还是构建复杂的 DSL 查询,都能满足各种数据分析需求。如果您正在寻找一个强大的搜索和分析解决方案,Easysearch 绝对值得一试。它不仅能帮助您更高效地处理和分析大数据集,还能为数据驱动的决策提供有力支持。
作者:韩旭,亚马逊云技术支持,亚马逊云科技技领云博主,目前专注于云计算开发和大数据领域。





















 152
152

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








