Netfilter在网络层实现的详细分析见下面文章:
linux Netfilter在网络层的实现详细分析(iptables)_yg@hunter的博客-CSDN博客
本文分析的源码版本为4.18.0-80。
4.3以下的内核版本是通过nf_register_hook来注册,nf_unregister_hook来注销;
4.3-4.13之间版本,nf_register_hook里面会调用nf_register_net_hook来逐个net命名空间注册,此时可以使用这俩函数中的任一个来注册,注销对应nf_unregister_hook/nf_unregister_net_hook;
4.13及以上版本内核是通过nf_register_net_hook/nf_unregister_net_hook来注册/注销,删掉了nf_register_hook函数。
我画了张图,描述了netfilter hook的整个过程所涉及的数据结构(基于内核代码版本4.18.0-80):
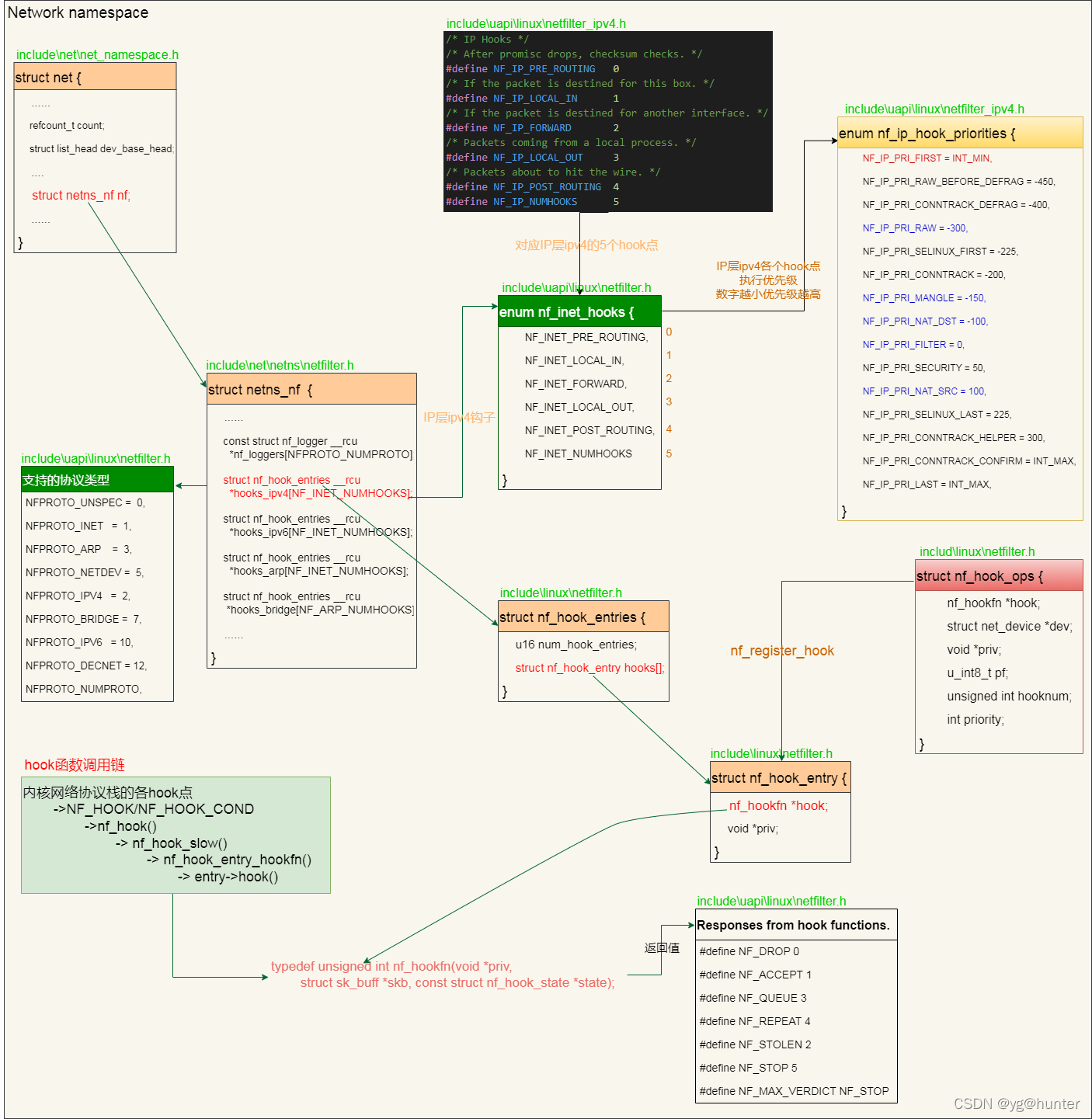
目录
1、钩子函数的注册
nf_register_net_hook函数的源码如下:
net\netfilter\core.c
int nf_register_net_hook(struct net *net, const struct nf_hook_ops *reg)
{
int err;
if (reg->pf == NFPROTO_INET) { // inet协议包含ipv4、ipv6
err = __nf_register_net_hook(net, NFPROTO_IPV4, reg);
if (err < 0)
return err;
err = __nf_register_net_hook(net, NFPROTO_IPV6, reg);
if (err < 0) {
__nf_unregister_net_hook(net, NFPROTO_IPV4, reg);
return err;
}
} else {
err = __nf_register_net_hook(net, reg->pf, reg);
if (err < 0)
return err;
}
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(nf_register_net_hook);对于注册的hook协议类型为NFPROTO_INET的话,会先后注册ipv4、ipv6的hook,然后会根据注册的协议类型调用__nf_register_net_hook函数:
static int __nf_register_net_hook(struct net *net, int pf,
const struct nf_hook_ops *reg)
{
struct nf_hook_entries *p, *new_hooks;
struct nf_hook_entries __rcu **pp;
//处理netdev层的ingress hook点
if (pf == NFPROTO_NETDEV) {
#ifndef CONFIG_NETFILTER_INGRESS
if (reg->hooknum == NF_NETDEV_INGRESS)
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
#endif
if (reg->hooknum != NF_NETDEV_INGRESS ||
!reg->dev || dev_net(reg->dev) != net)
return -EINVAL;
}
//获取该协议下对应hook点的数组首地址
pp = nf_hook_entry_head(net, pf, reg->hooknum, reg->dev);
if (!pp)
return -EINVAL;
mutex_lock(&nf_hook_mutex);
p = nf_entry_dereference(*pp);
//将新reg插入到该数组,里面重新为该数组申请空间,然后会按priority排序好,重新插入所有的hook
new_hooks = nf_hook_entries_grow(p, reg);
if (!IS_ERR(new_hooks))
rcu_assign_pointer(*pp, new_hooks);
mutex_unlock(&nf_hook_mutex);
if (IS_ERR(new_hooks))
return PTR_ERR(new_hooks);
hooks_validate(new_hooks);
#ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER_INGRESS
if (pf == NFPROTO_NETDEV && reg->hooknum == NF_NETDEV_INGRESS)
net_inc_ingress_queue();
#endif
#ifdef HAVE_JUMP_LABEL
static_key_slow_inc(&nf_hooks_needed[pf][reg->hooknum]);
#endif
BUG_ON(p == new_hooks);
nf_hook_entries_free(p);
return 0;
}nf_hook_entries 获取对应协议的对应hook链的首地址:
static struct nf_hook_entries __rcu **
nf_hook_entry_head(struct net *net, int pf, unsigned int hooknum,
struct net_device *dev)
{
switch (pf) {
case NFPROTO_NETDEV:
break;
#ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER_FAMILY_ARP
case NFPROTO_ARP:
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(ARRAY_SIZE(net->nf.hooks_arp) <= hooknum))
return NULL;
return net->nf.hooks_arp + hooknum;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER_FAMILY_BRIDGE
case NFPROTO_BRIDGE:
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(ARRAY_SIZE(net->nf.hooks_bridge) <= hooknum))
return NULL;
return net->nf.hooks_bridge + hooknum;
#endif
case NFPROTO_IPV4:
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(ARRAY_SIZE(net->nf.hooks_ipv4) <= hooknum))
return NULL;
return net->nf.hooks_ipv4 + hooknum;
case NFPROTO_IPV6:
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(ARRAY_SIZE(net->nf.hooks_ipv6) <= hooknum))
return NULL;
return net->nf.hooks_ipv6 + hooknum;
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_DECNET)
case NFPROTO_DECNET:
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(ARRAY_SIZE(net->nf.hooks_decnet) <= hooknum))
return NULL;
return net->nf.hooks_decnet + hooknum;
#endif
default:
WARN_ON_ONCE(1);
return NULL;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER_INGRESS
if (hooknum == NF_NETDEV_INGRESS) {
if (dev && dev_net(dev) == net)
return &dev->nf_hooks_ingress;
}
#endif
WARN_ON_ONCE(1);
return NULL;
}然后调用nf_hook_entries_grow将要注册的hook按优先级priority插入到该链中:
static struct nf_hook_entries *
nf_hook_entries_grow(const struct nf_hook_entries *old,
const struct nf_hook_ops *reg)
{
unsigned int i, alloc_entries, nhooks, old_entries;
struct nf_hook_ops **orig_ops = NULL;
struct nf_hook_ops **new_ops;
struct nf_hook_entries *new;
bool inserted = false;
alloc_entries = 1;
old_entries = old ? old->num_hook_entries : 0;
if (old) {
orig_ops = nf_hook_entries_get_hook_ops(old);
for (i = 0; i < old_entries; i++) {
if (orig_ops[i] != &dummy_ops)
alloc_entries++;
}
}
if (alloc_entries > MAX_HOOK_COUNT)
return ERR_PTR(-E2BIG);
new = allocate_hook_entries_size(alloc_entries);
if (!new)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
new_ops = nf_hook_entries_get_hook_ops(new);
i = 0;
nhooks = 0;
while (i < old_entries) {
if (orig_ops[i] == &dummy_ops) {
++i;
continue;
}
if (inserted || reg->priority > orig_ops[i]->priority) {
new_ops[nhooks] = (void *)orig_ops[i];
new->hooks[nhooks] = old->hooks[i];
i++;
} else {
new_ops[nhooks] = (void *)reg;
new->hooks[nhooks].hook = reg->hook;
new->hooks[nhooks].priv = reg->priv;
inserted = true;
}
nhooks++;
}
if (!inserted) {
new_ops[nhooks] = (void *)reg;
new->hooks[nhooks].hook = reg->hook;
new->hooks[nhooks].priv = reg->priv;
}
return new;
}2、自定义hook钩子函数的调用链
内核网络协议栈的各hook点
->NF_HOOK/NF_HOOK_COND
->nf_hook()
-> nf_hook_slow()
-> nf_hook_entry_hookfn()
-> entry->hook()①内核网络协议栈中安装的钩子
会在相关位置调用NF_HOOK/NF_HOOK_COND宏,触发钩子函数:
include\linux\netfilter.h
static inline int
NF_HOOK_COND(uint8_t pf, unsigned int hook, struct net *net, struct sock *sk,
struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *in, struct net_device *out,
int (*okfn)(struct net *, struct sock *, struct sk_buff *),
bool cond)
{
int ret;
if (!cond ||
((ret = nf_hook(pf, hook, net, sk, skb, in, out, okfn)) == 1))
ret = okfn(net, sk, skb);
return ret;
}
static inline int
NF_HOOK(uint8_t pf, unsigned int hook, struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb,
struct net_device *in, struct net_device *out,
int (*okfn)(struct net *, struct sock *, struct sk_buff *))
{
int ret = nf_hook(pf, hook, net, sk, skb, in, out, okfn);
if (ret == 1)
ret = okfn(net, sk, skb);
return ret;
}比如,net\ipv4\ip_input.c中,进入本地的网络数据包,会调用NF_HOOK触发NF_INET_LOCAL_IN钩子:
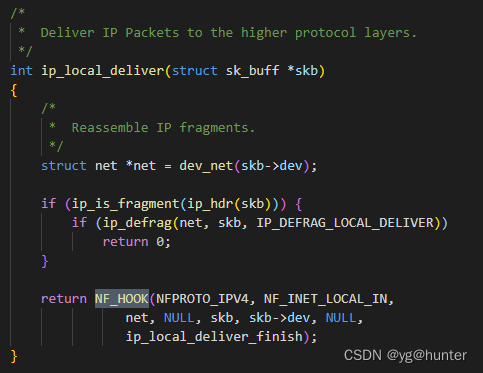
②调用nf_hook函数
实际执行时调用nf_hook函数,函数定义如下:
include\linux\netfilter.h
/**
* nf_hook - call a netfilter hook
*
* Returns 1 if the hook has allowed the packet to pass. The function
* okfn must be invoked by the caller in this case. Any other return
* value indicates the packet has been consumed by the hook.
*/
static inline int nf_hook(u_int8_t pf, unsigned int hook, struct net *net,
struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb,
struct net_device *indev, struct net_device *outdev,
int (*okfn)(struct net *, struct sock *, struct sk_buff *))
{
struct nf_hook_entries *hook_head = NULL;
int ret = 1;
#ifdef HAVE_JUMP_LABEL
if (__builtin_constant_p(pf) &&
__builtin_constant_p(hook) &&
!static_key_false(&nf_hooks_needed[pf][hook]))
return 1;
#endif
rcu_read_lock();
//根据传入的协议类型,及hook点,获取对应hook链的数组首地址
switch (pf) {
case NFPROTO_IPV4:
hook_head = rcu_dereference(net->nf.hooks_ipv4[hook]);
break;
case NFPROTO_IPV6:
hook_head = rcu_dereference(net->nf.hooks_ipv6[hook]);
break;
case NFPROTO_ARP:
#ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER_FAMILY_ARP
hook_head = rcu_dereference(net->nf.hooks_arp[hook]);
#endif
break;
case NFPROTO_BRIDGE:
#ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER_FAMILY_BRIDGE
hook_head = rcu_dereference(net->nf.hooks_bridge[hook]);
#endif
break;
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_DECNET)
case NFPROTO_DECNET:
hook_head = rcu_dereference(net->nf.hooks_decnet[hook]);
break;
#endif
default:
WARN_ON_ONCE(1);
break;
}
if (hook_head) {
struct nf_hook_state state;
nf_hook_state_init(&state, hook, pf, indev, outdev,
sk, net, okfn);
//最后进入nf_hook_slow函数流程
ret = nf_hook_slow(skb, &state, hook_head, 0);
}
rcu_read_unlock();
return ret;
}③调用nf_hook_slow函数
根据传入的协议类型,及hook点,获取对应hook链的数组首地址后,最终调用nf_hook_slow函数:
net\netfilter\core.c
/* Returns 1 if okfn() needs to be executed by the caller,
* -EPERM for NF_DROP, 0 otherwise. Caller must hold rcu_read_lock. */
int nf_hook_slow(struct sk_buff *skb, struct nf_hook_state *state,
const struct nf_hook_entries *e, unsigned int s)
{
unsigned int verdict;
int ret;
for (; s < e->num_hook_entries; s++) {
// 调用对应钩子函数
verdict = nf_hook_entry_hookfn(&e->hooks[s], skb, state);
// 判断钩子函数的返回值,决定该数据包的后续处理流程
switch (verdict & NF_VERDICT_MASK) {
case NF_ACCEPT: // 允许数据包继续下一步
break;
case NF_DROP: // 丢弃该数据包,直接返回EPERM
kfree_skb(skb);
ret = NF_DROP_GETERR(verdict);
if (ret == 0)
ret = -EPERM;
return ret;
case NF_QUEUE: // 数据包加入用户队列,给用户程序处理,然后返回
ret = nf_queue(skb, state, e, s, verdict);
if (ret == 1)
continue;
return ret;
default: // NF_STOLEN,让netfilter框架忽略该数据包的处理
/* Implicit handling for NF_STOLEN, as well as any other
* non conventional verdicts.
*/
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(nf_hook_slow);④调用内联函数nf_hook_entry_hookfn
include\linux\netfilter.h
static inline int
nf_hook_entry_hookfn(const struct nf_hook_entry *entry, struct sk_buff *skb,
struct nf_hook_state *state)
{
return entry->hook(entry->priv, skb, state);
}⑤最终就调用到hook_entry的hook回调函数
此时entry->hook就是我们自定义的nf_hook_ops中的hook函数了。
⑥钩子函数的返回值
它的返回值为以下几种:
include\uapi\linux\netfilter.h
/* Responses from hook functions. */
#define NF_DROP 0 // 丢弃该数据包
#define NF_ACCEPT 1 // 当前hook点,允许该数据包继续在协议栈中流转
#define NF_STOLEN 2 // 让netfilter框架忽略该数据包的处理
#define NF_QUEUE 3 // 该数据包加入到用户队列,供用户程序处理
#define NF_REPEAT 4
#define NF_STOP 5 /* Deprecated, for userspace nf_queue compatibility. */
#define NF_MAX_VERDICT NF_STOP3、钩子函数的注销
net\netfilter\core.c
⑴nf_unregister_net_hook
void nf_unregister_net_hook(struct net *net, const struct nf_hook_ops *reg)
{
if (reg->pf == NFPROTO_INET) {
__nf_unregister_net_hook(net, NFPROTO_IPV4, reg);
__nf_unregister_net_hook(net, NFPROTO_IPV6, reg);
} else {
__nf_unregister_net_hook(net, reg->pf, reg);
}
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(nf_unregister_net_hook);⑵__nf_unregister_net_hook
跟注册类似处理之后,里面会调用__nf_unregister_net_hook函数:
static void __nf_unregister_net_hook(struct net *net, int pf,
const struct nf_hook_ops *reg)
{
struct nf_hook_entries __rcu **pp;
struct nf_hook_entries *p;
pp = nf_hook_entry_head(net, pf, reg->hooknum, reg->dev);
if (!pp)
return;
mutex_lock(&nf_hook_mutex);
p = nf_entry_dereference(*pp);
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(!p)) {
mutex_unlock(&nf_hook_mutex);
return;
}
// 将该hook从对应hook数组中移除
if (nf_remove_net_hook(p, reg)) {
#ifdef CONFIG_NETFILTER_INGRESS
if (pf == NFPROTO_NETDEV && reg->hooknum == NF_NETDEV_INGRESS)
net_dec_ingress_queue();
#endif
#ifdef HAVE_JUMP_LABEL
static_key_slow_dec(&nf_hooks_needed[pf][reg->hooknum]);
#endif
} else {
WARN_ONCE(1, "hook not found, pf %d num %d", pf, reg->hooknum);
}
// 尝试缩容,移除hook为accept_all的hook函数操作
p = __nf_hook_entries_try_shrink(p, pp);
mutex_unlock(&nf_hook_mutex);
if (!p)
return;
nf_queue_nf_hook_drop(net);
nf_hook_entries_free(p);
}①nf_remove_net_hook
里面会调用nf_remove_net_hook,从对应的hook数组中移除该hook,这里移除并没有删掉,而是将该hook数组对应下标的hook改成了accept_all,nf_hook_ops设置为dummy_ops:
/*
* nf_remove_net_hook - remove a hook from blob
*
* @oldp: current address of hook blob
* @unreg: hook to unregister
*
* This cannot fail, hook unregistration must always succeed.
* Therefore replace the to-be-removed hook with a dummy hook.
*/
static bool nf_remove_net_hook(struct nf_hook_entries *old,
const struct nf_hook_ops *unreg)
{
struct nf_hook_ops **orig_ops;
unsigned int i;
orig_ops = nf_hook_entries_get_hook_ops(old);
for (i = 0; i < old->num_hook_entries; i++) {
if (orig_ops[i] != unreg)
continue;
WRITE_ONCE(old->hooks[i].hook, accept_all);
WRITE_ONCE(orig_ops[i], &dummy_ops);
return true;
}
return false;
}②__nf_hook_entries_try_shrink
然后调用__nf_hook_entries_try_shrink,尝试缩容hook数组,这里是重新申请了个nf_hook_entries,把旧的nf_hook_entries里hook数组中除了元素为dummy_ops的所有元素都按顺序拷贝到新nf_hook_entries中:
/*
* __nf_hook_entries_try_shrink - try to shrink hook array
*
* @old -- current hook blob at @pp
* @pp -- location of hook blob
*
* Hook unregistration must always succeed, so to-be-removed hooks
* are replaced by a dummy one that will just move to next hook.
*
* This counts the current dummy hooks, attempts to allocate new blob,
* copies the live hooks, then replaces and discards old one.
*
* return values:
*
* Returns address to free, or NULL.
*/
static void *__nf_hook_entries_try_shrink(struct nf_hook_entries *old,
struct nf_hook_entries __rcu **pp)
{
unsigned int i, j, skip = 0, hook_entries;
struct nf_hook_entries *new = NULL;
struct nf_hook_ops **orig_ops;
struct nf_hook_ops **new_ops;
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(!old))
return NULL;
orig_ops = nf_hook_entries_get_hook_ops(old);
for (i = 0; i < old->num_hook_entries; i++) {
if (orig_ops[i] == &dummy_ops)
skip++;
}
/* if skip == hook_entries all hooks have been removed */
hook_entries = old->num_hook_entries;
if (skip == hook_entries)
goto out_assign;
if (skip == 0)
return NULL;
hook_entries -= skip;
new = allocate_hook_entries_size(hook_entries);
if (!new)
return NULL;
new_ops = nf_hook_entries_get_hook_ops(new);
for (i = 0, j = 0; i < old->num_hook_entries; i++) {
if (orig_ops[i] == &dummy_ops)
continue;
new->hooks[j] = old->hooks[i];
new_ops[j] = (void *)orig_ops[i];
j++;
}
hooks_validate(new);
out_assign:
rcu_assign_pointer(*pp, new);
return old;
}③nf_queue_nf_hook_drop
在当前net网络命名空间中删除旧的nf_hook_entries。
④nf_hook_entries_free
释放旧nf_hook_entries_free所占空间。

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








