介绍
jdk解释:
public class FileInputStream
extends InputStream
A FileInputStream从文件系统中的文件获取输入字节。 什么文件可用取决于主机环境。
FileInputStream用于读取诸如图像数据的原始字节流。 要阅读字符串,请考虑使用FileReader 。
属性
/* File Descriptor - handle to the open file */
private final FileDescriptor fd;
/**
* The path of the referenced file
* (null if the stream is created with a file descriptor)
*/
private final String path;
private FileChannel channel = null;
private final Object closeLock = new Object();
private volatile boolean closed = false;
值得注意的是private final FileDescriptor fd;
FileDescriptor类jdk 1.8解释:
文件描述符类的实例用作表示打开文件,开放套接字或其他字节源或信宿的底层机器特定结构的不透明句柄。 文件描述符的主要实际用途是创建一个FileInputStream或FileOutputStream来包含它。
FileDescriptor详解http://wangkuiwu.github.io/2012/05/09/FileDescriptor/
构造方法
public FileInputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException {
this(name != null ? new File(name) : null);
}
public FileInputStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException {
String name = (file != null ? file.getPath() : null);
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead(name);
}
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (file.isInvalid()) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("Invalid file path");
}
fd = new FileDescriptor();
fd.attach(this);
path = name;
open(name);
}
public FileInputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj) {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (fdObj == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead(fdObj);
}
fd = fdObj;
path = null;
/*
* FileDescriptor is being shared by streams.
* Register this stream with FileDescriptor tracker.
*/
fd.attach(this);
}
先看jdk1.8的解释
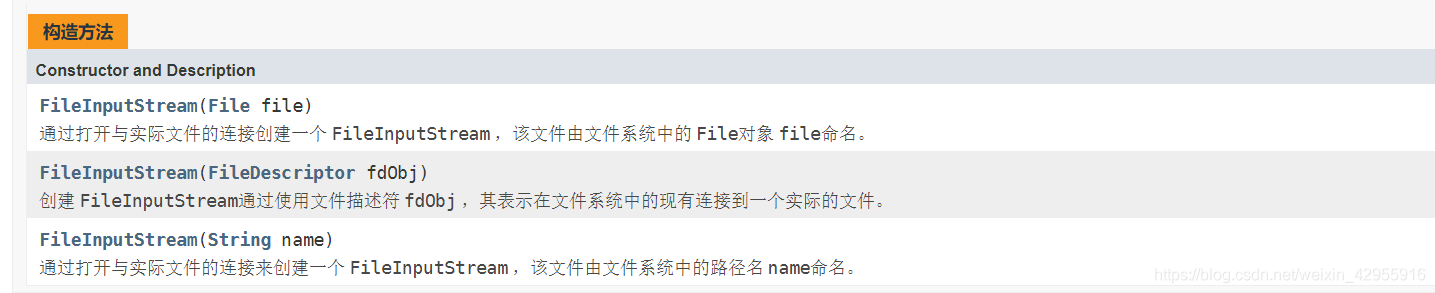
这三个构造方法的实现,终归还是回归到private final FileDescriptor fd;属性上.
public FileInputStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException:这个构造方法的实现,首先判断传入的参数是否合法,然后在为属性
fd = new FileDescriptor();fd.attach(this);值得注意的是fd.attach(this);源码查看attach方法
synchronized void attach(Closeable c) {
if (parent == null) {
// first caller gets to do this
parent = c;
} else if (otherParents == null) {
otherParents = new ArrayList<>();
otherParents.add(parent);
otherParents.add(c);
} else {
otherParents.add(c);
}
}
注意传入的参数是Closeable,而我们传入的是FileInputStream,这是因为FileInputStream继承了InputStream,InputStream实现了Closeable接口;
最后open(name);是FileInputStream类的一个本地方法
private native void open0(String name) throws FileNotFoundException:打开指定的文件进行读取。
同理下面的构造方法 public FileInputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj) 也是一样.
@Test
@Test
public void toPath() throws FileNotFoundException {
File file = new File("F:\\FileStudy\\test2.txt");//存在的文件
File file1 = new File("F:\\FileStudy\\test2.t1xt");//不存在存在的文件
File file2 = new File("F:\\FileStudy");//存在的目录
File file3 = new File("F:\\FileStud");//不存在存在的文件
FileInputStream fileInputStream =new FileInputStream(file);//1
FileInputStream fileInputStream1 =new FileInputStream(file1);//2
FileInputStream fileInputStream2 =new FileInputStream(file2);//3
FileInputStream fileInputStream3 =new FileInputStream(file3);//4
}
输出结果:
除了第一个能成功
2会返回:java.io.FileNotFoundException: F:\FileStudy\test2.t1xt (系统找不到指定的文件。)
3会返回:java.io.FileNotFoundException: F:\FileStudy (拒绝访问。)
4会返回:java.io.FileNotFoundException: F:\FileStud (系统找不到指定的文件。)
由测试可以知,如果该文件是目录,则创建不成功,抛出异常.
方法
(1) read()方法类:
public int read() throws IOException {
return read0();
}
private native int read0() throws IOException;
private native int readBytes(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException;
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return readBytes(b, 0, b.length);
}
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
return readBytes(b, off, len);
}
这几类方法都是对本地方法进行重载
@Test
@Test
public void read() throws IOException {
File file = new File("F:\\FileStudy\\test2.txt");//存在的文件
FileInputStream fileInputStream =new FileInputStream(file);
System.out.println(fileInputStream.read());
while (fileInputStream.read()>1){
System.out.println(fileInputStream.read());
}
byte[] bytes =new byte[4];
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
System.out.println(fileInputStream.read(bytes));
System.out.println(fileInputStream.read(bytes,1,1));
}
输出结果:
183
183
181
203
183
181
-1
--------------------------------------
-1
-1
(2)
public native long skip(long n) throws IOException;
也是本地方法
public long skip(long n) throws IOException
跳过并从输入流中丢弃n个字节的数据。
由于各种原因, skip方法可能会跳过一些较小数量的字节,可能是0 。 如果n为负,则该方法将尝试向后跳。 如果后台文件不支持其当前位置的向后跳过,则会抛出IOException 。 返回实际跳过的字节数。 如果它向前跳,它返回一个正值。 如果它向后跳,它返回一个负值。
该方法可能会跳过比后备文件中剩余的字节更多的字节。 这不会产生异常,并且跳过的字节数可能包括超出后台文件的EOF的一些字节数。 尝试在跳过结束后从流中读取将导致-1表示文件的结尾。
重写:
skip在 InputStream
参数
n - 要跳过的字节数。
结果
实际跳过的字节数。
异常
IOException - 如果n为负,如果流不支持查询,或者发生I / O错误。
(3)
public native int available() throws IOException;
本地方法
public int available() throws IOException
返回从此输入流中可以读取(或跳过)的剩余字节数的估计值,而不会被下一次调用此输入流的方法阻塞。 当文件位置超出EOF时返回0。 下一个调用可能是同一个线程或另一个线程。 这个多个字节的单个读取或跳过将不会被阻塞,但可以读取或跳过较少的字节。
在某些情况下,非阻塞读取(或跳过)在缓慢时可能会被阻止,例如在慢速网络中读取大文件时。
重写:
available在 InputStream
结果
可以从该输入流中读取(或跳过)而不阻塞的剩余字节数的估计。
异常
IOException - 如果此文件输入流已通过调用 close关闭或发生I / O错误。
@Test
@Test
public void available() throws IOException {
File file = new File("F:\\FileStudy\\test2.txt");//存在的文件
FileInputStream fileInputStream =new FileInputStream(file);
while (fileInputStream.read()>1){
System.out.println(fileInputStream.available());
}
}
输出结果:
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
可以看出read()方法是一个字节读取;
(4) public void close() throws IOException;
public void close() throws IOException {
synchronized (closeLock) {
if (closed) {
return;
}
closed = true;
}//这一段没看懂
if (channel != null) {
channel.close();
}
fd.closeAll(new Closeable() {
public void close() throws IOException {
close0();
}
});
}
public void close() throws IOException
关闭此文件输入流并释放与流相关联的任何系统资源。
如果该流具有相关联的信道,则该信道也被关闭。
Specified by:
close在接口 Closeable
Specified by:
close在界面 AutoCloseable
重写:
close在 InputStream类
异常
IOException - 如果发生I / O错误。
看源码分析可知,先判断属性closed是否为true,为true直接返回
然后在判断channel属性是否为空,不为空调用channel.close();
最后利用FileDescriptor里面的方法closeAll,重写Closeable类里面的方法,最后掉成了FileInputStream中的本地方法close0();
(5)
public final FileDescriptor getFD() throws IOException {
if (fd != null) {
return fd;
}
throw new IOException();
}
public FileChannel getChannel() {
synchronized (this) {
if (channel == null) {
channel = FileChannelImpl.open(fd, path, true, false, this);
}
return channel;
}
}
该方法是获取属性的get方法,返回属性实例.
值得注意的是public FileChannel getChannel(),
FileChannel类基本使用:https://blog.csdn.net/KingBoyWorld/article/details/72417461
FileChannel类Jdk1.8文档解释:http://www.matools.com/api/java8
总结
未完待续






















 819
819











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








