一、Bean 注解标记和扫描
1、注解理解
和 XML 配置文件一样,注解本身并不能执行,注解本身仅仅只是做一个标记,具体的功能是框架检测到注解标记的位置,然后针对这个位置按照注解标记的功能来执行具体操作。
本质上:所有一切的操作都是 Java 代码来完成的,XML 和注解只是告诉框架中的 Java 代码如何执行。
2、扫描理解
Spring 为了知道程序员在哪些地方标记了什么注解,就需要通过扫描的方式,来进行检测。然后根据注解进行后续操作。
3、准备Spring项目和组件
a.准备项目 pom.xml
<dependencies>
<!--spring context依赖-->
<!--当你引入Spring Context依赖之后,表示将Spring的基础依赖引入了-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit5测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>b.准备组件类
普通组件
/**
* projectName: com.atguigu.components
*
* description: 普通的组件
*/
public class CommonComponent {
}
Controller 组件
/**
* projectName: com.atguigu.components
*
* description: controller类型组件
*/
public class XxxController {
}
Service 组件
/**
* projectName: com.atguigu.components
*
* description: service类型组件
*/
public class XxxService {
}
Dao 组件
/**
* projectName: com.atguigu.components
*
* description: dao类型组件
*/
public class XxxDao {
}
4、组件添加标记注解
a.组件标记注解和区别
Spring 提供了以下多个注解,这些注解可以直接标注在 Java 类上,将它们定义成 Spring Bean。
| 注解 | 说明 |
| @Component | 该注解用于描述 Spring 中的 Bean,它是一个泛化的概念,仅仅表示容器中的一个组件(Bean),并且可以作用在应用的任何层次,例如 Service 层、Dao 层等。 使用时只需将该注解标注在相应类上即可。 |
| @Repository | 该注解用于将数据访问层(Dao 层)的类标识为 Spring 中的 Bean,其功能与 @Component 相同。 |
| @Service | 该注解通常作用在业务层(Service 层),用于将业务层的类标识为 Spring 中的 Bean,其功能与 @Component 相同。 |
| @Controller | 该注解通常作用在控制层(如SpringMVC 的 Controller),用于将控制层的类标识为 Spring 中的 Bean,其功能与 @Component 相同。 |
通过查看源码我们得知,@Controller、@Service、@Repository这三个注解只是在@Component注解的基础上起了三个新的名字。
对于Spring使用IOC容器管理这些组件来说没有区别,也就是语法层面没有区别。所以@Controller、@Service、@Repository这三个注解只是给开发人员看的,让我们能够便于分辨组件的作用。
注意:虽然它们本质上一样,但是为了代码的可读性、程序结构严谨!我们肯定不能随便胡乱标记。
b.使用注解标记
普通组件
/**
* projectName: com.atguigu.components
*
* description: 普通的组件
*/
@Component
public class CommonComponent {
}
Controller组件
/**
* projectName: com.atguigu.components
*
* description: controller类型组件
*/
@Controller
public class XxxController {
}
Service组件
/**
* projectName: com.atguigu.components
*
* description: service类型组件
*/
@Service
public class XxxService {
}
Dao组件
/**
* projectName: com.atguigu.components
*
* description: dao类型组件
*/
@Repository
public class XxxDao {
}
5、配置文件确定扫描范围
情况1:基本扫描配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 配置自动扫描的包 -->
<!-- 1.包要精准,提高性能!
2.会扫描指定的包和子包内容
3.多个包可以使用,分割 例如: com.atguigu.controller,com.atguigu.service等
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.components"/>
</beans>情况2:指定排除组件
<!-- 情况三:指定不扫描的组件 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.components">
<!-- context:exclude-filter标签:指定排除规则 -->
<!-- type属性:指定根据什么来进行排除,annotation取值表示根据注解来排除 -->
<!-- expression属性:指定排除规则的表达式,对于注解来说指定全类名即可 -->
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>情况3:指定扫描组件
<!-- 情况四:仅扫描指定的组件 -->
<!-- 仅扫描 = 关闭默认规则 + 追加规则 -->
<!-- use-default-filters属性:取值false表示关闭默认扫描规则 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.ioc.components" use-default-filters="false">
<!-- context:include-filter标签:指定在原有扫描规则的基础上追加的规则 -->
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>6、组件BeanName问题
在我们使用 XML 方式管理 bean 的时候,每个 bean 都有一个唯一标识——id 属性的值,便于在其他地方引用。现在使用注解后,每个组件仍然应该有一个唯一标识。
默认情况:类名首字母小写就是 bean 的 id。例如:SoldierController 类对应的 bean 的 id 就是 soldierController。
使用value属性指定:
@Controller(value = "tianDog")
public class SoldierController {
}当注解中只设置一个属性时,value属性的属性名可以省略:
@Service("smallDog")
public class SoldierService {
}二、Bean 作用域和周期方法注解
1、组件周期方法配置
a.周期方法概念
我们可以在组件类中定义方法,然后当IoC容器实例化和销毁组件对象的时候进行调用。这两个方法我们成为生命周期方法。
类似于 Servlet 的 init/destroy 方法,我们可以在周期方法完成初始化和释放资源等工作。
b.周期方法声明
public class BeanOne {
//周期方法要求: 方法命名随意,但是要求方法必须是 public void 无形参列表
@PostConstruct //注解制指定初始化方法
public void init() {
// 初始化逻辑
}
}
public class BeanTwo {
@PreDestroy //注解指定销毁方法
public void cleanup() {
// 释放资源逻辑
}
}2、组件作用域配置
a.Bean作用域概念
<bean 标签声明 Bean,只是将 Bean 的信息配置给 Spring IoC 容器。
在 IoC 容器中,这些 <bean 标签对应的信息转成 Spring 内部 BeanDefinition 对象,BeanDefinition 对象内,包含定义的信息(id,class,属性等等)。
这意味着,BeanDefinition 与类概念一样,SpringIoC 容器可以可以根据 BeanDefinition 对象反射创建多个 Bean 对象实例。
具体创建多少个 Bean 的实例对象,由 Bean的作用域 Scope 属性指定。
b.作用域可选值
| 取值 | 含义 | 创建对象的时机 | 默认值 |
| singleton | 在 IOC 容器中,这个 bean 的对象始终为单实例 | IOC 容器初始化时 | 是 |
| prototype | 这个 bean 在 IOC 容器中有多个实例 | 获取 bean 时 | 否 |
c.作用域配置
@Scope(scopeName = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON) //单例,默认值
@Scope(scopeName = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE) //多例 二选一
public class BeanOne {
//周期方法要求: 方法命名随意,但是要求方法必须是 public void 无形参列表
@PostConstruct //注解制指定初始化方法
public void init() {
// 初始化逻辑
}
}三、Bean 属性赋值
1、基本类型属性赋值
@Value 通常用于注入外部化属性
声明外部配置(application.properties)
catalog.name=MovieCatalogxml 引入外部配置
<!-- 引入外部配置文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="application.properties" />@Value 注解读取配置
package com.atguigu.components;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* projectName: com.atguigu.components
*
* description: 普通的组件
*/
@Component
public class CommonComponent {
/**
* 情况1: ${key} 取外部配置key对应的值!
* 情况2: ${key:defaultValue} 没有key,可以给与默认值
*/
@Value("${catalog:hahaha}")
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
2、引用类型属性赋值
(1)设定场景
- SoldierController 需要 SoldierService
- SoldierService 需要 SoldierDao
SoldierController中声明方法
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller(value = "tianDog")
public class SoldierController {
private SoldierService soldierService;
public void getMessage() {
soldierService.getMessage();
}
}SoldierService中声明方法
@Service("smallDog")
public class SoldierService {
private SoldierDao soldierDao;
public void getMessage() {
soldierDao.getMessage();
}
}SoldierDao中声明方法
@Repository
public class SoldierDao {
public void getMessage() {
System.out.print("I am a soldier");
}
}(2)自动装配实现
a. 前提
参与自动装配的组件(需要装配、被装配)全部都必须在 IoC 容器中。
注意:不区分 IoC 的方式,XML 和注解都可以。
b. @Autowired 注解
在成员变量上直接标记 @Autowired 注解即可,不需要提供 setXxx() 方法。以后我们在项目中的正式用法就是这样。
c. 给 Controller 装配 Service
@Controller(value = "tianDog")
public class SoldierController {
@Autowired
private SoldierService soldierService;
public void getMessage() {
soldierService.getMessage();
}
}d. 给 Service 装配 Dao
@Service("smallDog")
public class SoldierService {
@Autowired
private SoldierDao soldierDao;
public void getMessage() {
soldierDao.getMessage();
}
}(3)@Autowired 注解细节
a. 标记位置
成员变量
这是最主要的使用方式,与 xml 进行 bean ref 引用不同,他不需要有 set 方法。
@Service("smallDog")
public class SoldierService {
@Autowired
private SoldierDao soldierDao;
public void getMessage() {
soldierDao.getMessage();
}
}构造器
@Controller(value = "tianDog")
public class SoldierController {
private SoldierService soldierService;
@Autowired
public SoldierController(SoldierService soldierService) {
this.soldierService = soldierService;
}
……setXxx() 方法
@Controller(value = "tianDog")
public class SoldierController {
private SoldierService soldierService;
@Autowired
public void setSoldierService(SoldierService soldierService) {
this.soldierService = soldierService;
}
……b. 工作流程
首先根据所需要的组件类型到 IOC 容器中查找。
如果能够找到唯一的 bean:直接执行装配。
如果完全找不到匹配这个类型的 bean:装配失败。
如果和所需类型匹配的 bean 不止一个
- 没有 @Qualifier 注解:根据 @Autowired 标记位置成员变量的变量名作为 bean 的 id 进行匹配,能够找到:执行装配。找不到:装配失败
- 使用 @Qualifier 注解:根据 @Qualifier 注解中指定的名称作为 bean 的id进行匹配,能够找到:执行装配。找不到:装配失败。
@Controller(value = "tianDog")
public class SoldierController {
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "maomiService222")
// 根据面向接口编程思想,使用接口类型引入Service组件
private ISoldierService soldierService;(4)佛系装配
给 @Autowired 注解设置 required = false 属性表示:能装就装,装不上就不装。但是实际开发时,基本上所有需要装配组件的地方都是必须装配的,用不上这个属性。
@Controller(value = "tianDog")
public class SoldierController {
// 给@Autowired注解设置required = false属性表示:能装就装,装不上就不装
@Autowired(required = false)
private ISoldierService soldierService;(5)JSR-250 注解 @Resource
@Resource 注解也可以完成属性注入。那它和 @Autowired 注解有什么区别?
- @Resource 注解是 JDK 扩展包中的,也就是说属于 JDK 的一部分。所以该注解是标准注解,更加具有通用性。
- @Autowired 注解是 Spring 框架自己的。
- @Resource 注解默认根据 Bean 名称装配,未指定 name 时,使用属性名作为 name 。通过name 找不到的话会自动启动通过类型装配。
- @Autowired 注解默认根据类型装配,如果想根据名称装配,需要配合 @Qualifier 注解一起用。
- @Resource 注解用在属性上、setter 方法上。
- @Autowired 注解用在属性上、setter 方法上、构造方法上、构造方法参数上。
@Resource 注解属于 JDK 扩展包,所以不在 JDK 当中,需要额外引入以下依赖:【高于 JDK11或低于 JDK8 需要引入以下依赖】
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>@Resource 使用
@Controller
public class XxxController {
/**
* 1. 如果没有指定name,先根据属性名查找IoC中组件xxxService
* 2. 如果没有指定name,并且属性名没有对应的组件,会根据属性类型查找
* 3. 可以指定name名称查找! @Resource(name='test') == @Autowired + @Qualifier(value='test')
*/
@Resource
private XxxService xxxService;
//@Resource(name = "指定beanName")
//private XxxService xxxService;
public void show(){
System.out.println("XxxController.show");
xxxService.show();
}
}四、基于注解 + XML 方式整合三层架构组件
1、需求分析
搭建一个三层架构案例,模拟查询全部学生(学生表)信息,持久层使用 JdbcTemplate 和 Druid 技术,使用 XML + 注解方式进行组件管理。
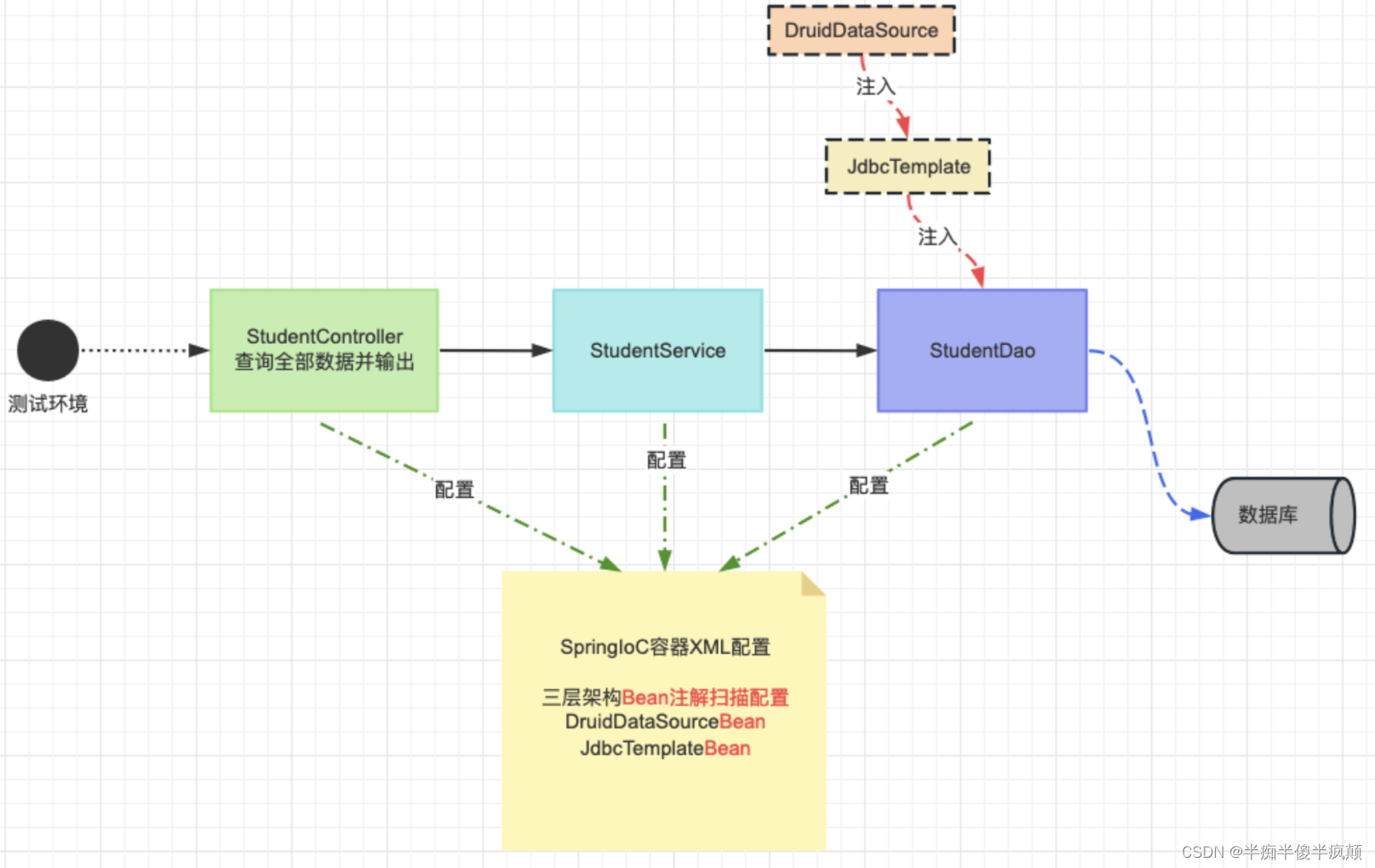
2、数据库准备
create database studb;
use studb;
CREATE TABLE students (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
gender VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
age INT,
class VARCHAR(50)
);
INSERT INTO students (id, name, gender, age, class)
VALUES
(1, '张三', '男', 20, '高中一班'),
(2, '李四', '男', 19, '高中二班'),
(3, '王五', '女', 18, '高中一班'),
(4, '赵六', '女', 20, '高中三班'),
(5, '刘七', '男', 19, '高中二班'),
(6, '陈八', '女', 18, '高中一班'),
(7, '杨九', '男', 20, '高中三班'),
(8, '吴十', '男', 19, '高中二班');
3、项目准备
a. 项目创建(spring-annotation-practice-04)
b. 依赖导入
<dependencies>
<!--spring context依赖-->
<!--当你引入SpringContext依赖之后,表示将Spring的基础依赖引入了-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据库驱动和连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.25</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring-jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>6.0.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies> c. 实体类准备
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String gender;
private Integer age;
private String classes;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getClasses() {
return classes;
}
public void setClasses(String classes) {
this.classes = classes;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", classes='" + classes + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
4、三层架构搭建和实现
a. 持久层
//接口
public interface StudentDao {
/**
* 查询全部学生数据
* @return
*/
List<Student> queryAll();
}
//实现类
@Repository
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
* 查询全部学生数据
* @return
*/
@Override
public List<Student> queryAll() {
String sql = "select id , name , age , gender , class as classes from students ;";
/*
query可以返回集合!
BeanPropertyRowMapper就是封装好RowMapper的实现,要求属性名和列名相同即可
*/
List<Student> studentList = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Student.class));
return studentList;
}
}
b. 业务层
//接口
public interface StudentService {
/**
* 查询全部学员业务
* @return
*/
List<Student> findAll();
}
//实现类
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentDao studentDao;
/**
* 查询全部学员业务
* @return
*/
@Override
public List<Student> findAll() {
List<Student> studentList = studentDao.queryAll();
return studentList;
}
}
c. 表述层
@Controller
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
public void findAll(){
List<Student> studentList = studentService.findAll();
System.out.println("studentList = " + studentList);
}
}
5、三层架构 IoC 配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 导入外部属性文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties" />
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean id="druidDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="url" value="${atguigu.url}"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${atguigu.driver}"/>
<property name="username" value="${atguigu.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${atguigu.password}"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource" />
</bean>
<!-- 扫描Ioc/DI注解 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.dao,com.atguigu.service,com.atguigu.controller" />
</beans>6、运行测试
public class ControllerTest {
@Test
public void testRun(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml");
StudentController studentController = applicationContext.getBean(StudentController.class);
studentController.findAll();
}
}





















 1072
1072

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








