练习1:求链表的中间元素
举例1:
输入:1 --> 2 --> 3
输出:2
举例2:
输入:1 --> 2 --> 3 --> 4
输出:2
数组:arr[(arr.length-1)/2]
链表:
1. 遍历链表,求链表的长度length
2. 从头遍历边表,找到索引为(length-1)/2的元素
public class Ex1 {
//已知头结点就可以遍历整个链表
public static int middleElement(Node head) {
// Caution:不要直接操作头结点
Node x = head;
// 遍历链表,求链表的长度length
int length = 0;
while (x != null) {
//x=null即表明遍历到末尾
length++;
x = x.next;
}
// 从头遍历边表,找到索引为(length-1)/2的元素
int index = 0;
x = head;
while (index < (length-1)/2) {
x = x.next;
index++;
}
return x.value;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1 --> 2 --> 3 --> 4
//头插法插入链表元素
Node head = new Node(4);
head = new Node(3, head);
head = new Node(2, head);
head = new Node(1, head);
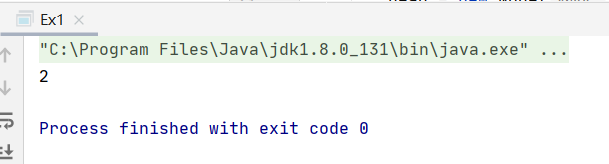
System.out.println(middleElement(head));
}
}
class Node {
int value;
Node next;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Node(int value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
public class Ex1 {
//已知头结点就可以遍历整个链表
public static int middleElement(Node head) {
// Caution:不要直接操作头结点
Node x = head;
// 遍历链表,求链表的长度length
int length = 0;
while (x != null) {
//x=null即表明遍历到末尾
length++;
x = x.next;
}
// 从头遍历边表,找到索引为(length-1)/2的元素
int index = 0;
x = head;
while (index < (length-1)/2) {
x = x.next;
index++;
}
return x.value;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1 --> 2 --> 3 --> 4
//头插法插入链表元素
Node head = new Node(4);
head = new Node(3, head);
head = new Node(2, head);
head = new Node(1, head);
System.out.println(middleElement(head));
}
}
class Node {
int value;
Node next;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Node(int value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
运行结果截图:
练习2:判断链表中是否有环

解法1:迷雾森林
a.创建集合visited,存储已经访问过的结点
b.遍历链表
c.判断结点是否已经在visited
是:返回true
否:把它添加到visited中,移动到下一个结点
d.链表遍历结束,返回false
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class Ex2 {
public static boolean hasCircle1(Node head) {
Collection c = new ArrayList();
Node x = head;
// 遍历链表
while (x != null) {
// 判断结点是否已经在visited中存在
if (c.contains(x)) return true;
c.add(x);
x = x.next;
}
// x == null
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1 --> 2 --> 3 --> 4 --> 2 --> ...
Node node = new Node(4);
Node head = new Node(3, node);
head = new Node(2, node);
node.next = head;
head = new Node(1, head);
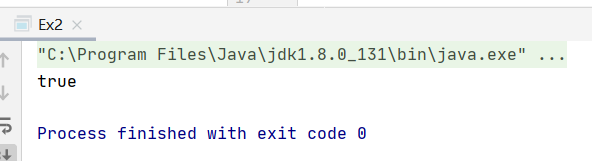
System.out.println(hasCircle1(head));
}
}
class Node {
int value;
Node next;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Node(int value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
运行结果截图:
时间复杂度:O(n^2)
空间复杂度:O(1)
解法二:跑道
a. 创建快慢指针,开始都指向head。快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步。
b. 遍历链表
快指针走到链表末尾,返回false
快慢指针相遇, 返回true
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class Ex2 {
/*
时间复杂度:O(n^2) --> O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
*/
public static boolean hasCircle1(Node head) {
Collection c = new ArrayList();
Node x = head;
// 遍历链表
while (x != null) {
// 判断结点是否已经在visited中存在
if (c.contains(x)) return true;
c.add(x);
x = x.next;
}
// x == null
return false;
}
/*
时间复杂度:O(n)
无环:要遍历n/2个结点,O(n)
有环:假设环外有a个结点,环内有r个结点
最好情况:O(a)
最坏情况:O(a + r)
平均情况:O(a + r/2)
空间复杂度:O(1)
*/
public static boolean hasCircle2(Node head) {
Node slow = head;
Node fast = head;
do {
// 判断快指针是否已经走到链表的末尾, 短路原则
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return false;
slow = slow.next;//慢指针每次走一步
fast = fast.next.next;//快指针每次走两步
} while (slow != fast);
// slow == fast
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1 --> 2 --> 3 --> 4 --> 4 --> ...
Node head = new Node(4);
head.next = head;
head = new Node(3, head);
head = new Node(2, head);
head = new Node(1, head);
System.out.println(hasCircle2(head));
}
}
class Node {
int value;
Node next;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Node(int value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
运行结果截图:

分析:
时间复杂度:O(n)
无环:要遍历n/2个结点,O(n)
有环:假设环外有a个结点,环内有r个结点
最好情况:O(a)
最坏情况:O(a + r)
平均情况:O(a + r/2)
空间复杂度:O(1)






















 407
407











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








