一、web容器的加载
首先我们要先知道一个web项目的启动过程。
-
将Web项目部署到Tomcat中的方法之一,是部署没有封装到WAR文件中的Web项目。要使用这一方法部署未打包的webapp目录,只要把我们的项目(编译好的发布项目,非开发项目)放到Tomcat的webapps目录下就可以了。
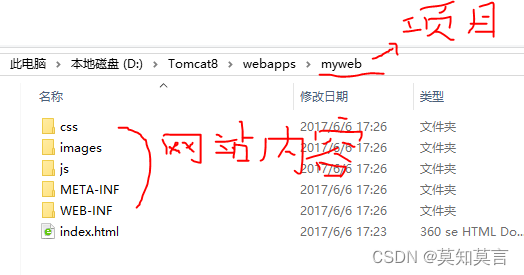
-
一个常规的Spring应用,在web容器启动时,默认会先去加载/WEB-INF/web.xml,它配置了:servletContext上下文、监听器(Listener)、过滤器(Filter)、Servlet等。
二、spring的启动
spring的启动过程其实就是ioc的启动过程。
spring的ioc支持了controller层注入service,service注入dao。打通了各层之间的桥梁,省去了原来的new service(),new Dao()的方法。
1、如上面所言,spring启动优先加载了web.xml,我们看看里面配置的内容。
web.xml 加载顺序为: context-param < listener < filter < servlet
<!--该元素用来声明应用范围(整个WEB项目)内的上下文初始化参数。 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:applicationContext*.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--监听器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!--servlet,mvc的前端控制器 -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<!--截获请求,匹配的请求都交由上面配置的mvc这个servlet处理 -->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!--过滤器 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>LoginValidateFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.tianque.clue.web.LoginValidateFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<!--截获请求,匹配的请求都经过上面配置的LoginValidateFilter过滤处理 -->
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>LoginValidateFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
在启动Web项目时,容器会读web.xml配置文件中的两个节点context-param和listener。
知晓web.xml配置内容后,我们详细看一下。
2.ContextLoaderListener
在启动Web项目时,容器(比如Tomcat)会读web.xml配置文件中的两个节点
listener和context-param
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
//该方法contextInitialized是重点
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
接着进入this.initWebApplicationContext方法,进入ContextLoader类中
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
} else {
//日志略
.......
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
if (this.context == null) {
//创建 WebApplicationContext
this.context = this.createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
ApplicationContext parent = this.loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
//该方法是重点,赋值初始化
this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
//略
........
return this.context;
} catch (Error | RuntimeException var8) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", var8);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, var8);
throw var8;
}
}
}
点进该方法细看源码
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
String configLocationParam;
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter("contextId");
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setId(configLocationParam);
} else {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX + ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
wac.setServletContext(sc);
//眼熟吧 contextConfigLocation就是web.xml里<context-param>
configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation");
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment)env).initPropertySources(sc, (ServletConfig)null);
}
this.customizeContext(sc, wac);
//重点方法,接来下会细看
wac.refresh();
}
点进去 wac.refresh();最后到了AbstractApplicationContext类中的refresh()
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Object var1 = this.startupShutdownMonitor;
//加锁
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//创建和准备了 Environment 对象
this.prepareRefresh();
//重点,该方法执行结束之后,xml中定义的bean就已经加载到IOC容器中了
//然而Bean 并没有完成初始化
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//完善 BeanFactory,设置 BeanFactory 的类加载器,添加 BeanPostProcessor,
//手动注册几个特殊的 bean。
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
//空方法
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//执行BeanFactory后置处理器,可以用来补充或修改 BeanDefinition
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//继续从 beanFactory 中找出 bean 后处理器,添加至 beanPostProcessors 集合中
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//国际化
this.initMessageSource();
//
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//空实现
this.onRefresh();
//注册监听器
this.registerListeners();
//这一步会将 beanFactory 的成员补充完毕,并初始化所有非延迟单例 bean
//Spring怎么解决循环依赖问题就在该方法里面的getBean再里面的
// doCreateBean()方法
//再往里的AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类的doCreateBean会判断
//是否有aop加强,在里面获得bean加强后的代理对象(aop源码)
//Spring为了解决单例的循环依赖问题,使用了三级缓存,当个问题写在文章最后
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//这一步会为 ApplicationContext 添加 lifecycleProcessor 成员,
//用来控制容器内需要生命周期管理的 bean
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var9);
throw var9;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
点进去 this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
//创建beanFactory
this.refreshBeanFactory();
return this.getBeanFactory();
}
进入 AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext类的refreshBeanFactory();
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (this.hasBeanFactory()) {
this.destroyBeans();
this.closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(this.getId());
this.customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//重点 加载bean定义
this.loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
Object var2 = this.beanFactoryMonitor;
synchronized(this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
} catch (IOException var5) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + this.getDisplayName(), var5);
}
}
点进去到XmlWebApplicationContext类的loadBeanDefinitions方法
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
//创建XmlBeanDefinitionReader对象,用于解析xml文件中定义的bean,
// 将xml文件转化为Resource流对象
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
this.initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
//重点方法
this.loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
点击进去细看
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws IOException {
//configLocations 获取到的就是applicationContext.xml文件
String[] configLocations = this.getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
String[] var3 = configLocations;
int var4 = configLocations.length;
//遍历每个配置文件,将配置文件中的标签解析成bean
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
String configLocation = var3[var5];
//重点方法
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocation);
}
}
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return this.loadBeanDefinitions(location, (Set)null);
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = this.getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot load bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
} else {
int count;
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
try {
//拿到resources 即配置文件转化的
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver)resourceLoader).getResources(location);
//继续进入方法
count = this.loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
Collections.addAll(actualResources, resources);
}
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
} catch (IOException var6) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", var6);
}
} else {
............
}
}
}
拿到resource[xml文件],进入this.loadBeanDefinitions(resources)方法,一路往下走,最终又会进入XmlBeanDefinitionReader类的loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource)方法
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
...略......
if (!((Set)currentResources).add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
} else {
int var5;
try {
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
//重点方法,进入细看
var5 = this.doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
} finally {
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException var15) {
.........
} finally {
..........
}
return var5;
}
}
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
//xml配置文件解析成document对象
Document doc = this.doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
//注册bean,重点
int count = this.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
return count;
} catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException var5) {
throw var5;
}
//各种try catch异常代码略
}
doLoadBeanDefinitions()方法中主要包含2个步骤,第一步根据inputSource和resource获取到一个Document对象,我们知道xml文档可以解析成一个document树,其中最外层标签就是root元素,子标签就是一个个的叶子node,具体的解析成Document对象的过程不用过于纠结,Spring提供了详细实现, 第二步就是讲document对象注册到Spring容器里,而resouce参数用来选择XmlReaderContext
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = this.createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = this.getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
//重点,点进去细看
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, this.createReaderContext(resource));
return this.getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
一步步点击
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = this.createDelegate(this.getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute("profile");
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(profileSpec, ",; ");
if (!this.getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec + "] not matching: " + this.getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
this.preProcessXml(root);
//重点方法,点进去细看
this.parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
this.postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for(int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); ++i) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element)node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
//重点方法,解析标签元素
this.parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
} else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
} else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, "import")) {
this.importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
} else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, "alias")) {
this.processAliasRegistration(ele);
} else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, "bean")) {
//重点看bean标签
this.processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
} else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, "beans")) {
this.doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
//不细看了,把bean标签的id,name解析返回BeanDefinitionHolder
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {//有需要就装饰
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
//重点,点进去细看
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, this.getReaderContext().getRegistry());
} catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException var5) {
this.getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" + bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, var5);
}
this.getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
public static void registerBeanDefinition(BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
//重点,点进去细看
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
String[] var4 = aliases;
int var5 = aliases.length;
for(int var6 = 0; var6 < var5; ++var6) {
String alias = var4[var6];
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
最终就是往Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap中放beanDefinition
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
至此this.obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法方法解析完毕。
该方法总结:
-
这一步获取(或创建) BeanFactory,它也是作为 ApplicationContext 的一个成员变量
-
BeanFactory 的作用是负责 bean 的创建、依赖注入和初始化,bean 的各项特征由 BeanDefinition 定义
-
BeanDefinition 作为 bean 的设计蓝图,规定了 bean 的特征,如单例多例、依赖关系、初始销毁方法等
-
BeanDefinition 的来源有多种多样,可以是通过 xml 获得、配置类获得、组件扫描获得,也可以是编程添加
-
所有的 BeanDefinition 会存入 BeanFactory 中的 beanDefinitionMap 集合
核心方法讲解完了,其他方法感兴趣可自行了解,不多赘述了。最后写个小问题。
spring管理的bean在默认情况下是会在服务器启动的时候初始化的。
bean设置了scope为prototype(原型)之后,会每次使用时生产一个
bean设置了lazy-init=”true”后,启动服务器不会马上实例化,而是在用到的时候被实例化。
问题:Spring怎么解决循环依赖问题?
循环依赖其实就是循环引用,也就是两个或则两个以上的bean互相持有对方,最终形成闭环。比如A依赖于B,B依赖于C,C又依赖于A。
doCreateBean 方法有三个核心流程。实例化,填充属性,初始化。
循环依赖主要发生在第一、第二步。也就是构造器循环依赖和field循环依赖。
那么我们要解决循环引用也应该从初始化过程着手,对于单例来说,在Spring容器整个生命周期内,有且只有一个对象,所以很容易想到这个对象应该存在Cache中,Spring为了解决单例的循环依赖问题,使用了三级缓存。
我们看一下doGetBean方法中的getSingleton方法。
Object sharedInstance = this.getSingleton(beanName);
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
//判断当前单例bean是否正在创建中,也就是没有初始化完成
//比如A的构造器依赖了B对象所以得先去创建B对象
// 或则在A的populateBean过程中依赖了B对象,得先去创建B对象,
//这时的A就是处于创建中的状态。
if (singletonObject == null && this.isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
Map var4 = this.singletonObjects;
synchronized(this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
// 是否允许从singletonFactories中通过getObject拿到对象
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = (ObjectFactory)this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
该方法还依赖于三个map,这三个map就是三级缓存。
分析getSingleton()的整个过程,Spring首先从一级缓存singletonObjects中获取。如果获取不到,并且对象正在创建中,就再从二级缓存earlySingletonObjects中获取。
如果还是获取不到且允许singletonFactories通过getObject()获取,就从三级缓存singletonFactory.getObject()(三级缓存)获取,如果获取到了则从singletonFactories中移除,并放入earlySingletonObjects中。
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
其实也就是从三级缓存移动到了二级缓存。
从上面三级缓存的分析,我们可以知道,Spring解决循环依赖的诀窍就在于singletonFactories这个三级cache里就是解决循环依赖的关键,这段代码发生在createBeanInstance之后,也就是说单例对象此时已经被创建出来(调用了构造器)。这个对象已经被生产出来了,虽然还不完美(还没有进行初始化的第二步和第三步),但是已经能被人认出来了(根据对象引用能定位到堆中的对象),所以Spring此时将这个对象提前曝光出来让大家认识,让大家使用。





















 219
219











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








