前提假设
字符串str1和str2,str1是否包含str2,如果包含返回str2在str1中开始的位置。如str1:ABC1234de str2:1234de str1就包含str2。
经典的做法是,依次遍历str1和str2进行比较,最差的情况例如:str1:11111111112(长度N) str2:1112(长度M),那么时间复杂度是O(N * M)
如何进行优化呢?实现时间复杂度是O(N)
KMP算法
str2的前缀和后缀
在实现KMP算法之前,我们首先需要知道的是str2的前缀和后缀相等时的最大长度,以此作为一个辅助数组,而这个数组在KMP算法中起到关键性的作用。记为next[i]。
next[i]: 在i字符之前的所有字符求其前缀和后缀相等时的最大长度(前缀和后缀不能是字符串本身),我们设定next[0] = -1; next[1] = 0;
例如:aabaabs next[0] = -1; next[1] = 0; next[2] = 1; next[3] = 0; next[4] = 1; next[5] = 2; next[6] = 3;
那该怎样求str2的next[i]数组呢?
我们求next[i]的时候要利用上next[i - 1]的值。参考下图:
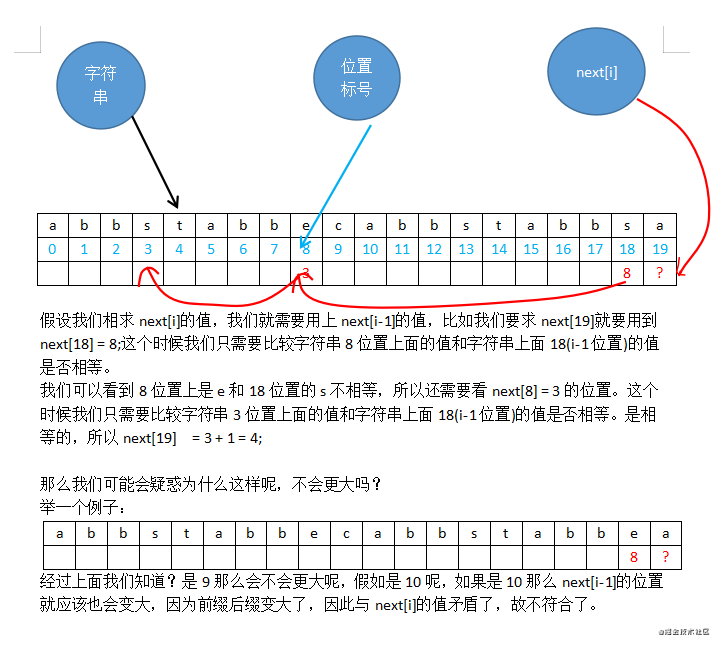
///
我们可以结合代码加深一下理解:
public static int[] getNextArray(char[] ms) {
//因为我们设定的就是next[0] = -1;
if (ms.length == 1) {
return new int[]{-1};
}
int[] next = new int[ms.length];
next[0] = -1;
next[1] = 0;
//因为next[0]和next[1]的值已经预定了,所以i直接从2开始
int i = 2;
//初始cn记录的是next[i- 1]的值,因为这里i的初始是2,所以next[i-1] = 0,所以cn = 0;
int cn = 0;
while (i < next.length) {
//类比图中的实例,就可以看懂,ms是字符串转变的字符型数组
if (ms[i - 1] == ms[cn]) {
//因为相等,那么next[i] = (cn+1);
//这是要进行求下一个i所以next[(i + 1)]
//因为经过这一步,会使下一个next[]到(ms[(cn+1)])来比较,所以cn也加1
next[i++] = ++cn;
} else if (cn > 0) {
//如果第一步不相等,按照图的实例继续比较ms[next[cn]]
cn = next[cn];
} else {
//等于0,表示到达ms[0]的位置,这个时候还不相等只有next[i++] = 0了;
next[i++] = 0;
}
}
return next;
}
KMP算法的实现
当我们有了next数组,我们就可以利用其进行比较了。
参考下图:
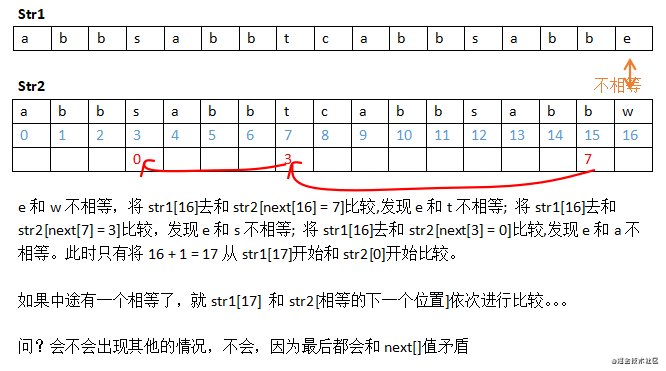
///
我们可以结合代码加深一下理解:
public static int KMP(String s,String m){
if (s == null || m == null || m.length() < 1 || s.length() < m.length()){
return -1;
}
char[] str1 = s.toCharArray();
char[] str2 = m.toCharArray();
//str1的光标
int i1 = 0;
//str2的光标
int i2 = 0;
//获得next数组
int[] next = getNextArray(str2);
//核心代码
while (i1 < str1.length && i2 < str2.length){
//如果两者相等,两者光标都向后移动
if (str1[i1] == str2[i2]){
i1++;
i2++;
}else if(next[i2] == -1){//或者写成i2 == 0;也就是来到了最开头了。
//在最开头比较还不相等,只有Str1的光标向后移动了
i1++;
}else {
//按图理解,前两个都不满足就重新定位str2光标
i2 = next[i2];
}
}
//str2正常跑完就代表找到了
return i2 == str2.length ? i1 - i2 : -1;
}
总体代码
public static int[] getNextArray(char[] ms) {
//因为我们设定的就是next[0] = -1;
if (ms.length == 1) {
return new int[]{-1};
}
int[] next = new int[ms.length];
next[0] = -1;
next[1] = 0;
//因为next[0]和next[1]的值已经预定了,所以i直接从2开始
int i = 2;
//初始cn记录的是next[i- 1]的值,因为这里i的初始是2,所以next[i-1] = 0,所以cn = 0;
int cn = 0;
while (i < next.length) {
//类比图中的实例,就可以看懂,ms是字符串转变的字符型数组
if (ms[i - 1] == ms[cn]) {
//因为相等,那么next[i] = (cn+1);
//这是要进行求下一个i所以next[(i + 1)]
//因为经过这一步,会使下一个next[]到(ms[(cn+1)])来比较,所以cn也加1
next[i++] = ++cn;
} else if (cn > 0) {
//如果第一步不相等,按照图的实例继续比较ms[next[cn]]
cn = next[cn];
} else {
//等于0,表示到达ms[0]的位置,这个时候还不相等只有next[i++] = 0了;
next[i++] = 0;
}
}
return next;
}
public static int KMP(String s,String m){
if (s == null || m == null || m.length() < 1 || s.length() < m.length()){
return -1;
}
char[] str1 = s.toCharArray();
char[] str2 = m.toCharArray();
//str1的光标
int i1 = 0;
//str2的光标
int i2 = 0;
//获得next数组
int[] next = getNextArray(str2);
//核心代码
while (i1 < str1.length && i2 < str2.length){
//如果两者相等,两者光标都向后移动
if (str1[i1] == str2[i2]){
i1++;
i2++;
}else if(next[i2] == -1){//或者写成i2 == 0;也就是来到了最开头了。
//在最开头比较还不相等,只有Str1的光标向后移动了
i1++;
}else {
//按图理解,前两个都不满足就重新定位str2光标
i2 = next[i2];
}
}
//str2正常跑完就代表找到了
return i2 == str2.length ? i1 - i2 : -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abcabcababaccc";
String str2 = "ababa";
System.out.println(KMP(str1, str2));
}




















 20万+
20万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








