Springboot+Security(一)自定义验证
使用springboot+springsecurity+mybatis 实现数据库动态的管理:用户-角色-权限
1.数据库表:

2.验证授权
2.1 实体类
User.Java
User这个实体类需要实现接口UserDetails 其他实体类直接创建
public class User implements UserDetails {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String nickname;
private boolean enabled;
private List<Role> roles;
private String email;
private String userface;
private Date regtime;
private List<GrantedAuthority> authorities;
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
return this.authorities;
}
public void setAuthorities(List<GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
this.authorities = authorities;
}
@Override
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return enabled;
}
//get和set...
}
2.2 Dao层
PermissionMapper.java
PermissionMapper实现用户所拥有的权限的查询和获取所有权限列表
@Repository
public interface PermissionMapper {
//通过用户的ID查找到用户所拥有的权限
List<Permission> findByUserid(@Param("userId") int userId);
//获得所有的权限即权限列表
List<Permission> findAll();
}
在src/resources/sqlmapper下创建对应的mapper.xml文件
PermissionMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="com.example.springsecurity.dao.PermissionMapper" >
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.example.springsecurity.Pojo.Permission" >
<id column="id" property="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
<result column="name" property="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="descritpion" property="descritpion" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="url" property="url" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result column="pid" property="pid" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
</resultMap>
<select id="findByUserid" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select p.*
from user u
LEFT JOIN user_role sru on u.id= sru.u_id
LEFT JOIN role r on sru.r_id=r.id
LEFT JOIN permission_role spr on spr.r_id=r.id
LEFT JOIN permission p on p.id =spr.permission_id
where u.id=#{userId}
</select>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select * from permission
</select>
</mapper>
之后在service层完成对dao层的调用,然后实际使用service层中的类和方法。
2.3 创建自定义的Handler
在这里只创建了两个自定的Handler,一个是登录成功,一个是登录失败。而且这里的Handler是返回的JSON数据。
MyAuthenticationFailHandler.java(登录失败)
//登录失败执行的操作 这里 是返回JSON数据给前端
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationFailHandler extends SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
logger.info("登录失败");
//以Json格式返回
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("code", "201");
map.put("msg", "登录失败");
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value());
response.setContentType("application/json");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(map));
}
}
MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler.java(登陆成功)
//登录成功执行的操作 这里 是返回JSON数据给前端
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler extends SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication)
throws IOException, ServletException {
//什么都不做的话,那就直接调用父类的方法
//super.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authentication);
//这里可以根据实际情况,来确定是跳转到页面或者json格式。
//如果是返回json格式,那么这么写
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("code", "200");
map.put("msg", "登录成功");
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(map));
//如果是要跳转到某个页面的 "/index" 表示跳转到index页面
//new DefaultRedirectStrategy().sendRedirect(request, response, "/index");
}
}
2.4 实现UserDetailsService接口,返回用户数据给自定义AuthenticationProvider来对用户验证授权
实质是AuthenticationManager来验证,AuthenticationManager是一个接口,只有一个authenticate()方法。
这个接口的常见的实现是ProviderManager,而ProviderManger它不自己处理验证,而是委托给所配置的AuthenticationProvider列表来验证。
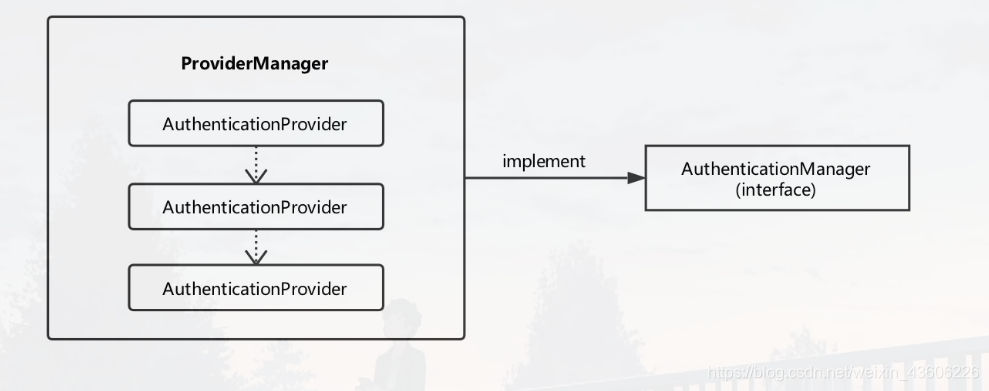
依次调用列表中的AuthenticationProvider验证,只要有一个AuthenticationProvider验证成功,就不再验证,直接以该验证的成果作为ProviderManager的验证结果
MyUserDetailsService.java(实现UserDetailsService接口)
// 返回用户信息给 AuthenticationProvider 去验证
@Component
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private PermissionService permissionService;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//通过用户名找到用户的信息
User user=userService.selectbyname(username);
if(user!=null) {
//通过用户的ID获得用户所拥有的权限
List<Permission> permissions= permissionService.findByUserid(user.getId());
List<GrantedAuthority> grantedAuthorities=new ArrayList<>();
for (Permission permission : permissions) {
if (permission != null && permission.getName()!=null) {
GrantedAuthority grantedAuthority = new SimpleGrantedAuthority(permission.getName());
//将权限信息添加到 GrantedAuthority 对象中,在后面进行全权限验证时会使用GrantedAuthority 对象。
grantedAuthorities.add(grantedAuthority);
}
}
//把用户的权限加入用户的信息中
user.setAuthorities(grantedAuthorities);
//把用户信息返回给AuthenticationProvider
return user;
}
return null;
}
}
MyAuthenticationProvider.java(自定义AuthenticationProvider)
在方法中调用UserDetailsService中的loadUserByUsername 获取用户信息然后验证,验证成功就把用户的详细信息放入spring的全局缓存SecurityContextHolder中,以便在后面访问资源时候方便调用用户信息。
//认证授权
// AuthenticationManager 将验证工作交给ProviderManager 而ProviderManager委托所配置的AuthenticationProvider列表 来验证
//验证用户通过后 授予用户权限 把用户信息保存在spring的全局缓存SecurityContextHolder 好让后面访问资源时 能够调用(比如访问资源时候鉴权)
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
@Autowired
private MyUserDetailsService userDetailService;
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String userName = authentication.getName();// 这个获取表单输入中返回的用户名;
String password = (String)authentication.getCredentials();// 这个是表单中输入的密码;
// 这里构建来判断用户是否存在和密码是否正确
User userInfo = (User) userDetailService.loadUserByUsername(userName); // 这里调用我们的自己写的获取用户的方法;
if (userInfo == null) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("用户名不存在");
}
if (!passwordEncoder.matches(password,userInfo.getPassword())) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("密码不正确");
}
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = userInfo.getAuthorities();
//getAuthorities()是获取权限信息的方法
// 构建返回的用户登录成功的token
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(userInfo, password, authorities);
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> aClass) {
return true;
}
}
3.完成securityConfig的配置
securityConfig.java
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationProvider provider; //注入我们自己的AuthenticationProvider
@Autowired
private MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler myAuthenticationSuccessHandler;
@Autowired
private MyAuthenticationFailHandler myAuthenticationFailHandler;
@Autowired
private MyFilterSecurityInterceptor myFilterSecurityInterceptor;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.
authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/").hasAnyRole("USER","ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.csrf().disable()
.formLogin().loginPage("/login").permitAll()
.loginProcessingUrl("/form")
.successHandler(myAuthenticationSuccessHandler)
.failureHandler(myAuthenticationFailHandler);
}
//配置我们自定义的验证授权 让 spring security使用我们自定义的验证器 而不是默认的验证器 也就是MyAuthenticationProvider
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//注册一个自定义的 AuthenticationProvider
auth.authenticationProvider(provider);
//再注册一个基于内存的 AuthenticationProvider
// auth
// .inMemoryAuthentication()
// .withUser("admin").password("123456").roles("USER")
// .and()
// .withUser("test").password("test123").roles("ADMIN");
}
//定义了密码的加密方式 这里用了BCrypt加密
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
4.创建测试用的控制器和页面
4.1控制器创建
TestController.java
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index(Model model){
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/admin")
@ResponseBody
public String hello(){
return "hello admin,拥有admin权限";
}
@RequestMapping("/whoim")
@ResponseBody
public Object whoIm() {
return SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
}
}
4.2 创建测试页面
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h5>
访问到了首页
</h5>
</body>
</html>
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html id="ng-app" ng-app="app" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>home</title>
</head>
<body>
<form class="form-signin" action="/form" method="post">
<h2 class="form-signin-heading">用户登录</h2>
<table>
<tr>
<td>用户名:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="username" class="form-control" placeholder="请输入用户名"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>密码:</td>
<td><input type="password" name="password" class="form-control" placeholder="请输入密码" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" >登录</button>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
5.测试
5.1 先创建测试数据
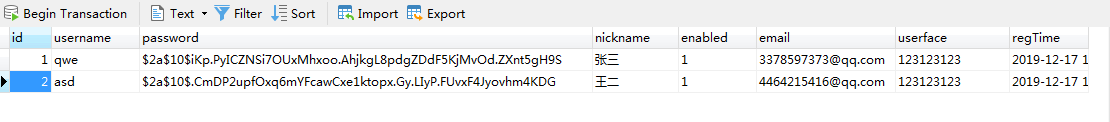
user表(用户表)自己创建两个用户 密码记得要用BCrypt加密 也就是在SecurityConfig中的PasswordEncoder Bean来加密密码。这里插入用户最好用mybatis来创建,能够在方法中调用PasswordEncoder Bean实现密码的加密。
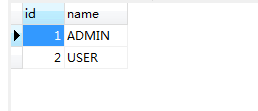
role表(角色表)创建两个角色 一个ADMIN,一个USER
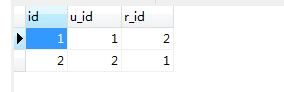
user_role表(用户角色关系表) 用户ID 1 拥有普通用户角色 用户ID 2拥有管理员的角色
role表(权限表)也设置两个权限 一个用户权限,一个管理员权限 。
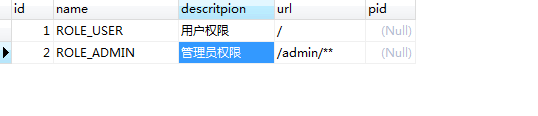
permission_role表(权限角色关系表) 管理员角色拥有用户权限和管理员权限,用户角色只拥有管理员权限
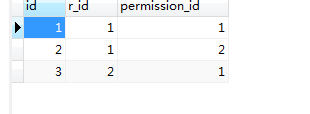
5.2 开始测试
直接访问localhost:8080 会跳转到localhost:8080/login 也就是登录页面

然后先用普通用户登录
登录成功的页面

再访问localhost:8080 就能成功访问到首页了 因为是普通用户角色 拥有Role_USER权限

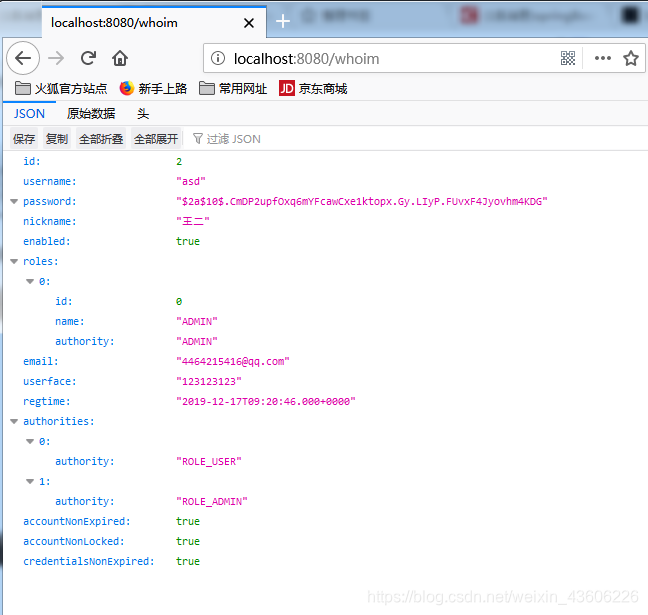
访问localhost:8080/whoim 可以看到自己拥有的权限
接着访问localhost:8080/admin会发现 报403的错误 表示没有访问这个资源的权限

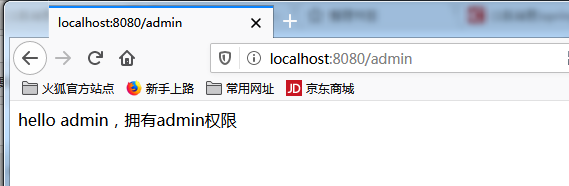
然后登陆用户2 拥有管理员角色的 再访问localhost:8080/admin
访问 localhost:8080/whoim 查看自己拥有的权限





















 1689
1689











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








