总体思路
- 1.首先是判断两个链表是否有环,有的话返回其环的入口 没有返回null
- 2.一共两种情况 (1)两个无环链表相交(2)两个有环链表相交 (至于为啥没有一个有环一个没环的相交 因为我们的是单链表)
- 其中两个有环链表相交又分为三种情况:
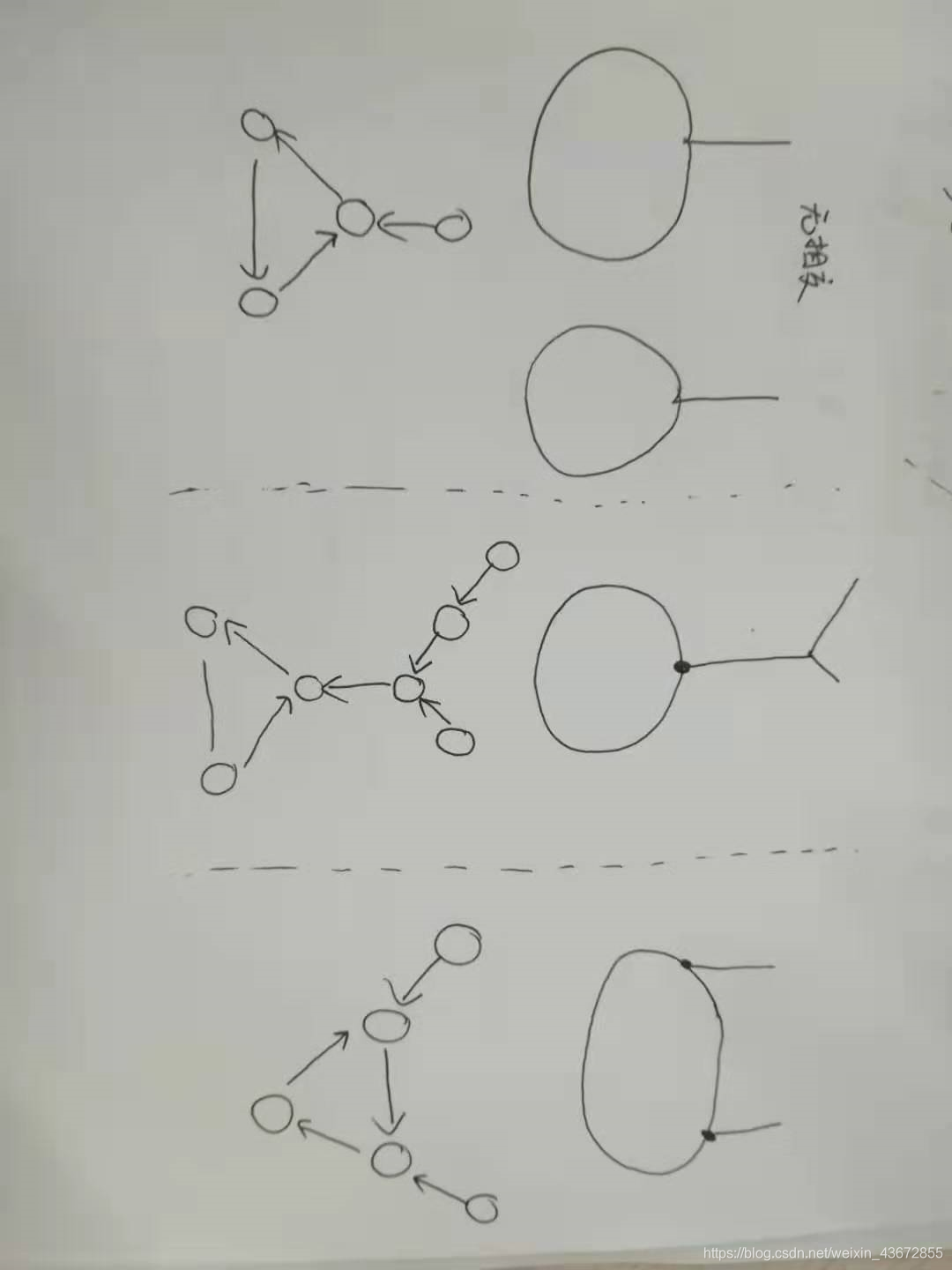
- 其中两个有环链表相交又分为三种情况:
先总结下涉及到的小知识点:
(1)求单链表是否有环 如果有环,返回环入口的第一个节点否则返回null
- 细节思路:利用快慢指针做,快的一次两步慢的一次一步,快慢相交后,快从头指针开始走,一次改为一步,快慢同时开始走,相遇的就是环的第一个节点(你也可以用哈希表,就是费空间)
(2)求两个无环单链表是否相交,相交返回第一个相交的节点否则返回null
- 细节思路:先求两个链表大小的差值,长的那个先走到跟短的一样长后,开始一起走,相遇到就是返回,到头了返回null
(3)两个有环单链表是否相交,相交返回第一个相交的几节点,否则返回null
-
细节思路:见图 对于两个链表的第一个入环节点相同的情况(其实比较的是第一个入环节点的内存地址是否相同)直接转化为求两个无环链表第一个相交的节点的情况
-
细节思路:对于两个链表的第一个入环节点不相同的情况,则从第一个链表的入环节点的下一个节点开始走,如果碰到了第二个链表的入环节点,那么,返回第一个链表或者第二个链表的入环节点均可,因为都是第一个,只是跟原先的链表的距离不同而已。如果走完没找到 那么就是图中的第一种情况了,直接返回null。
-
首先 让我们看一下实现总体功能的函数(就是我们直接调用的函数):
public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2){
// 1.首先是判断两个链表是否有环,有的话返回其环的入口 没有返回null
// 2.一共两种情况 (1)两个无环链表相交(2)两个有环链表相交
// 至于为啥没有一个有环一个没环的 相交 因为我们的是单链表
if(head1 == null || head2 == null){
return null;
}
//1.先求两个节点的入环节点
Node loop1 = getLoopNode(head1);
Node loop2 = getLoopNode(head2);
if(loop1 == null && loop2 == null){
return noLoop(head1, head2);
}
if (loop1 != null && loop2 != null){
return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2);
}
return null;
}
- 下面是求单链表是否有环的代码:
//给一个链表 返回其入环第一个节点
public static Node getLoopNode(Node head){
//首先是最少三个节点才能成环
if(head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null){
return null;
}
Node slow = head.next;
Node first = head.next.next;
while (first != slow){
if(first.next == null || first.next.next == null){
return null;
}
first = first.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
first = head;
while (first != slow){
first = first.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return first;
}
- 下面是求两个无环单链表是否相交的代码:
//这是求 两个无环链表相交的第一个节点
public static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2){
int len1 = 0;
int len2 = 0;
Node cur1 = head1;
Node cur2 = head2;
while (head1 != null){
len1++;
head1 = head1.next;
}
while (head2 != null){
len2++;
head2 = head2.next;
}
int n = len1 - len2;
if(n > 0){
while (n > 0){
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur1 != null){
if(cur1 == cur2){
return cur1;
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return null;
}else if(n < 0){
n = Math.abs(n);
while (n > 0){
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
while (cur1 != null){
if(cur1 == cur2){
return cur1;
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return null;
}else{
while (cur1 != null){
if(cur1 == cur2){
return cur1;
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return null;
}
}
- 下面是求有环单链表是否相交的代码:
//(2)两个有环链表相交 一共三种情况:
// 1.无交点
// 2.两个环的交点是一个
// 3.两个环的交点不是一个
public static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2){
Node cur1 = null;
Node cur2 = null;
int n1 = 0;
int n2 = 0;
//第2种情况
if(loop1 == loop2){
cur1 = head1;
cur2 = head2;
while (cur1 != loop1){
n1++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2 != loop2){
n2++;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
int n3 = n1 - n2;
cur1 = head1;
cur2 = head2;
if(n3 > 0){
while (n3 > 0){
n3--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur1 != loop1){
if(cur1 == cur2){
return cur1;
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}else if(n3 < 0){
n3 = Math.abs(n3);
while (n3 > 0){
n3--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
while (cur1 != loop2){
if(cur1 == cur2){
return cur1;
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}else {
while (cur1 != loop1){
if(cur1 == cur2){
return cur1;
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
} else{
Node p = loop1.next;
while (p != loop1){
if(p == loop2){
return loop1;
}
p = p.next;
}
return null;
}
}
- 最后是我们的主函数,就是测试函数:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->null
Node head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(3);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
// 0->9->8->6->7->null
Node head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
System.out.println(noLoop(head1, head2).value);
// 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->4...
head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(3);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next; // 7->4
// 0->9->8->2...
head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next; // 8->2
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
// 0->9->8->6->4->5->6..
head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
}






















 1269
1269











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








