保存配置方法
一、Settings.setting 文件
- 方便保存和读取参数
1.1 配置Settings.settings文件

自由配置参数名称和值,
注:范围的选择(用户运行时可更改,应用程序则运行时不可更改)
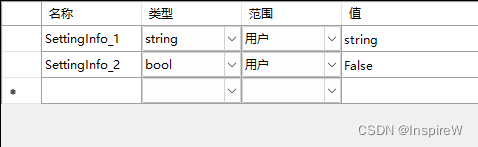
1.2 加载配置信息
在窗体加载时,直接载入
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.label1.Text = Properties.Settings.Default.SettingInfo_1;
this.checkBox1.Checked = Properties.Settings.Default.SettingInfo_2;
}
1.3 保存配置信息
private void Form1_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
Properties.Settings.Default.SettingInfo_1 = "NewSettingInfo_1";
Properties.Settings.Default.SettingInfo_2 = true;
Properties.Settings.Default.Save(); //使用Save方法保存更改,必要
}
二、使用文本保存
- 通过类【iniHelper】对数据进行直接保存,文件名:Config.ini 保存结果如下
[PLC参数]
IP=192.168.2.4
Port=19622
2.1 引入命名空间
using System.IO;
2.2 新增IniConfigHelper 类
using System;
using System.Text;
using System.IO;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Helper
{
public class IniConfigHelper
{
public static string filePath = "";
#region API函数声明
[DllImport("kernel32")]
private static extern long WritePrivateProfileString(string section, string key,
string val, string filePath);
//需要调用GetPrivateProfileString的重载
[DllImport("kernel32", EntryPoint = "GetPrivateProfileString")]
private static extern long GetPrivateProfileString(string section, string key,
string def, StringBuilder retVal, int size, string filePath);
[DllImport("kernel32", EntryPoint = "GetPrivateProfileString")]
private static extern uint GetPrivateProfileStringA(string section, string key,
string def, Byte[] retVal, int size, string filePath);
#endregion
#region 获取所有的Sections
/// <summary>
/// 获取所有的Sections
/// </summary>
/// <param name="iniFilename">文件路径</param>
/// <returns>Sections集合</returns>
public static List<string> ReadSections(string iniFilename)
{
List<string> result = new List<string>();
Byte[] buf = new Byte[65536];
uint len = GetPrivateProfileStringA(null, null, null, buf, buf.Length, iniFilename);
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
if (buf[i] == 0)
{
result.Add(Encoding.Default.GetString(buf, j, i - j));
j = i + 1;
}
return result;
}
#endregion
#region 获取指定Section下的所有Keys
/// <summary>
/// 获取指定Section下的所有Keys
/// </summary>
/// <param name="SectionName">SectionName</param>
/// <param name="iniFilename">文件路径</param>
/// <returns>Keys集合</returns>
public static List<string> ReadKeys(string SectionName, string iniFilename)
{
List<string> result = new List<string>();
Byte[] buf = new Byte[65536];
uint len = GetPrivateProfileStringA(SectionName, null, null, buf, buf.Length, iniFilename);
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
if (buf[i] == 0)
{
result.Add(Encoding.Default.GetString(buf, j, i - j));
j = i + 1;
}
return result;
}
#endregion
#region 读Ini文件
public static string ReadIniData(string Section, string Key, string NoText)
{
return ReadIniData(Section, Key, NoText, filePath);
}
public static string ReadIniData(string Section, string Key, string NoText, string iniFilePath)
{
if (File.Exists(iniFilePath))
{
StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder(1024);
GetPrivateProfileString(Section, Key, NoText, temp, 1024, iniFilePath);
return temp.ToString();
}
else return string.Empty;
}
#endregion
#region 写Ini文件
public static bool WriteIniData(string Section, string Key, string Value)
{
return WriteIniData(Section, Key, Value, filePath);
}
public static bool WriteIniData(string Section, string Key, string Value, string iniFilePath)
{
long OpStation = WritePrivateProfileString(Section, Key, Value, iniFilePath);
if (OpStation == 0)
return false;
else return true;
}
#endregion
}
}
2.3 测试新建数据
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Helper.IniConfigHelper.WriteIniData("PLC参数", "IP", "192.168.2.4", Application.StartupPath + "\\Settings.ini");
}
2.4 关闭窗口时保存数据
private void Form1_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
// 如果文件不存在则创建文件后再保存
if (!File.Exists(configPath))
{
FileStream fileStream = new FileStream(configPath, FileMode.Create);
fileStream.Close();
}
IniConfigHelper.WriteIniData("PLC参数", "IP", this.textBoxIPAddress.Text.Trim(), configPath);
IniConfigHelper.WriteIniData("PLC参数", "Port", this.textBoxPort.Text.Trim(), configPath);
}
2.5 窗口加载时读取数据
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 如果文件存在,则读取相应的参数信息
if (File.Exists(configPath))
{
this.textBoxIPAddress.Text = IniConfigHelper.ReadIniData("PLC参数", "IP", "", configPath);
this.textBoxPort.Text = IniConfigHelper.ReadIniData("PLC参数", "Port", "", configPath);
}
}
三、序列化与反序列化
- 更方便读取和写入大量配置信息
- 数据更安全
3.1 引入命名空间
using System.IO;
using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary;
3.2 新增Student 类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace #此处修改为项目名称
{
[Serializable] // 对象可序列化标记,必须
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Gender { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public DateTime Birthday { get; set; }
}
}
3.3 保存配置
private void btnSerialize_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//封装对象信息
Student objStu = new Student()
{
Name = this.txtName.Text.Trim(),
Age = Convert.ToInt16(this.txtAge.Text.Trim()),
Gender = this.txtGender.Text.Trim(),
Birthday = Convert.ToDateTime(this.txtBirthday.Text.Trim())
};
//【1】创建文件流
FileStream fs = new FileStream("C:\\objStu.obj", FileMode.Create);
//【2】创建二进制格式化器
BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
//【3】调用序列化方法
formatter.Serialize(fs, objStu);
//【4】关闭文件流
fs.Close();
}
3.4 打开配置
private void btnDeserialize_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//【1】创建文件流
FileStream fs = new FileStream("C:\\objStu.obj", FileMode.Open);
//【2】创建二进制格式化器
BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
//【3】调用序列化方法
Student objStu = (Student)formatter.Deserialize(fs);
//【4】关闭文件流
fs.Close();
//显示对象属性
this.txtName.Text = objStu.Name;
this.txtAge.Text = objStu.Age.ToString();
this.txtGender.Text = objStu.Gender;
this.txtBirthday.Text = objStu.Birthday.ToShortDateString();
}
四、XML
(更新:本文不是LinQ 进行操作,推荐使用C#中的Linq to Xml详解)
4.1 引入命名空间
using System.Xml;
4.2 XML示范文件
<Students>
<Student>
<StuName>王永利</StuName>
<StuAge>19</StuAge>
<Gender>男</Gender>
<ClassName>计算机1班</ClassName>
</Student>
<Student>
<StuName>王大拿</StuName>
<StuAge>22</StuAge>
<Gender>男</Gender>
<ClassName>计算机2班</ClassName>
</Student>
<DataInfo>
<Version vNo="1.2" pTime="2012-12-12">数据版本信息</Version>
</DataInfo>
</Students>
4.3 写入XML文件(待补充)
4.4 读取XML文件
private void btnLoadXML_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
XmlDocument objDoc = new XmlDocument(); //【1】创建XML文档操作对象
objDoc.Load("StuScore.xml"); //【2】加载XML文件到文档对象中
XmlNode rootNode = objDoc.DocumentElement; //【3】获取XML文档根目录
List<Student> list = new List<Student>();//创建对象集合
foreach (XmlNode stuNode in rootNode.ChildNodes) //【4】遍历根节点(根节点包含所有节点)
{
if (stuNode.Name == "Student")
{
Student objStu = new Student();
foreach (XmlNode subNode in stuNode) //【5】遍历子节点
{
switch (subNode.Name)//根据子节点的名称封装到对象的属性
{
case "StuName":
objStu.StuName = subNode.InnerText;//获取《节点名称》对应的《节点值》
break;
case "StuAge":
objStu.StuAge = Convert.ToInt16(subNode.InnerText);
break;
case "Gender":
objStu.Gender = subNode.InnerText;
break;
case "ClassName":
objStu.ClassName = subNode.InnerText;
break;
}
}
list.Add(objStu);
}
}
this.dgvStuList.DataSource = list;
}
4.5 查找方法
private void btnShowVersion_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//创建XML读取器
XmlTextReader tReader = new XmlTextReader("StuScore.xml");
string info = string.Empty;
//循环查询
while (tReader.Read())
{
if (tReader.Name == "Version")
{
info = "版本:" + tReader.GetAttribute("vNo") + " 发布时间:" + tReader.GetAttribute("pTime");
break;
}
}
MessageBox.Show(info,"数据版本");
}
写在最后
本博文只是我在学习c#的过程中所做的笔记,方便以后查阅实现过程。资料均来自网上,如果有侵权请联系我删除,谢谢。





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








