前言
在实际的项目中,对于一些用时比较长的代码片段或者函数,我们可以采用异步的方式来执行,这样就不会影响整体的流程了。比如我在一个用户请求中需要上传一些文件,但是上传文件的耗时会相对来说比较长,这个时候如果上传文件的成功与否不影响主流程的话,就可以把上传文件的操作异步化,在spring boot中比较常见的方式就是把要异步执行的代码片段封装成一个函数,然后在函数头使用@Async注解,就可以实现代码的异步执行(当然首先得在启动类上加上@EnableAsync注解了)。
千万不要这样使用@Async注解
先说一下我遇到的坑吧,做文件上传的时候因为耗时比较长,就直接在类里面封装了一个方法去做上传,代码提交后进行测试发现效率并没有什么提升,让我怀疑方法还是同步进行的。网上也没有看见谁提到了这个问题,基本上都是说少加了@EnableAsync注解导致的,我们先来看看在类里面的方法直接加上注解这种情况。
先是启动类加上注解@EnableAsync
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncTestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AsyncTestApplication.class, args);
}
}
再看看测试类
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;
@SpringBootTest
class AsyncTestApplicationTests {
@Test
void doTask() throws Exception {
StopWatch stopWatch=new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start("Task");
doTaskOne();
doTaskTwo();
doTaskThree();
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println("总耗时:"+stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis());
}
@Async
public void doTaskOne() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(10000);
}
@Async
public void doTaskTwo() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(10000);
}
@Async
public void doTaskThree() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(10000);
}
}
执行代码后的结果
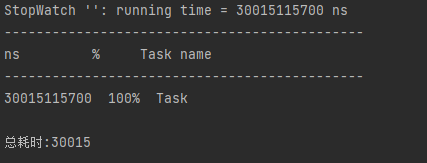
可以看到总耗时是30s左右,很明显代码就是同步进行了。原因就是这种使用方式绕过了代理而直接调用了方法,所以肯定是同步的了。从这里,我们也知道了另外一个知识点,就是@Async注解其实是通过代理的方式来实现异步调用的。
注解并没有起作用
然后再新建一个类Task,用来放三个异步任务doTaskOne、doTaskTwo、doTaskThree:
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Task {
@Async
public void doTaskOne() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(10000);
}
@Async
public void doTaskTwo() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(10000);
}
@Async
public void doTaskThree() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(10000);
}
}
回到测试类
@SpringBootTest
class AsyncTestApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Task task;
@Test
void doTask() throws Exception {
StopWatch stopWatch=new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start("Task");
task.doTaskOne();
task.doTaskTwo();
task.doTaskThree();
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println(stopWatch.prettyPrint());
System.out.println("总耗时:"+stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis());
}
}
执行代码
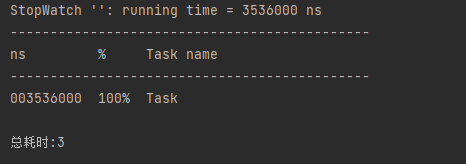
比较总耗时,可以发现注解生效了。说明代码是异步执行的
其实@Async的这个性质在官网上已经有过说明了,官网:https://www.baeldung.com/spring-async是这样说的:
First – let’s go over the rules – @Async has two limitations:
it must be applied to public methods only
self-invocation – calling the async method from within the same class – won’t work
The reasons are simple – 「the method needs to be public」 so that it can be proxied. And 「self-invocation doesn’t work」 because it bypasses the proxy and calls the underlying method directly.
简单来说就是@Async有两个限制:
1.它只能应用于公共方法
2.从同一个类中调用异步方法将不起作用
原因很简单方法需要是公共以便可以代理。“自我调用不起作用”,因为它绕过了代理,直接调用底层方法。






















 151
151











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








