这个是南邮通达的操作系统实验,实验内容相对比较简单,就是实现一下银行家算法。
我没有参考任何源码,纯属 made by myself,如果差错,欢迎指出。
import java.util.*;
/**
*
* @author 陆振宇
* @version data:2019/11/10
*/
/*
* 进程类
* 继承Comparable是为了调用Collections.shuffle()方法
* 以此来乱序进程类数组
*/
class Process implements Comparable<Process>{
int number; // 进程序号
int[] max; // 最大数据
int[] allocation; // 最大需求矩阵
int[] need; // 需求矩阵
boolean finish = false;
public Process(int number, int[] max, int[] allocation) {
this.number = number;
this.max = max;
this.allocation = allocation;
this.need = BankerAlgorithm.arrayPlus(max, allocation);
}
public Process(){
// 空构造方法,测试用
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Process process) {
/*
* 如何和控制对象排序已经无关紧要
* 转换思路为,利用将对象矩阵
* 打乱多次(>1000次)来寻找安全序列
*/
// 以矩阵每位数字的差的总和控制排序
/*int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0 ; i < process.need.length ; i++){
sum += BankerAlgorithm.arrayPlus(this.need,process.need)[i];
}
return sum;*/
// 以need矩阵的差的第一位数字控制排序
return BankerAlgorithm.arrayPlus(this.need,process.need)[0];
}
}
public class BankerAlgorithm {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
/*******************获取进程数************************/
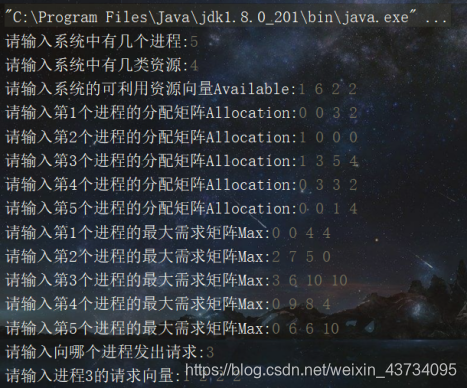
System.out.print("请输入系统中有几个进程:");
int processNum = scanner.nextInt(); // 进程数
Process[] processes = new Process[processNum]; // 存放进程对象的数组
/*******************获取资源************************/
System.out.print("请输入系统中有几类资源:");
int resourceNum = scanner.nextInt();
int[][] allocation = new int[processNum][resourceNum];// 二维allocation数组
int[][] max = new int[processNum][resourceNum]; // 二维max数组
int[] request = new int[resourceNum]; // request数组,存放Request
int[] available = new int[resourceNum]; // available数组,存放Request
/*******************获取可利用资源向量Available************************/
System.out.print("请输入系统的可利用资源向量Available:");
scanner.nextLine(); // 控制格式
String availableStr = scanner.nextLine();
String[] availableSplit = availableStr.trim().split("\\s+|,");
for (int i = 0 ; i < resourceNum ; i++){
available[i] = Integer.parseInt(availableSplit[i]);
}
/**********获取每个进程的可用资源向量Allocation***********/
for (int i = 1 ; i <= processNum ; i++){
System.out.print("请输入第" + i + "个进程的分配矩阵Allocation:");
/*if (i == 1){
scanner.nextLine(); // 控制输入格式,存疑
}*/
String allocationStr = scanner.nextLine();
// 正则匹配空格或逗号,分隔字符串
String[] allocationSplit = allocationStr.trim().split("\\s+|,");
/*原思路是使用二维矩阵逐个赋值,较为繁琐,后修改
for (int j = (i-1)*resourceNum ; j < i*resourceNum ; j++){
allocation[j] = Integer.parseInt(allocationSplit[j%resourceNum]);
}*/
for (int j = 0 ; j < resourceNum ; j++){
allocation[i-1][j] = Integer.parseInt(allocationSplit[j]);
}
}
/****************获取每个进程的最大需求矩阵Max****************/
for (int i = 1 ; i <= processNum ; i++){
System.out.print("请输入第" + i + "个进程的最大需求矩阵Max:");
/*if (i == 1){
scanner.nextLine(); // 控制输入格式,存疑
}*/
String maxStr = scanner.nextLine();
String[] maxSplit = maxStr.trim().split("\\s|,"); //正则匹配空格或逗号,分隔字符串
/*原思路是使用二维矩阵逐个赋值,较为繁琐,后修改
for (int j = (i-1)*resourceNum ; j < i*resourceNum ; j++){
max[j] = Integer.parseInt(maxSplit[j%resourceNum]);
}*/
for (int j = 0 ; j < resourceNum ; j++){
max[i-1][j] = Integer.parseInt(maxSplit[j]);
}
}
/*********************获取请求向量request****************/
System.out.print("请输入向哪个进程发出请求:");
int requestNum = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入进程" + requestNum + "的请求向量:");
scanner.nextLine();
String requestStr = scanner.nextLine();
String[] requestSplit = requestStr.trim().split("\\s+|,");
for (int i = 0 ; i < request.length ; i++){
request[i] = Integer.parseInt(requestSplit[i]); // 输入的请求向量存放到 request 数组中
}
/***************根据上面的输入创建进程*******************/
for (int i = 0 ; i < processNum ; i++){
processes[i] = new Process(i+1,max[i],allocation[i]);
}
/********************执行银行家算法**********************/
bankerAlo(processes,available,request,requestNum-1);
}
/*
* 银行家算法
* 系统向某个进程申请资源
* 判断是否能分配给它
*/
public static void bankerAlo(Process[]processes,int[]available,int[]request,int n){
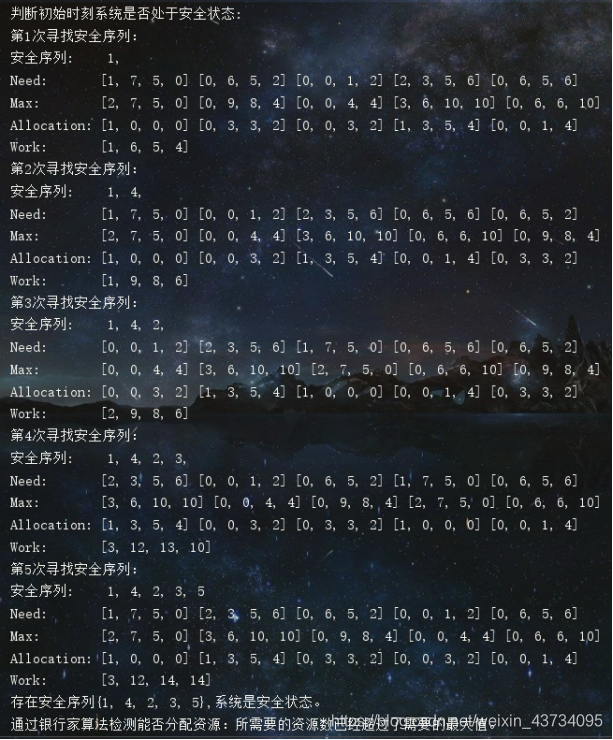
System.out.println("\n判断初始时刻系统是否处于安全状态:");
if (!safe(processes,available)){
System.out.println("初始时刻系统不处于安全状态!");
System.exit(0);
}
/***************防止进程对象的地址传递**************/
Process processRequest = null;
for (int i = 0 ; i < processes.length ; i++){
if (processes[i].number == n){
processRequest = processes[i];
}
}
/**************************************************/
System.out.print("通过银行家算法检测能否分配资源:");
if (arrayCompare(request, processRequest.need)) {// request <= Need 则进行下一步,否则错误
if (arrayCompare(request, available)) { // request <= availabl 则进行下一步,否则错误
available = arrayPlus(available, request); // available = available - request
// allocation = allocation + request
processRequest.allocation = arrayAdd(processRequest.allocation, request);
// need = need + request
processRequest.need = arrayPlus(processRequest.need, request);
} else {
System.out.println("尚无足够资源,当前进程仍需等待。");
System.exit(0); // 程序停止
}
} else {
System.out.println("所需要的资源数已经超过了需要的最大值。");
System.exit(0); // 程序停止
}
System.out.println("资源分配完成,判断系统是否处于安全状态:");
safe(processes,available);
}
/*
* 安全性算法
* 如何寻找出一个安全序列?
* 我的思路:通过将每个进程对象存在一个对象矩阵中,
* 然后将对象矩阵打乱多次(>1000次),以此来寻找
* 一个满足条件的安全序列
* 注:安全序列并不唯一,找到一个即不再继续运行,
* 但是如果不存在,那是必定找不到的。
*/
private static boolean safe(Process[] processes,int[] available) {
/******************************************************/
int n = processes[0].allocation.length; // 资源个数
int[] work = new int[n];
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){
work[i] = available[i]; // Work = Available
}
// System.out.println("\nWork=Available=" + Arrays.toString(work));
for (Process process : processes) {
process.finish = false; // Finish = false
}
/* 测试用代码
System.out.println("初始状态:");
System.out.print("\nNeed:\t\t");
for (int i = 0 ; i < processes.length ; i++){
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(processes[i].need) + " ");
}
System.out.print("\nMax:\t\t");
for (int i = 0 ; i < processes.length ; i++){
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(processes[i].max) + " ");
}
System.out.print("\nAllocation:\t");
for (int i = 0 ; i < processes.length ; i++){
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(processes[i].allocation) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
*/
/*************************寻找安全序列***********************/
StringBuffer safeNumber = new StringBuffer(); // 可变字符串记录安全序列
int count = 0; // 循环次数
int num = processes.length; // 进程个数5
while (true){
if (num == 0){
System.out.println("存在安全序列{" + safeNumber + "},系统是安全状态。");
break;
}
// 如果不存在安全序列,无论寻找多少次都不可能找到
// 所以循环次数越大越精准,但时间复杂度会增大
if (count > 10000){
System.out.println("没有找到安全序列,系统不安全!");
return false;
}
/***************乱序对象数组***********/
ArrayList<Process> processList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Process process1 : processes) {
processList.add(process1);
}
// 原本的思路是正常排序,后改为乱序多次
//Collections.sort(processList);
/*for (Process process1 : processList) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(process1.need));
}*/
Collections.shuffle(processList); // 乱序
int m = 0;
for (Process process1 : processList) {
processes[m] = process1;
m++;
}
/***************************************/
for (Process process : processes) {
//Finish = false && need <= work
if(process.finish == false && arrayCompare(process.need, work)){
work = arrayAdd(work, process.allocation); // work = work + Allocation
process.finish = true;
if (num == 1){
safeNumber.append(process.number);
}else{
safeNumber.append(process.number+", ");
}
num--;
System.out.println("第" + (count+1) + "次寻找安全序列:");
System.out.println("安全序列:\t " + safeNumber);
System.out.print("Need:\t\t");
for (int i = 0 ; i < processes.length ; i++){
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(processes[i].need) + " ");
}
System.out.print("\nMax:\t\t");
for (int i = 0 ; i < processes.length ; i++){
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(processes[i].max) + " ");
}
System.out.print("\nAllocation:\t");
for (int i = 0 ; i < processes.length ; i++){
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(processes[i].allocation) + " ");
}
System.out.println("\nWork:\t\t" + Arrays.toString(work));
break;
}
}
count++;
}
return true;
}
/*
* 矩阵相加运算,返回一个新的矩阵
*/
public static int[] arrayAdd(int[]a,int[]b){
int n = a.length;
int[] array = new int[n];
for(int i = 0 ; i < array.length ; i++){
array[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
return array;
}
/*
* 矩阵相减运算,返回一个新的矩阵
*/
public static int[] arrayPlus(int[]a,int[]b){
int n = a.length;
int[] array = new int[n];
for(int i = 0 ; i < array.length ; i++){
array[i] = a[i] - b[i];
}
return array;
}
/*
* 矩阵比较
* 矩阵A每一位都<矩阵B,则为 true
* 否则为 false
*/
public static boolean arrayCompare(int[]a,int[]b){
for(int i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i++){
if(a[i] > b[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
测试数据:
5
4
1 6 2 2
0 0 3 2
1 0 0 0
1 3 5 4
0 3 3 2
0 0 1 4
0 0 4 4
2 7 5 0
3 6 10 10
0 9 8 4
0 6 6 10
3
1 2 2 2
























 5529
5529











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










