
一、JDK8之前日期时间API
1.1.System类中的currentTimeMillis()
- 此方法返回的是:当前时间与1970年1月1日0时0分0秒之间以毫秒为单位的事件差,我们称为
时间戳
@Test
public void test1(){
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(time);
}
此方法适用于计算时间差,如计算不同程序的时间差来查看代码执行的效率
1.2.Date类:
a.两个Date类
- 两个Date类分别是
java.util.Date类和java.sql.Date类 java.sql.Date是java.util.Date的子类
b.java.util.Date类说明:
- 1.两个构造器的使用
- 构造器一:
Date():创建了一个对应当前时间的Date对象

- 构造器二:
Date(long date)创建指定毫秒数的Date对象

- 构造器一:
- 2.两个方法的使用:
toString();显示当前的年、月、日、时、分、秒,把Date类型转换成StringgetTiem():获取自1970年1月1日0时0分0秒以Date对象表示的时间戳
c.完整代码:
package com.Java常用类;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Date;
public class DateTimeTest {
@Test
public void test2(){
//构造器一:Date():创建了一个对应当前时间的Date对象
Date date1 = new Date();
System.out.println(date1.toString());
System.out.println(date1.getTime());//1632310401687
//构造器二: 创建指定毫秒数的Date对象
Date date = new Date(1632310401687L);
System.out.println(date);
}
}
1.3.java.sql.Date:
a.与数据库中数据类型的对应:
- 1.java.sql.Date:对应着数据库中
date日期类型的对象
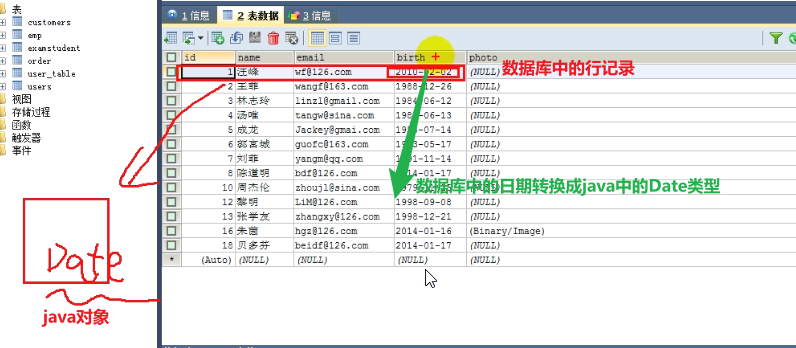
b.java.sql.Date实例化

c.java.util.Date转java.sql.Date:
- 1.将java.util.Date对象转换为java.sql.Date对象:直接赋值,原理就是面相对象中的多态

d.字符串日期转java.sql.Date:

1.4.SimpleDateFormat的使用
a.格式化:日期 与 字符串的转换:
package com.Java常用类;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class DateeTimeTest {
/*
* SimpleDateFromat的使用:SimpleDateFormat对日期Date类的格式化和解析
* */
@Test
public void test1() throws ParseException {
//实例化SimpleDateFormat:使用默认的构造器
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat();
//************不指定格式化和解析方式******************************
//格式化:日期--->字符串
Date date1 = new Date();
System.out.println(date1);//Wed Sep 22 19:53:13 CST 2021
String format = sdf.format(date1);
System.out.println(format);//2021/9/22 下午7:54
//************按指定的方式格式化和解析******************************
SimpleDateFormat format1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
//格式化
String format2 = format1.format(new Date());
System.out.println(format2+"--------");//2021-09-22 08:01:46--------
//解析:要求字符串必须是符合SimpleDateFormat识别的格式(通过构造器参数体现)
//否则,抛异常
Date parse1 = format1.parse(format2);
System.out.println(parse1);
}
}
1.5.Calendar日历类
a.Calendar日历类分析:
- Calendar是个抽象类,下面有多个实现类
- 抽象类不能实例化,所以就分析其子类

b.子类GregorianCalendar分析:
1、实例化方式:
- 方式一:创建其子类(GregorianCalendar) 的对象
- 方式二:调用其静态方法getInstance()
public class CalendarTest {
/*
* Calendar日历类(抽象类)的使用
* */
@Test
public void testCalendar(){
//1、实例化
//方式一:创建其子类(GregorianCalendar) 的对象
Calendar calendar1 = new GregorianCalendar();
// System.out.println(claender1.getClass());
//方式二:调用其静态方法getInstance()
Calendar claender2 = Calendar.getInstance()
// System.out.println(claender2 .getClass());
}
}
2、常用方法测试:
package com.Java常用类;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
public class CalendarTest {
/*
* Calendar日历类(抽象类)的使用
* */
@Test
public void testCalendar(){
//1、实例化
//方式一:创建其子类(GregorianCalendar) 的对象
//方式二:调用其静态方法getInstance()
Calendar calendar = new GregorianCalendar();
// System.out.println(calendar.getClass());
//2、常用方法
//get()
int days = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);//当前对象是这个月的第几天
System.out.println(days);
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR));//今天是这一年的第几天
//set()
calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,2);//修改当前对象的值,将其修改为本月的第2天
days = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(days);
//add()
calendar.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,2);//在本月的基础上增加或减少 x天
days = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(days);
//getTime():将日历类 -->Date类
Date time = calendar.getTime();
//setTime():Date---> 日历类
Date date = new Date();
calendar.setTime(date);
days = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);//当前对象是这个月的第几天
System.out.println(days);
}
}
二、Calendar与Date类存在的问题:
问题1:可变性 - 像日期和时间这样的类应该是不可变的

问题2: 偏移性 - Date中的年份是从1900开始的,而月份都从0开始

问题3: 格式化 - 格式化只对Date有用,Calendar则不行
- SimpleDateFormat()仅适用于Date类,不适用于Calendar,无法进行格式化
问题4:此外,它们也不是线程安全的;不能处理闰秒等
三、JDK8中新日期时间API
2.1.新的日期API概述:
- 1.Java 8 以一个新的开始为 Java 创建优秀的 API。新的日期时间API包含:
java.time– 包含值对象的基础包java.time.chrono– 提供对不同的日历系统的访问。java.time.format– 格式化和解析时间和日期java.time.temporal– 包括底层框架和扩展特性java.time.zone– 包含时区支持的类
- 2.说明:新的 java.time 中包含了所有关于时钟(Clock),本地日期(LocalDate)、本地时间(LocalTime)、本地日期时间(LocalDateTime)、时区(ZonedDateTime)和持续时间(Duration)的类,尽管有68个新的公开类型,但是大多数开发者只会用到基础包和format包,大概占总数的三分之一
2.2.本地日期时间:LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime
a.API介绍:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
now() / now(ZoneId zone) | 静态方法,根据当前时间创建对象/指定时区的对象 |
of(xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xxx) | 静态方法,根据指定日期/时间创建对象 |
| getDayOfMonth()/getDayOfYear() | 获得月份天数(1-31) /获得年份天数(1-366) |
| getDayOfWeek() | 获得星期几(返回一个 DayOfWeek 枚举值) |
| getMonth() | 获得月份, 返回一个 Month 枚举值 |
| getMonthValue() / getYear() | 获得月份(1-12) /获得年份 |
| getHours()/getMinute()/getSecond() | 获得当前对象对应的小时、分钟、秒 |
| withDayOfMonth()/withDayOfYear()/withMonth()/withYear() | 将月份天数、年份天数、月份、年份修改为指定的值并返回新的对象 |
| with(TemporalAdjuster t) | 将当前日期时间设置为校对器指定的日期时间 |
| plusDays(), plusWeeks(), plusMonths(), plusYears(),plusHours() | 向当前对象添加几天、几周、几个月、几年、几小时 |
| minusMonths() / minusWeeks()/minusDays()/minusYears()/minusHours() | 从当前对象减去几月、几周、几天、几年、几小时 |
| plus(TemporalAmount t)/minus(TemporalAmount t) | 添加或减少一个 Duration 或 Period |
| isBefore()/isAfter() | 比较两个 LocalDate |
| isLeapYear() | 判断是否是闰年(在LocalDate类中声明) |
| format(DateTimeFormatter t) | 格式化本地日期、时间,返回一个字符串 |
| parse(Charsequence text) | 将指定格式的字符串解析为日期、时间 |
b.编码使用:
import org.junit.Test;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
public class TestLocalDateTime {
@Test
public void test01(){
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println(now);
}
@Test
public void test02(){
LocalTime now = LocalTime.now();
System.out.println(now);
}
@Test
public void test03(){
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(now);
}
@Test
public void test04(){
LocalDate lai = LocalDate.of(2019, 5, 13);
System.out.println(lai);
}
@Test
public void test05(){
LocalDate lai = LocalDate.of(2019, 5, 13);
System.out.println(lai.getDayOfYear());
}
@Test
public void test06(){
LocalDate lai = LocalDate.of(2019, 5, 13);
LocalDate go = lai.plusDays(160);
System.out.println(go);//2019-10-20
}
@Test
public void test7(){
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate before = now.minusDays(100);
System.out.println(before);//2019-02-26
}
}
2.3.瞬时:Instant
a.API介绍:
- Instant:时间线上的一个瞬时点。 这可能被用来记录应用程序中的事件时间戳
- 时间戳是
指格林威治时间1970年01月01日00时00分00秒(北京时间1970年01月01日08时00分00秒)起至现在的总秒数
- 时间戳是
java.time.Instant表示时间线上的一点,而不需要任何上下文信息,例如,时区。概念上讲,它只是简单的表示自1970年1月1日0时0分0秒(UTC)开始的秒数
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
now() | 静态方法,返回默认UTC时区的Instant类的对象 |
ofEpochMilli(long epochMilli) | 静态方法,返回在1970-01-01 00:00:00基础上加上指定毫秒数之后的Instant类的对象 |
| atOffset(ZoneOffset offset) | 结合即时的偏移来创建一个 OffsetDateTime |
toEpochMilli() | 返回1970-01-01 00:00:00到当前时间的毫秒数,即为时间戳 |
b.时区说明
- 1.中国大陆、中国香港、中国澳门、中国台湾、蒙古国、新加坡、马来西亚、菲律宾、西澳大利亚州的时间与UTC的时差均为+8,也就是UTC+8
- 2.instant.atOffset(ZoneOffset.ofHours(8));
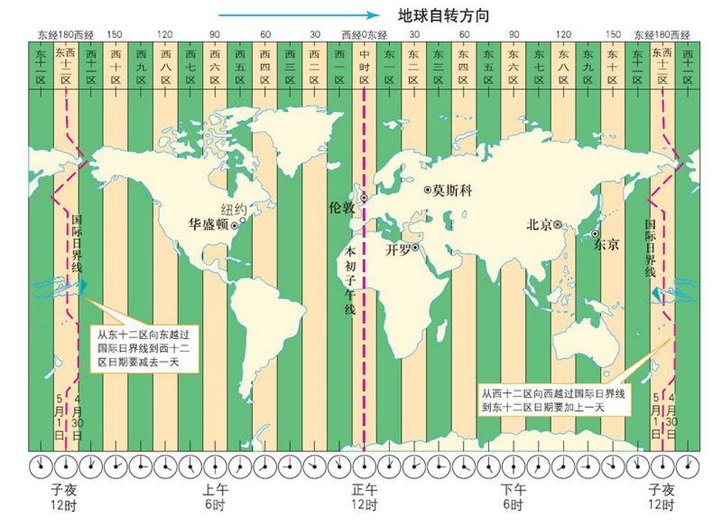
说明:
- 整个地球分为二十四时区,每个时区都有自己的本地时间。北京时区是东八区,领先UTC八个小时,在电子邮件信头的Date域记为+0800。如果在电子邮件的信头中有这么一行:
- Date: Fri, 08 Nov 2002 09:42:22 +0800
- 说明信件的发送地的地方时间是二00二年十一月八号,星期五,早上九点四十二分(二十二秒),这个地方的本地时领先UTC八个小时(+0800, 就是东八区时间)。电子邮件信头的Date域使用二十四小时的时钟,而不使用AM和PM来标记上下午
b.编码使用:
@Test
public void test3(){
//now():获取本初子午线上的时间
Instant instant = Instant.now();//2021-09-23T08:12:46.327701200Z
System.out.println(instant);//本初子午线上的时间,需要加上8个小时
//添加时间的偏移量
OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime = instant.atOffset(ZoneOffset.ofHours(8));
System.out.println(offsetDateTime); //当地正确的时间
//toEpochMilli():获取对应的毫秒数 (距离1970年1月1日0分0秒)
long l = instant.toEpochMilli();
System.out.println(l);
//ofEpochMilli():通过给定的毫秒数获取Instant实例--->Date(long millis)
Instant instant1 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(1632385079910L);
System.out.println(instant1);
}
2.4.格式化与解析日期或时间:DateTimeFormatter
a.API介绍:
- 该类提供了三种格式化方法:
- (了解)预定义的标准格式。如:ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME、ISO_LOCAL_DATE、ISO_LOCAL_TIME
- (了解)本地化相关的格式。如:ofLocalizedDate(FormatStyle.LONG)
// 本地化相关的格式。如:ofLocalizedDateTime() // FormatStyle.MEDIUM / FormatStyle.SHORT :适用于LocalDateTime // 本地化相关的格式。如:ofLocalizedDate() // FormatStyle.FULL / FormatStyle.LONG / FormatStyle.MEDIUM / FormatStyle.SHORT : 适用于LocalDate自定义的格式, 如:ofPattern(“yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss”)
| 方 法 | 描 述 |
|---|---|
| ofPattern(String pattern) | 静态方法,返回一个指定字符串格式的DateTimeFormatter |
| format(TemporalAccessor t) | 格式化一个日期、时间,返回字符串 |
| parse(CharSequence text) | 将指定格式的字符序列解析为一个日期、时间 |
b.编码使用:
/*
* DateTimeFormatter:格式化或解析日期、时间
* 类似于SimpleDateFormat
*
* */
@Test
public void test4(){
// 方式一:预定义的标准格式。如ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;ISO_LOCAL_DATE;ISO_LOCAL_TIME
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;
//格式化:日期-->字符串
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
String format = formatter.format(localDateTime);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
System.out.println(format);
//解析:字符串--> 日期
TemporalAccessor parse = formatter.parse(format);
System.out.println(parse);
// 方式二:本地化相关格式。
// 本地化相关的格式。如:ofLocallizedDateTime()
// FormatStyle.LONG / FormatStyle.MEDIUM / FormatStyle.SHORT :适用于LocalDateTime
DateTimeFormatter formatter1 = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.SHORT);
//格式化
String format1 = formatter1.format(localDateTime);
System.out.println(format1);
// 本地化相关格式。如:ofLocalizedDate()
// FormatStyle.FULL / FormatStyle.LONG / FormatStyle.MEDIUM / FormatStyle.SHORT
DateTimeFormatter formatter2 = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDate(FormatStyle.FULL);
//格式化
String format2 = formatter2.format(LocalDate.now());
System.out.println(format2);
// 重点:方式三:自定义的格式.如:ofPattern(“yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss”)
DateTimeFormatter formatter3 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
// 格式化
String format3 = formatter3.format(LocalDateTime.now());
System.out.println(format3);//2021-09-23 04:40:50
// 解析
TemporalAccessor parse1 = formatter3.parse(format3);
System.out.println(parse1);
}

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








