1.关于JSR-303
JSR-303规范(Bean Validation规范)提供了对 Java EE 和 Java SE 中的 Java Bean 进行验证的方式。该规范主要使用注解的方式来实现对 Java Bean 的验证功能 。
Hibernate Validator 提供了 JSR 303 规范中所有内置 constraint 的实现,除此之外还有一些附加的 constraint。
Bean Validation 中内置的 constraint
| 约束注解名称 | ** 约束注解说明** |
|---|---|
| @Null | 验证对象是否为空 |
| @NotNull | 验证对象是否为非空 |
| @AssertTrue | 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true |
| @AssertFalse | 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false |
| @Min | 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否大等于指定的值 |
| @Max | 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否小等于指定的值 |
| @DecimalMin | 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否大等于指定的值,小数存在精度 |
| @DecimalMax | 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否小等于指定的值,小数存在精度 |
| @Size | 验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内 |
| @Digits | 验证 Number 和 String 的构成是否合法 |
| @Past | 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前 |
| @Future | 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后 |
| @Pattern | 验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则 |
2. 基本使用
-
在参数上加上校验注解,如果参数是自定义类型,则在类的属性上加校验注解。
-
使校验注解生效
2.1 直接在参数上加校验注解,需要在类上加
@Validated2.1 自定义类型,变量前面加
@Validated或者@Valid
@Data
public class Emp {
//不能为空且不能为空串
@NotBlank(message = "账号不能为空")
private String username;
}
@PostMapping("/emp/add")
public Result demo1(@Valid Emp emp,@NotBlank String email){
return Result.success(200,"成功");
}
@Validated和@Valid的区别
@Validated:
- Spring提供的
- 支持分组校验
- 可以用在类型、方法和方法参数上。但是不能用在成员属性(字段)上
- 由于无法加在成员属性(字段)上,所以无法单独完成级联校验,需要配合@Valid
@Valid:
- JDK提供的(标准JSR-303规范)
- 不支持分组校验
- 可以用在方法、构造函数、方法参数和成员属性(字段)上
- 可以加在成员属性(字段)上,能够独自完成级联校验
3. 级联验证
一个待验证的pojo类,其中又包含了一个待验证的对象。
@Data
public class Emp implements Serializable {
//不能为空且不能为空串(调用trim()后)
@NotBlank(message = "账号不能为空")
private String username;
@Valid //需要加上,否则不会验证Dept类中的校验注解
@NotNull //并且需要触发该字段的验证才会进行嵌套验证。
private Dept dept;
}
@Data
public class Dept implements Serializable {
@NotBlank(message = "deptNameb不能为空")
private String deptName;
}
4. 分组验证
验证时只对特定的属性进行校验,不知道默认为Default
1、定义接口,充当标识
public interface IGroup {
interface Registry extends Default {}
interface Update extends Default {}
}
2、指定校验的组
@Data
public class Emp implements Serializable {
//当校验的组为update时才校验该字段
@NotNull(message = "编号不能为空",groups = {IGroup.Update.class})
@Min(value = 1,groups = {IGroup.Update.class})
private Integer empNo;
//不能为空且不能为空串(调用trim()后)
@NotBlank(message = "账号不能为空")
private String username;
@Pattern(regexp = "^[0-9A-z]{10,18}$",message = "密码只能使用数字+字母",groups = IGroup.Registry.class)
private String password;
@Valid
@NotNull
private Dept dept;
}
@PostMapping("/emp/add") //指定需要校验的组
public Result addEmp(@RequestBody @Validated(IGroup.Registry.class) Emp emp){
return Result.success(200,"成功");
}
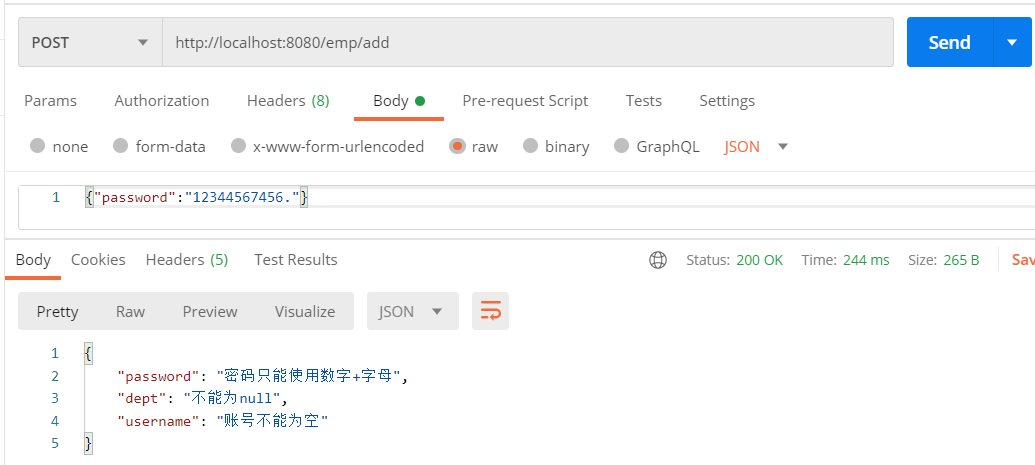
5. 组序列
指定组与组之间的检验顺序,如果第一个组校验没过,就不会校验后面的组
@GroupSequence({Default.class,IGroup.Update.class, IGroup.Registry.class})
public interface IGroup {
interface Registry extends Default {}
interface Update extends Default {}
}
@PostMapping("/emp/add")
public Result addEmp(@RequestBody @Validated({IGroup.class}) Emp emp){
return Result.success(200,"成功");
}
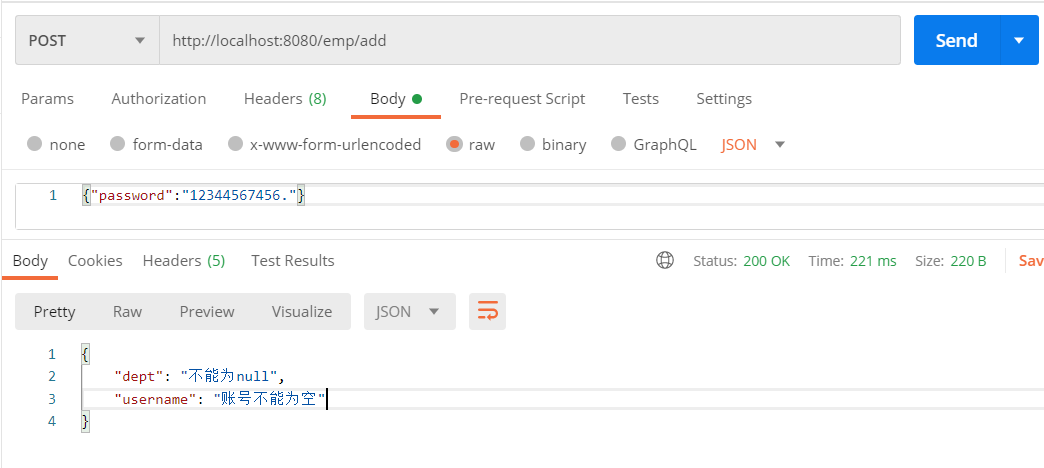
随便定义一个接口然后在接口上使用@GroupSequence就行。
还有一个注解是@GroupSequenceProvider,使用这个注解需要实现DefaultGroupSequenceProvider接口,重写里面getValidationGroups方法,然后根据情况动态的添加需要需要校验的分组。
6. 自定义校验注解
按照官网的示例
检查当前字符串是否为全大写,或者全小写
- 定义模型
public interface CaseMode{
String UPPER="大写";
String LOWER="小写";
}
- 创建自定义注解
@Target({ FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, ANNOTATION_TYPE, TYPE_USE })
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Constraint(validatedBy = CheckCaseValidator.class) //指定自定义验证器
@Documented
@Repeatable(CheckCase.List.class) //表示可以在同一位置重复多次
public @interface CheckCase {
//默认的错误信息
String message() default "{verification.default.Errormessage}";
Class<?>[] groups() default { };
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default { };
String value();
@Target({ FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, ANNOTATION_TYPE })
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Documented
@interface List {
CheckCase[] value();
}
}
- 创建自定义验证器,第一个泛型是自定义注解、第二个是校验值的类型,也就是注解标注的字段的类型
public class CheckCaseValidator implements ConstraintValidator<CheckCase, String> {
private String caseMode;
@Override
public void initialize(CheckCase constraintAnnotation) {
this.caseMode = constraintAnnotation.value();
}
/**
* 判断是否通过校验
* @param value 传入的值
* @param context
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean isValid(String value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
if ( value == null ) {
return true;
}
if (CaseMode.UPPER.equals(caseMode) ) {
return value.equals( value.toUpperCase() );
}
else {
return value.equals( value.toLowerCase() );
}
}
}
- 在
resources目录下创建一个ValidationMessages.properties配置文件,key是第二步message设置的默认值,value是自定义错误信息。{value}为 @CheckCase的value属性的值
verification.default.Errormessage=字母必须为全为{value}
7. 校验结果的处理
7.1 全局异常处理
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(BindException.class)
public HashMap<String, String> bindExceptionHandler(BindException e){
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
e.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors().forEach(field -> {
map.put(field.getField(), field.getDefaultMessage());
});
return map;
}
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public HashMap<String, String> methodArgumentNotValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e){
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
e.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors().forEach(field -> {
map.put(field.getField(), field.getDefaultMessage());
});
return map;
}
@ExceptionHandler(ConstraintViolationException.class)
public HashMap<String, String> handle(ConstraintViolationException e) {
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
e.getConstraintViolations().forEach(item->{
map.put(item.getPropertyPath().toString(),item.getMessage());
});
return map;
}
}
7.2 BindRequest
@PostMapping("/emp/test")
public Result test(@Validated Emp emp, BindingResult validResult){
if (validResult.hasErrors()){
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
validResult.getFieldErrors().forEach(error->{
map.put(error.getField(),error.getDefaultMessage());
});
return Result.error(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(),map);
}
return Result.success(HttpStatus.OK.value(),"成功");
}
7.3 Validator
@SpringBootTest
public class ValidatorTest {
private static Validator validator = Validation.byProvider(HibernateValidator.class)
.configure()
.failFast(false) // 是否开启快速失败模式
.buildValidatorFactory()
.getValidator();
@Test
public void test1(){
Emp emp = new Emp();
//单独校验某个属性
//Set<ConstraintViolation<Emp>> validProperty = validator.validateProperty(emp, "username");
//检验对象
Set<ConstraintViolation<Emp>> validBean = validator.validate(emp);
Iterator<ConstraintViolation<Emp>> iterator = validBean.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
ConstraintViolation<Emp> next = iterator.next();
String property = next.getPropertyPath().toString();
String message = next.getMessage();
System.out.println(property+":"+message);
}
}
}





















 4351
4351











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








