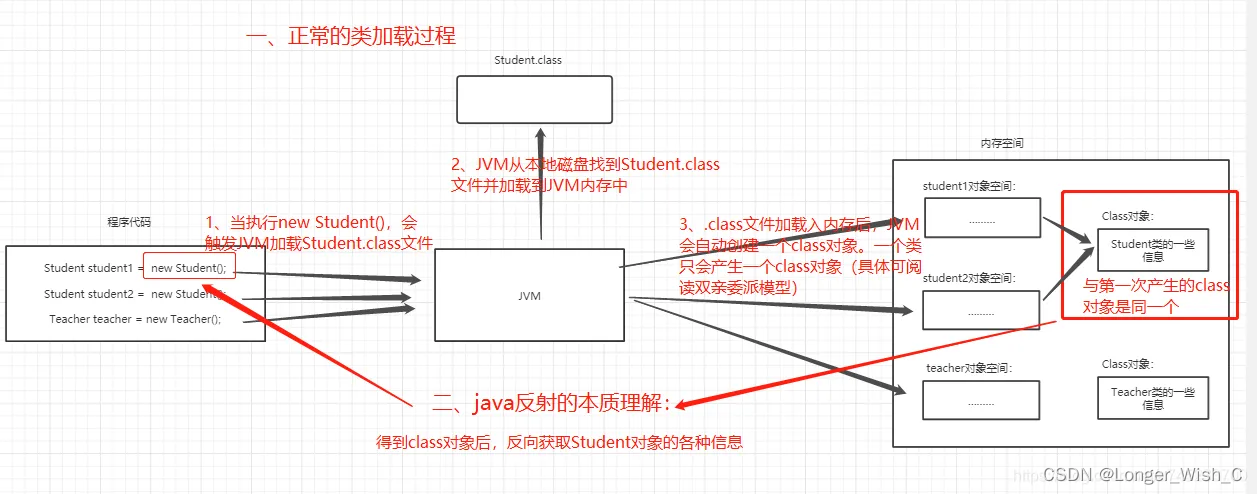
1. 什么是反射?
● 在运行时获取类的完整信息,从而操作类或对象的属性或方法。本质是JVM在得到class对象之后,通过class对象进行反编译,从而获取类的各种信息。
● Java属于先编译再运行的语言,程序中对象的类型在编译期就确定下来了,而当程序在运行时可能需要动态加载某些类,这些类因为之前用不到,所以没有被加载到JVM。通过反射,可以在运行时动态地创建对象并调用其属性,不需要提前在编译期知道运行的对象是谁。
2. 代码示例
public class Apple {
private int price;
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//正常的调用
Apple apple = new Apple();
apple.setPrice(5);
System.out.println("Apple Price:" + apple.getPrice());
//使用反射调用
Class clz = Class.forName("com.chenshuyi.api.Apple");
Method setPriceMethod = clz.getMethod("setPrice", int.class);
Constructor appleConstructor = clz.getConstructor();
Object appleObj = appleConstructor.newInstance();
setPriceMethod.invoke(appleObj, 14);
Method getPriceMethod = clz.getMethod("getPrice");
System.out.println("Apple Price:" + getPriceMethod.invoke(appleObj));
}
}
3. 应用
1、JDBC连接数据库中通过 Class.forName 来动态获取数据库驱动
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class JdbcExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
try {
// 加载数据库驱动程序
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 建立连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydatabase";
String username = "root";
String password = "password";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 执行SQL语句...
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭连接
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
2、反射机制在Spring框架的应用
反射机制允许Spring在运行时动态检查类的构造函数、属性和方法,并根据依赖关系来创建对象、设置属性值或调用方法。这样以来,依赖注入就可以在不修改源代码的情况下实现。
2.1、创建 Bean 实例时的反射
// 通过类加载器,根据 class 路径,得到其类对象
Class<?> clz = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().loadClass("org.deppwang.litespring.v1.service.PetStoreService");
// 根据类对象生成 Bean 实例
return clz.newInstance();
反射体现在 clz.newInstance(); 中,核心代码可分为两部分:
● 利用反射获取当前类 PetStoreService 的所有构造方法信息(Constructor 对象)
● 利用反射通过默认构造方法生成实例
2.2、构造方法依赖注入时的反射
// 通过反射获取当前类所有的构造方法信息(Constructor 对象)
Constructor<?>[] candidates = beanClass.getDeclaredConstructors();
// 设置构造方法参数实例
Object[] argsToUse = new Object[parameterTypes.length];
argsToUse[i] = getBean(beanNames.get(i));
// 使用带有参数的 Constructor 对象实现实例化 Bean。此时使用反射跟上面一样(newInstance0),只是多了参数
return constructorToUse.newInstance(argsToUse);
2.3、setter() 方法依赖注入时的反射
// 通过反射获取当前类所有的方法信息(Method 对象)
Method[] methods = bean.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
// 获得方法参数实例
Object propertyBean = getBean(propertyName);
// 通过反射执行调用 setter() 方法。invoke:调用方法,propertyBean 作为方法的参数
method.invoke(bean, propertyBean);
@Autowired 依赖注入时的反射
// 通过反射得到当前类所有的字段信息(Field 对象)
Field[] fields = bean.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
// 判断字段是否有 @Autowired 注解
Annotation ann = field.getAnnotation(Autowired.class);
// 设置字段可连接,相当于将非 public(private、default、protect)更改为 public
field.setAccessible(true);
// 通过反射设置字段的值
field.set(bean, getBean(field.getName()));























 23万+
23万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








