简单手写spring的依赖注入
什么是依赖注入?
IOC(DI)-控制反转(依赖注入)
所谓的IOC称之为控制反转,简单来说就是将对象 的创建的权力及对象的生命周期的管理过程交由Spring框架来处理,从此在开发过程中不在需要关注对象的创建和生命周期的管理,而是在需要的时候由Spring框架提供,这个由Spring框架管理对象创建和生命周期的机制称之为控制反转。而在创建对象的过程中Spring可以依据配置对象的属性进行设置,这个过程称之为依赖注入,也即DI
个人理解
目前的java开发,spring仍是最主流的框架,换句话说如果你不了解spring,那么你将很难拿到offer,所以学习并且理解spring是很重要的一件事,依赖注入是spring的一个特性,在工作中几乎无时无刻不在使用,本题只是简单的一个手写实现
spring中原本的代码健壮性是很强的,让人看起来就会感觉很繁琐复杂,所以本篇只是粗略实现一下DI的功能,本篇仅供初学者参考,如果觉得本篇比较简单或者完全理解本篇内容后,请移步spring源码
手写DI步骤
所需要的环境
1.JDK 1.8
2.IDEA或者ecilpese皆可以,建议使用IDEA
3.maven
4.一颗求知的心
需要提前了解的内容
1.反射(重要,不太理解的话可以先掌握常用方法)
2.xml解析(了解xml解析)
项目结构

pom文件
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jdom</groupId>
<artifactId>jdom</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jaxen</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxen</artifactId>
<version>1.2.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
手写步骤
1.创建实体类
我们先在pojo包下创建一个实体类Student
package com.tao.spring.DItest.pojo;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private String className;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public void setClassName(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", className='" + className + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
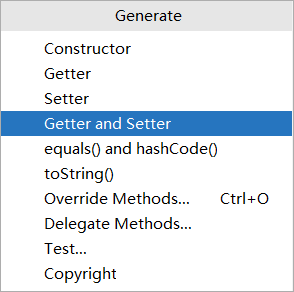
小提示:
在写完属性后按下alt+insert,选择Getter and Setter可以快速生成get和set方法和tostring方法。如果是按下去没出现下面提示框的话,就按下alt+fn+insert
2.创建xml文件用于记录要注入的属性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<bean id="Student" class="com.tao.spring.DItest.pojo.Student">
<property name="name" value="李四"/>
<property name="age" value="18"/>
<property name="classname" value="8班"/>
</bean>
</beans>
3.解析XML文件,使用反射实现依赖注入
在iocFactory包下创建ApplicationContext接口
public interface ApplicationContext {
Object getBean(String name);
}
在本包下再创建impl包,然后新建ClassPathApplicationContext去实现ApplicationContext接口
package com.tao.spring.DItest.iocFactory.impl;
import com.tao.spring.DItest.iocFactory.ApplicationContext;
import org.jdom2.Document;
import org.jdom2.Element;
import org.jdom2.JDOMException;
import org.jdom2.input.SAXBuilder;
import org.jdom2.xpath.XPathExpression;
import org.jdom2.xpath.XPathFactory;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.*;
public class ClassPathApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext {
//要解析的配置文件
private File file;
//存放bean 贯穿全局的属性 请在项目中一直留意
private Map map=new HashMap();
//解析配置文件 类似于 ApplicationContext=new ClassPathApplicationContext("application.xml")
public ClassPathApplicationContext(String configfile) throws URISyntaxException, IOException, JDOMException, ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//获取xml文件路径
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(configfile);
System.out.println(url.toString());
File file = new File(url.toURI());
//解析xml
xmlParse(file);
}
//解析文件
private void xmlParse(File file) throws IOException, JDOMException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
//创建document对象
Document document = new SAXBuilder().build(file);
// 获取所有的Bean节点
XPathFactory xPathFactory = XPathFactory.instance();
XPathExpression expression = xPathFactory.compile("//bean");
//遍历bean集合
List beans = expression.evaluate(document);
Iterator iterator = beans.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Element bean = (Element) iterator.next();
//获取配置文件的id属性值
String id = bean.getAttributeValue("id");
String cls = bean.getAttributeValue("class");
//通过反射拿到类相应信息
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(cls);
Object object = aClass.newInstance();
//存储bean中属性的类型
Map<String, String> filedTypeMap = new HashMap<>();
filedTypeMap=getFiledType(aClass);
//拿取该类所有方法,通过set赋值 (DI实现方法之一 set注入)
Method[] methods = aClass.getDeclaredMethods();
//遍历bean下面所有属性 和set方法一一对应 再进行赋值
List<Element> propertys = bean.getChildren("property");
for (Element property : propertys) {
for (Method method : methods) {
//获取属性名字 去匹配
String name = method.getName().toLowerCase();
//普通对象属性
if (property.getAttribute("name")!=null) {
if (name.startsWith("set")) {
String tempName = name.substring(3);
if (tempName.equals(property.getAttributeValue("name"))) {
String s = filedTypeMap.get(tempName);
if (s!=null){
if (s.equals("int")){
method.invoke(object, Integer.parseInt(property.getAttributeValue("value")));
}else {
method.invoke(object, property.getAttributeValue("value"));
}
}
}
}
}else {
method.invoke(object,map.get(property.getAttributeValue("ref")));
}
}
}
//将bean添加到map中
map.put(id,object);
}
}
private Map<String, String> getFiledType(Class<?> aClass) {
Map<String, String> filedTypeMap = new HashMap<>();
Field[] declaredFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
filedTypeMap.put(declaredField.getName().toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT),declaredField.getGenericType().getTypeName());
}
return filedTypeMap;
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) {
return map.get(name);
}
}
如果对xml结构不太了解的话,请参考下图

4.测试类
package com.tao.spring.DItest.test;
import com.tao.spring.DItest.iocFactory.ApplicationContext;
import com.tao.spring.DItest.iocFactory.impl.ClassPathApplicationContext;
import com.tao.spring.DItest.pojo.Student;
import org.jdom2.JDOMException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
public class ApplicationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws URISyntaxException, IOException, JDOMException, ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathApplicationContext("application.xml");
Student student1 = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("Student");
Student student2 = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("Student");
System.out.println(student1);
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println(student2);
System.out.println(student1==student2);
}
}
5.输出结果

根据结果可以看出成功给Student对象注入xml中的属性值,并且是单例模式,并且两个对象为同一个对象
思考与改进
这个项目能成功的注入简单属性,如果是引用类型的属性该如何注入?
比如说现在有个实体类Clothes
package com.tao.spring.DIreftest.pojo;
public class Clothes {
private String jacket;
private String shirt;
private String pants;
public String getJacket() {
return jacket;
}
public void setJacket(String jacket) {
this.jacket = jacket;
}
public String getShirt() {
return shirt;
}
public void setShirt(String shirt) {
this.shirt = shirt;
}
public String getPants() {
return pants;
}
public void setPants(String pants) {
this.pants = pants;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Clothes{" +
"jacket='" + jacket + '\'' +
", shirt='" + shirt + '\'' +
", pants='" + pants + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
然后Student持有这个属性
package com.tao.spring.DIreftest.pojo;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private String className;
private Clothes clothes;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public void setClassName(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
public Clothes getClothes() {
return clothes;
}
public void setClothes(Clothes clothes) {
this.clothes = clothes;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", className='" + className + '\'' +
", clothes=" + clothes +
'}';
}
}
如果理解了前面的项目的话,这个也很好实现注入的,无非是在xml中写明需要注入的实例,然后在set方法注入的时候进行判断,试试看自己实现一下吧
改进后的项目
1.结构图
只是增加了一个实体类Clothes

2.修改xml文件
复制之前的xml文件,然后粘贴后改名为refapplication.xml
写入被引用的bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans>
<bean id="clothes" class="com.tao.spring.DIreftest.pojo.Clothes">
<property name="jacket" value="LiNing"/>
<property name="shirt" value="T-shirt"/>
<property name="pants" value="zhwnweisi"/>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.tao.spring.DIreftest.pojo.Student">
<property name="name" value="lisan"/>
<property name="age" value="20"/>
<property name="classname" value="6班"/>
<property ref="clothes"/>
</bean>
</beans>
3.修改注入逻辑
for (Element property : propertys) {
for (Method method : methods) {
//获取属性名字 去匹配
String name = method.getName().toLowerCase();
//普通对象属性
if (property.getAttribute("name")!=null) {
if (name.startsWith("set")) {
String tempName = name.substring(3);
if (tempName.equals(property.getAttributeValue("name"))) {
String s = filedTypeMap.get(tempName);
if (s!=null){
if (s.equals("int")){
method.invoke(object, Integer.parseInt(property.getAttributeValue("value")));
}else {
method.invoke(object, property.getAttributeValue("value"));
}
}
}
}
//引用对象
}else {
String tempName = name.substring(3);
if (name.startsWith("set")) {
if (tempName.equals(property.getAttributeValue("ref"))) {
String s = filedTypeMap.get(tempName);
method.invoke(object, map.get(property.getAttributeValue("ref")));
}
}
}
}
}
//将bean添加到map中
map.put(id,object);
4.测试类
xml文件名不要写错哦
public static void main(String[] args) throws URISyntaxException, IOException, JDOMException, ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathApplicationContext("refapplication.xml");
Student student1 = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("student");
Student student2 = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student1);
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println(student2);
System.out.println(student1==student2);
}
5.输出结果
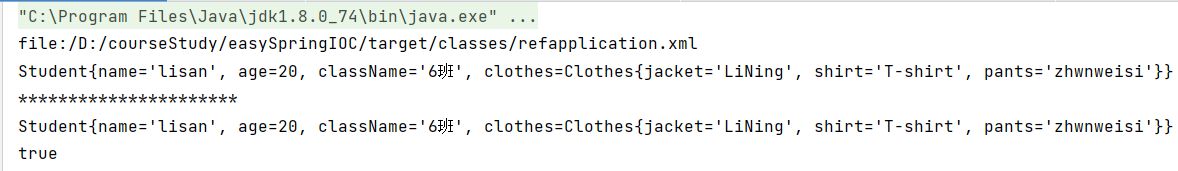
从结果可以看出注入还是很成功的!
本篇文档仅供参考,如果有疏漏和不足之处欢迎在评论区指出!





















 127
127











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








