函数模板:
- 函数模板
- 类模板
函数模板
函数模板语法
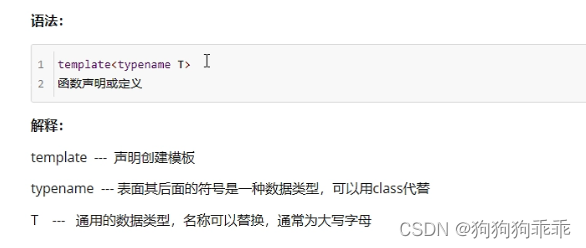
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//两个整形交换
void swapInt(int& a, int& b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
//两个浮点形交换
void swapDouble(double & a, double& b)
{
double temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
//函数模板
template<typename T>
void mySwap(T &a, T &b)
{
T temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
double c = 0.211;
double d = 1.25545;
//swapDouble(c, d);
//利用函数模板交换
//1.自动类型推导
mySwap(a, b);
//2.显示指定类型
mySwap<int>(a, b);
swapInt(a, b);
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
cout << "c = " << c << endl;
cout << "d = " << d << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
函数模板注意事项

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void mySwap(T& a, T& b)
{
T temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
void test01()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
char c = 'c';
mySwap(a, b); //正确
//mySwap(a, c); 错误 推到不出一致的类型
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
}
template <class T>
void func()
{
cout << "func 调用" << endl;
}
void test02()
{
//func();//模板没有确定T的数据类型 错误
func<int>();//正确
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
函数模板案例

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Swap(T &a, T &b)
{
T temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
template<class T>
void mySort(T arr[],int len)
{
for (int i = 0;i < len;i++)
{
int max = i;
for (int j = i + 1;j < len;j++)
{
if (arr[max] < arr[j])
{
max = j;
}
}
if (max != i)
{
Swap(arr[max], arr[i]);
}
}
}
template<class T>
void printarray(T arr[], int len)
{
for (int i = 0;i < len;i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
char charArr[] = "adasdasff";
int num = sizeof(charArr) / sizeof(char);
mySort(charArr, num);
printarray(charArr, num);
}
void test02()
{
int intArr[] = {7,54,545,54,414,541,5,5};
int num = sizeof(intArr) / sizeof(int);
mySort(intArr, num);
printarray(intArr, num);
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
普通函数与函数模板的区别

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int myAdd01(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
template <class T>
T myAddo2(T a, T b)
{
return a + b;
}
void test01()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
char c = 'c';
cout << myAdd01(a, c) << endl;
//自动类型推导出错
//cout << myAddo2(a, c) << endl;
//指定类型可以
cout << myAddo2<int>(a, c) << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

普通函数与模板函数的调用规则

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void myPrint(int a, int b)
{
cout << "调用普通函数" << endl;
}
template <class T>
void myPrint(T a, T b)
{
cout << "调用函数模板" << endl;
}
template <class T>
void myPrint(T a, T b,T c)
{
cout << "调用重载函数模板" << endl;
}
void test01()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
myPrint(a, b);
//通过空模板参数列表,强调调用函数模板
myPrint<>(a, b);
myPrint<>(a, b,100);
char c1 = 'a';
char c2 = 'w';
//函数模板有更加好的匹配
myPrint(c1, c2);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
模板的局限性
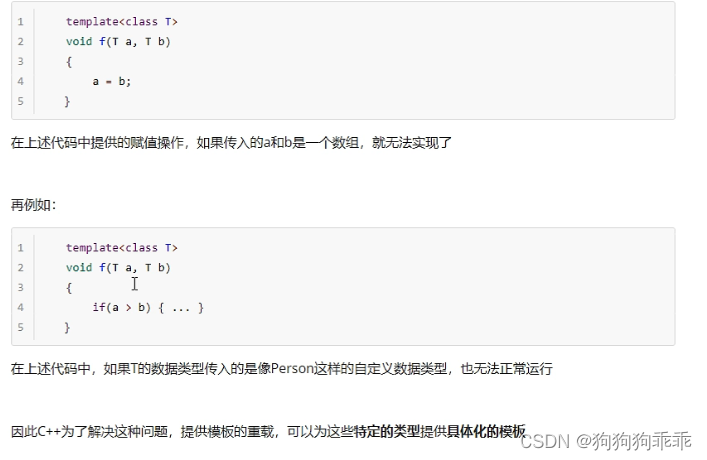
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
string m_Name;
int m_age;
private:
};
template <class T>
bool myComputer(T& a, T& b)
{
if (a == b)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
template<> bool myComputer(Person& p1, Person& p2)
{
if (p1.m_age == p2.m_age && p1.m_Name == p2.m_Name)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void test01()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
bool ret = myComputer(a, b);
if (ret)
{
cout << "相等" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "不相等" << endl;
}
}
void test02()
{
Person p1("Tom", 10);
Person p2("Tom", 10);
bool ret = myComputer(p1, p2);
if (ret)
{
cout << "相等" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "不相等" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

类模板
类模板语法
类模板作用:建立一个通用类,类中的成员 数据类型可以不具体制定,用一个虚拟的类型来代表
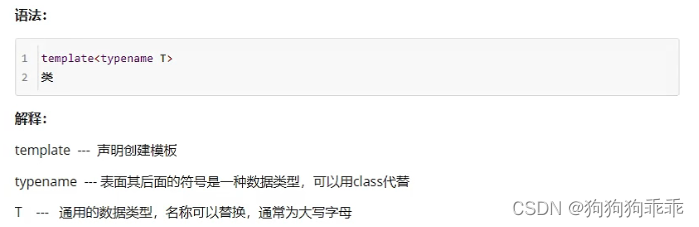
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//类模板
template <class NameType, class AgeType>
class Person
{
public:
Person(NameType name, AgeType age)
{
m_name = name;
m_age = age;
}
void showperson()
{
cout << "name: " << this->m_name
<< "age; " << this->m_age << endl;
}
NameType m_name;
AgeType m_age;
};
void test01()
{
Person<string, int> p1("孙悟空", 999);
p1.showperson();
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
类模板与函数模板区别

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
template <class Nametype, class Agetype = int>
class Person
{
public:
Person(Nametype name, Agetype age)
{
this->m_Age = age;
this->m_Name = name;
}
void showPerson()
{
cout << "name: " << this->m_Name
<< "age: " << this->m_Age << endl;
}
Nametype m_Name;
Agetype m_Age;
};
void test01()
{
//Person p("孙悟空", 1000); 错误的
Person <string, int> p("孙悟空", 100);
p.showPerson();
}
void test02()
{
Person<string> p("老猪", 100);
p.showPerson();
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
类模板中成员函数创建时机

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Person1
{
public:
void showPerson1()
{
cout << "Person1 show" << endl;
}
private:
};
class Person2
{
public:
void showPerson2()
{
cout << "Person2 show" << endl;
}
private:
};
template<class T>
class Myclass
{
public:
T obj;
void func1()
{
obj.showPerson1();
}
void func2()
{
obj.showPerson2();
}
};
void test01()
{
Myclass<Person1>m;
m.func1();
//m.func2();
}
int main()
{
system("pause");
return 0;
}

类模板对象做函数参数

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
template <class T1,class T2>
class Person
{
public:
Person(T1 name, T2 age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
void showPerson()
{
cout << "姓名: " << this->m_Name
<< "年龄: " << this->m_Age << endl;
}
T1 m_Name;
T2 m_Age;
};
//指定参数类型
void printPerson1(Person<string, int> &p)
{
p.showPerson();
}
void test01()
{
Person<string, int>p("孙悟空", 100);
printPerson1(p);
}
//参数模板化
template <class T1,class T2>
void printPerson2(Person<T1, T2>& p)
{
p.showPerson();
}
void test02()
{
Person<string, int>p("老猪", 100);
printPerson2(p);
}
//整个类模板化
template<class T>
void printPerson3(T &p)
{
p.showPerson();
}
void test03()
{
Person<string, int>p("沙老板", 100);
printPerson3(p);
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
test03();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

类模板与继承

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class Base
{
T m;
};
// class Son :public Base{}; 错误的,必须知道父类中的T类型,才能继承给子类
class Son :public Base<int>
{
};
void test01()
{
Son s1;
}
//如果想灵活指定父类中的T类型,子类也需要变成类模板
template <class T1, class T2>
class Son2 :public Base<T2>
{
public:
Son2()
{
cout << typeid(T1).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(T2).name() << endl;
}
T1 obj;
};
void test02()
{
Son2<int, char> S2;
}
int main()
{
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

类模板成员函数类外实现
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T1, class T2>
class Person
{
public:
Person(T1 age, T2 name);
void showPerson();
int m_Age;
string m_Name;
private:
};
template<class T1,class T2>
Person<T1,T2>::Person(T1 age, T2 name)
{
m_Age = age;
m_Name = name;
}
template<class T1, class T2>
void Person<T1,T2>::showPerson()
{
cout << "姓名:" << this->m_Name
<< "年龄: " << this->m_Age << endl;
}
void test01()
{
Person<int, string>p(18, "啊啊");
p.showPerson();
}
int main()
{
test01();
}
类模板分文件编写

类模板和友元

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
template<class T1, class T2>
class Person;
template <class T1, class T2>
void printPerson(Person<T1, T2>p)
{
cout << "类外实现" << p.m_Age << endl;
}
template <class T1, class T2>
class Person
{
//全局函数 雷内实现
friend void showPerson(Person<T1,T2>p)
{
cout << p.m_Age << " " << p.m_Name << endl;
}
friend void printPerson<>(Person<T1, T2>p);
public:
Person(T1 name, T2 age)
{
this->m_Age = age;
this->m_Name = name;
}
T1 m_Name;
T2 m_Age;
};
void test01()
{
Person<string, int>p("ada", 15);
showPerson(p);
}
void test02()
{
Person<string, int>p("asd", 23);
printPerson(p);
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}






















 1672
1672











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








