一、数据的准备
1.1创建数据表
--创建"京东"数据库
create database jing_dong charset=utf8;
--使用“京东”数据库
use jing_dong;
--创建一个商品goods数据表
create table goods(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null,
name varchar(150) not null,
cate_name varchar(40) not null,
brand_name varchar(40) not null,
price decimal(10,3) not null default 0,
is_show bit not null default 1,
is_saleoff bit not null default 0
);
1.2插入数据
--向goods中插入数据
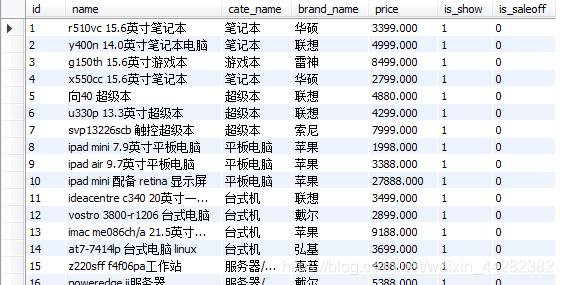
insert into goods values(0,'r510vc 15.6英寸笔记本','笔记本','华硕','3399',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'y400n 14.0英寸笔记本电脑','笔记本','联想','4999',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'g150th 15.6英寸游戏本','游戏本','雷神','8499',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'x550cc 15.6英寸笔记本','笔记本','华硕','2799',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'x240 超级本','超级本','联想','4880',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'u330p 13.3英寸超级本','超级本','联想','4299',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'svp13226scb 触控超级本','超级本','索尼','7999',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'ipad mini 7.9英寸平板电脑','平板电脑','苹果','1998',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'ipad air 9.7英寸平板电脑','平板电脑','苹果','3388',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'ipad mini 配备 retina 显示屏','平板电脑','苹果','27888',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'ideacentre c340 20英寸一体电脑','台式机','联想','3499',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'vostro 3800-r1206 台式电脑','台式机','戴尔','2899',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'imac me086ch/a 21.5英寸一体电脑','台式机','苹果','9188',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'at7-7414lp 台式电脑 linux','台式机','弘基','3699',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'z220sff f4f06pa工作站','服务器/工作站','惠普','4288',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'poweredge ii服务器','服务器/工作站','戴尔','5388',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'mac pro专业级台式电脑','服务器/工作站','苹果','28888',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'hmz-t3w 头戴式显示设备','笔记本配件','索尼','6999',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'商务双肩背包','笔记本配件','索尼','99',default,default);
insert into goods values(0,'x3250 m4机架式服务器','服务器/工作站','ibm','6888',default,default);
二、sql演练
2.1语句强化
1.查询类型cate_name为‘超级本’的商品名称、价格
2.显示商品种类
3.求所有电脑产品的平均价格,并保留两位小数
4.显示每种商品的平均价格
5.查询每种类型的商品中 最贵、最便宜、平均价、数量
6.查询所有价格大于平均价格的商品,并且按降序排列
7.查询每种类型中最贵的电脑信息
更多mysql练习
#1.查询类型cate_name为‘超级本’的商品名称、价格
select name as 商品名称,price as 商品价格 from goods
where cate_name="超级本";
#2.显示商品种类,下面两种都可以
select distinct cate_name from goods;
select cate_name from goods group by cate_name;
#3.求所有电脑产品的平均价格,并保留两位小数
select round(avg(price),2) from goods;
#4.显示每种类型商品的平均价格
select cate_name,avg(price) from goods group by cate_name;
#5.查询每种类型的商品中 最贵、最便宜、平均价、数量
select cate_name,max(price),min(price),avg(price),count(*) from goods group by cate_name;
#6.查询所有价格大于平均价格的商品,并且按降序排列
select name,price from goods
where price>(select round(avg(price),2) from goods)
order by price desc;
#7.查询每种类型中最贵的电脑信息
select g_new.cate_name,g.name,g.price
from (select cate_name,max(price) as max_price from goods group by cate_name) as g_new
left join goods as g
on g_new.cate_name=g.cate_name and g_new.max_price=g.price ;
2.2创建商品表
-创建商品分类表,!!如果不存在才可以建
create table if not exists goods_cates(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(40) not null
);
--查询商品表中的商品的种类
select cate_name from goods group by cate_name;
--将商品的种类插入新表中
insert into goods_cates (name) select cate_name from goods group by cate_name;
2.3同步表数据
update goods as g inner join goods_cates as c on g.cate_name=c.name set g.cate_name=c.id;
2.4创建“商品品牌表”表
CREATE TABLE `goods_brands` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(40) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=10 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
2.5 同步品牌表数据
update goods as g inner join goods_brands as b on g.brand_name=b.name set g.brand_name=b.id;
2.6修改表结构
- 查看goods数据表结构,会发现cate_name和brand_name对应的类型为 varchar 但是存储的都是数字
- 通过alter table语句修改表结构
desc goods;
alter table goods
change cate_name cate_id int unsigned not null,
change brand_name brand_id int unsigned not null;
2.7 外键
三、python与数据库交互
下面是使用python 访问数据库流程图
#第一步,链接数据库
conn = connect(host=‘localhost’,port=3306,user=‘root’,password=‘1111’,database=‘jing_dong’,charset=‘utf8’)
#第二步,获取游标对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
#第三步,通过execute执行SQL语句,进行增删改查
cursor.execute(“select * from goods;”)
#如果是个查询语句,她就在这个游标对象中存着
#以下三条是逐一取出
#查询一行数据,返回的是元组
line_content = cursor.fetchone()
#查询几行数据,返回的是元组套元组
lines = cursor.fetchmany(3)
#取出剩余的所有数据
line_all =cursor.fetchmany()
#第四步,关闭游标,关闭链接
cursor.close()
conn.close()
3.1 查询模板
import pymysql
def main():
#创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='root',password='****',database='jing_dong',charset='utf8')
#获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor()
#执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询一条数据
count = cs1.execute('select id,name from goods where id>=4')
#打印受影响的行数
print("查询到%d条数据:"%count)
for i in range(count):
#获取查询的结果
result = cs1.fetchone()
#打印查询的结果
print(result)
#获取查询的结果
#关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
conn.close()
__name__=='__main__'
main()
补充:
游标:游标是系统为用户开设的一个数据缓冲区,存放SQL语句的执行结果。
用户可以用SQL语句逐一从游标中获取记录,并赋值给主变量,交由python进一步处理,一组主变量一次只能存放一条记录。
-
仅使用主变量并不能完全满足SQL语句向应用程序输出数据的要求
-
游标和游标的优点:在数据库中,游标是一个十分重要的概念。游标提供了一种从表中检索出的数据进行操作的灵活手段,就本质而言,游标实际上是一种能从包括多条数据记录的结果集中每次提取一条记录的机制。游标总是与一条SQL选择语句相关联因为游标由结果集(可以是零条,一条或由相关的选择语句检索出的多条记录)和结果集中指向特定记录的游标位置组成。当决定对结果进行处理时,必须声明一个指向该结果的游标。
3.1.1京东商城查询实战
from pymysql import connect
class JD(object):
def __init__(self):
#创建Connection连接
self.conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='root',password='1111',database='jing_dong',charset='utf8')
#获得Cursor对象
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor()
def __del__(self):
#关闭Cursor对象
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close()
def execute_sql(self,sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
for temp in self.cursor.fetchall():
print(temp)
def show_all_items(self):
"""显示所有商品"""
sql = "select * from goods;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
def show_cates(self):
sql = "select name from goods_cates;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
def show_brands(self):
sql = "select name from goods_brands;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
@staticmethod
def print_menu():
print("-----京东-----")
print("1:所有的商品")
print("2:所有的商品分类")
print("1:所有的商品品牌分类")
return input("请输入功能对应的序号:")
def run(self):
while True:
num = self.print_menu()
if num == "1":
#查询所有的商品
self.show_all_items()
elif num =="2":
#查询分类
self.show_cates()
elif num =="3":
#查询品牌分类
self.show_brands()
else:
print("输入有误,重新输入.....")
def main():
#1.创建一个京东商城对象
jd = JD()
#2.调用这个函数的run方法,让其运行
jd.run()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
3.2增、删、改模板
import pymysql
def main():
#创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='root',password='****',database='jing_dong',charset='utf8')
#获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor()
#执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:添加一条数据
count = cs1.execute('insent into goods_cates(name) values("硬盘")')
#打印受影响的行数
print(count)
count = cs1.execute('insent into goods_cates(name) values("光盘")')
print(count)
##更新
# count = cs1.execute('upset goods_cate set name="机械键盘" where name="硬盘"')
##删除
# count = cs1.execute('delete from goods_cates where id=6')
**提交之前的操作,如果之前已经执行过多次execute,那么就都进行提交**
conn.commit()
#关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
conn.close()
__name__=='__main__'
main()
- 注比查询多一个conn.commit()的过程,如果操作的需要重新提交,可以用conn.rollback()进行回滚






















 216
216











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








