文章目录
lamda接口语法
lamda表达式本质:作为接口的一个实例
内置函数式接口
| 函数式接口 | 参数类型 | 返回类型 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer<T,> | T | void | void accept(T t) |
| Supplier<T ,> | 无 | T | T get() |
| Function<T,R > | T | R | R accept(T t) |
| Predicate<T, > | T | boolean | boolean test(T t) |
| BiFunction<T,U,R > | T,R | U | R apply(T t,U u) |
| UnaryOperator<T, > | T | T | T apply(T t) |
| BinaryOperator<T, > | T,T | T | T apply(T t1,T t2) |
| BiConsumer<T, U> | T,U | void | void accept(T t,U u) |
| BiPredicate<T, U> | T,U | boolean | boolean test(T t,U u) |
| ToIntFunction<T,> | T | int | 计算int值 |
| ToLongFunction<T,> | T | long | 计算long值 |
| ToDoubleFunction<T,> | T | double | 计算double值 |
| IntFunction<R,> | int | R | 为int计算 返回R类型 |
| LongFunction<R,> | long | R | 为long计算 返回R类型 |
| DoubleFunction<R,> | double | R | 为double计算 返回R类型 |
方法引用
语法
- 对象::非静态方法
- 类::静态方法
- 类::非静态方法
使用要求
- 当要传递给Lambda表达式体的操作,已经有实现的方法了,可以使用
- (对象::非静态方法)(类::静态方法)这两种情况接口中的抽象方法要和已实现的方法的形参列表和返回值类型都相同
//对象::方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
// void accept(T t)
Consumer<String> consumer = str-> System.out.println(str);
//System.out = PrintStream 对象
// void println (String x)
Consumer<String> consumer2 = System.out::println;
}
//类::静态方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int compare(T o1, T o2);
//就一行可以隐藏return 和大括号
//Comparator<Integer> com = (x,y)-> {return Integer.compare(x,y);};
Comparator<Integer> com = (x,y)-> Integer.compare(x,y);
//int compare(int x, int y)
Comparator<Integer> com1 = Integer::compare;
}
//类::实例方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
BiPredicate<String,String> predicate = (x,y)->x.equals(y);
//两个参数。第一个参数作为被调用的对象,第二个对象为方法的传参
BiPredicate<String,String> predicate1 = String::equals;
//R accept(T t) 传入Dog 对象 返回String
Function<Dog,String> f = x-> x.getName();
//因为getName不需要参数
Function<Dog,String> f2 = Dog::getName;
}
class Dog {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
构造器引用以及数组引用
构造器引用
- 语法 类::new
public class test {
//构造器引用(主要看接口的抽象方法和哪个构造方法相同)
public static void main(String[] args) {
//无参构造(根据Supplier接口,无参。自动匹配到无参构造函数)
Supplier<Dog> supplier = ()-> new Dog();
Dog dog = supplier.get();
Supplier<Dog> supplier1 = Dog::new;
Dog dog1 = supplier1.get();
//一个参数构造器(Function需要一个参数,匹配到一个参数对应类型的构造方法)
Function<String,Dog> f = name-> new Dog(name);
Dog ck = f.apply("ck");
Function<String,Dog> f1 = Dog::new;
Dog ck1 = f1.apply("ck");
//多个构造参数(匹配到多个参数)
BiFunction<String,Integer,Dog > biFunction = (name,age)->new Dog(name,age);
Dog ck2 = biFunction.apply("ck", 100);
BiFunction<String,Integer,Dog > biFunction1 = Dog::new;
Dog ck3= biFunction1.apply("ck", 100);
}
static class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Dog(){};
public Dog(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Dog(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
}
数组引用
- 语法 String[]::new
Function<Integer,String[]> f = leng-> new String[leng];
String[] apply = f.apply(10);
Function<Integer,String[]> f1 = String[]::new;
f1.apply(10);
Stream流
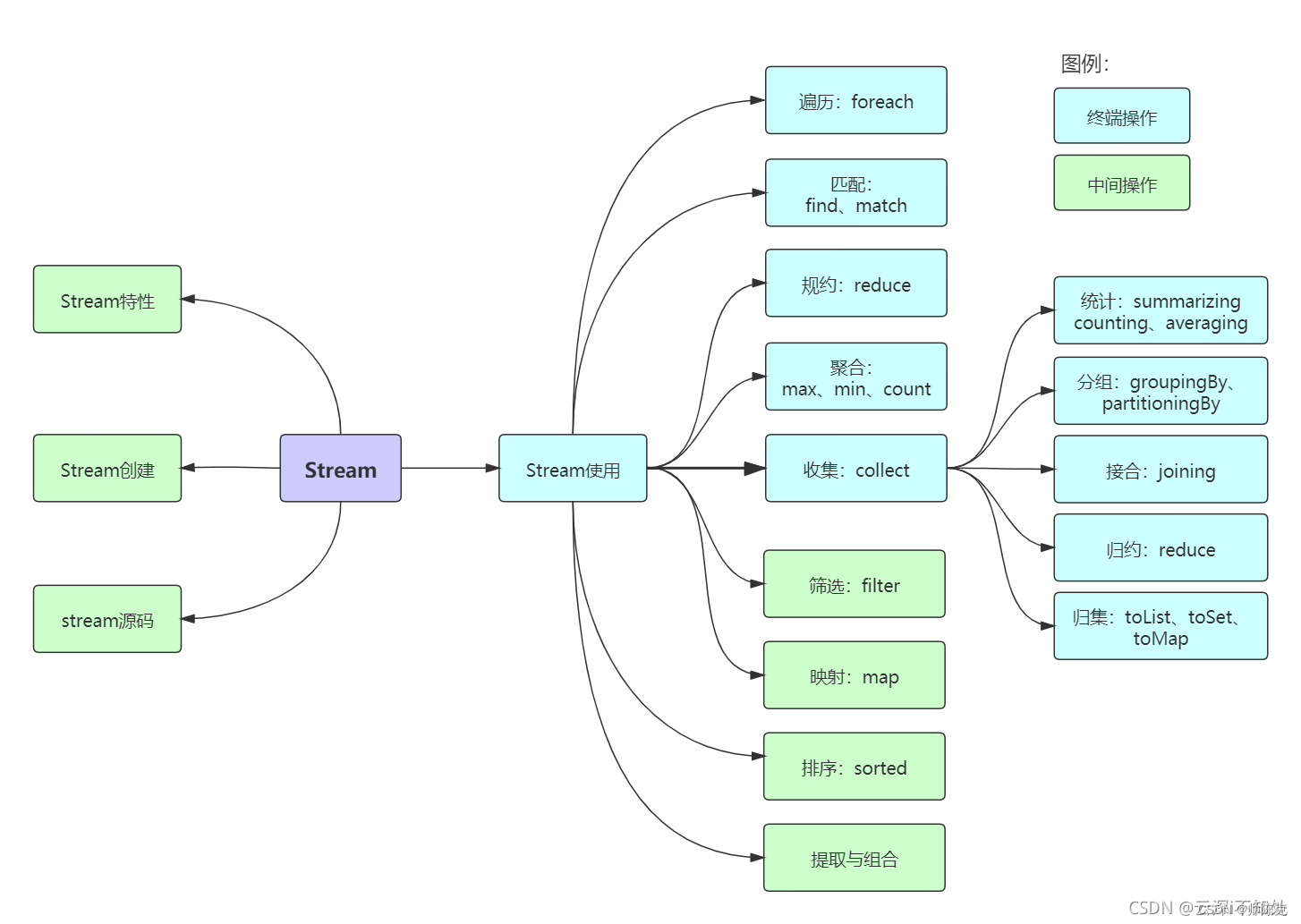
串行流和并行流
list.stream();//串行流,俺顺序遍历
list.parallelStream();//并行流,多线程随机获取值
创建Stream流的四种方式
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.集合
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream();
//2.数组
int[] array = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
long[] array1 = {1L,2L,3L,4L,5L,6L,7L};
double[] array2 = {1.1,2.1,3.1,4.1,5.1,6.1,7.1};
Integer[] array3 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
//对应的Int long double 返回 IntStream,LongStream,DoubleStream,只有这三个基本数据类型
IntStream stream1 = Arrays.stream(array);
LongStream stream2 = Arrays.stream(array1);
DoubleStream stream3 = Arrays.stream(array2);
Stream<Integer> stream4 = Arrays.stream(array3);//对象
//3. Stream.of
Stream<Integer> integerStream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
//4. 无限流,用来造数据
// public static<T> Stream<T> iterate(final T seed, final UnaryOperator<T> f)
//UnaryOperator 参数T 返回值T
Stream.iterate("s",x->x+"s").limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
Stream.iterate(1,x->x+2).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);//1,3,5,7...19
//public static<T> Stream<T> generate(Supplier<? extends T> s)
//Supplier =》 T get();
Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); //随机十个数
}
流的形式
- 带泛型的流 Stream<T,>
- 基本类型流 IntStream,LongStream,DoubleStream
| 流 | 简述 |
|---|---|
| Stream<T,> | collect提供了便捷的Collectors快速收集,没有求和平均值的终端操作,但是在Collectors中有提供对应的方法,求最大最小要提供比较器,提供了方法可以转换成基本类型流 |
| IntStream,LongStream,DoubleStream | collect只能使用三个参数来自己定义如何收集,有求和,平均值等终端操作,最大最小不用提供比较器,提供了装箱方法转换成泛型形式的流 |
中间操作
惰性处理,中间操作只有在终端操作时一次性执行。
筛选和切片
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| filter(Predicate p) | 接受lambda(boolean test(T t)),排除某些元素 |
| distinct() | 筛选,通过流元素的hashCode()和equals()去重 |
| limit(long n) | 截断流,取前n个 |
| skip(long n) | 跳过前n个元素,不足则返回一个空流 |
映射
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| map(Function f) | 接受lambda(R apply(T t)),对每一个元素进行操作,返回的R没指定,可以是任意元素 |
| mapToDouble(ToDoubleFunction f) | 接受lambda(double applyAsDouble(T value)),对每一个元素进行操作 |
| mapToInt(ToIntFunction f) | 接受lambda(int applyAsInt(T value))同上 |
| mapToLong(ToLongFunction f) | 接受lambda(long applyAsLong(T value))同上 |
| flatMap(Function f) | 接受lambda(Function<T, ? extends Stream>)将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后将所有流连成一个流 |
flatMap的使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
//flatMap使用例子
String[] strings = {"Hello","world"};
//输出Helloworld
//1. x->x.split("") 得到两个String[]数组 {"H","e","l","l","o"},{"w","o","r","l","d"}
//2. flatMap(x->Arrays.stream(x)) 将每个数组又转换成两个流 {"H","e","l","l","o"}流,{"w","o","r","l","d"}流
//3. 最后两个流合并 {"H","e","l","l","o","w","o","r","l","d"}
Arrays.stream(strings).map(x->x.split("")).flatMap(x->Arrays.stream(x)).forEach(System.out::print);
}
参考:flatMap的使用
排序
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| sorted() | 产生一个新流,其中按自然顺序排序 |
| sorted(Comparator com) | 产生一个新流,其中按比较器排序 |
sorted() 排序的类要实现Comparable接口,不然报错
终止操作
匹配与查找
Predicate =》boolean test(T t)
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| allMatch(Predicate p) | 检查是否匹配所有元素 |
| allMatch(Predicate p) | 检查是否至少匹配一个元素 |
| allMatch(Predicate p) | 检查是否没有匹配所有元素 |
| findFirst() | 返回第一个元素 |
| findAny() | 返回任意元素 |
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] strings = {1,4,5,6,7,2,3};
boolean a = Arrays.stream(strings).allMatch(x -> x < 0); //是否有所元素都小于0 false
boolean b = Arrays.stream(strings).anyMatch(x -> x < 0); //是否任意一个元素小于0 false
boolean c = Arrays.stream(strings).noneMatch(x -> x < 0);//是否所有元素都不小于0 true
Optional<Integer> any = Arrays.stream(strings).findAny();//Optional 里面是1
Optional<Integer> first = Arrays.stream(strings).findFirst();//Optional 里面是随机一个数
}
规约
BinaryOperator =>T apply(T t1, T t2)
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| T reduce(T iden,BinaryOperator b) | 可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值返回T,iden为任意对象作为初始对象 |
| Optional<T,> reduce(BinaryOperator<T,> accumulator) | 可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值返回Optional<T,>,没有初始对象 |
| U reduce(U identity,BiFunction<U, ? super T, U> accumulator,BinaryOperator<U,> combiner); | 可以将流中元素反复结合起来,第三个参数为并行流才生效,表示并行流合并时的操作 |
备注:经常和map合用
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] strings = {1,4,5,6,7,2,3};
Integer reduce = Arrays.stream(strings).reduce(6, (x, y) -> x + y); //34
Optional<Integer> reduce2 = Arrays.stream(strings).reduce((x, y) -> x + y); //28
//对象使用 求dog的age总和
ArrayList<Dog> dogs = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
dogs.add(new Dog(i+50));
}
Integer reduce3 = dogs.stream().map(x -> x.getAge()).reduce(0, (x, y) -> x + y);//260
Dog reduce1 = dogs.stream().reduce(new Dog(50), (x, y) -> new Dog(x.getAge() + y.getAge()));//dog对象 其中age=310
Optional<Dog> reduce4 = dogs.stream().reduce((x, y) -> new Dog(x.getAge() + y.getAge()));//Optional对象
}
static class Dog
{
private Integer age;
public Dog(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
收集
将得到的流收集成对应的类型
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| collect(Collector c) | 将流转换为其他形式,接受一个Collector接口的实现,用于给Stream中元素做汇总的方法(只存在Stream类型中,基本类型IntStream,LongStream,DoubleStream没有这个) |
| collect(Supplier<R,> supplier,ObjIntConsumer<R,> accumulator,BiConsumer<R, R> combiner) | 根据一定规则收集(IntStream,LongStream,DoubleStream) |
| collect(Supplier<R,> supplier,BiConsumer<R, ? super T> accumulator,BiConsumer<R, R> combiner) | 根据一定规则收集(Stream) |
Collectors 类提供了很多静态方法:
方法以及例子
按规则收集例子:
- 第一个参数:Supplier<R.> supplier 代表用什么东西收集 返回值确定类型R
- 第二个参数: BiConsumer<R, ? super T> 代表要如何处理一个个的元素。 R类型已由第一个参数确定,T为收集到的元素。
- 第三个参数:BiConsumer<R, R> 代表要怎么整合前面处理好的一个个元素
- 先创建一个容器,然后流中的每个元素如何存进这个容器,流中的每一个元素都会有一个容器,最后所有的容器如何整合起来
int[] a = {1,23,4,5,6,7,8};
//collect2 等价于 collect2_1
HashMap collect2 = Arrays.stream(a).collect(() -> new HashMap(), (x, y) -> x.put(y, y), (x, y) -> x.putAll(y));
HashMap collect2_1 = Arrays.stream(a).collect(HashMap::new, (x, y) -> x.put(y, y), HashMap::putAll);
//collect3 等价于 collect3_1
ArrayList collect3 = Arrays.stream(a).collect(() -> new ArrayList(), (x, y) -> x.add(y, y), (x, y) -> x.addAll(y));
ArrayList collect3_1 = Arrays.stream(a).collect(ArrayList::new, (x, y) -> x.add(y, y), ArrayList::addAll);
Optional类
创建Optional类对象的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Optional.of(T t) | 创建一个Optional实例,t必须为非空 |
| Optional.empty() | 创建一个空的Optional实例 |
| Optional.ofNullable(T t) | 创建一个Optional实例,t可以为空 |
判断Optional容器中是否够包含对象
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| boolean isPresent() | 判断是否包含对象 |
| void ifPresent(Consumer<? super T> action) | 不为空,执行Consumer接口(void apply(T))的实现,参数为该值 |
| void ifPresentOrElse(Consumer<? super T> action, Runnable emptyAction) | 不为空,执行Consumer接口(void apply(T))的实现,参数为该值。否则执行Runnable(void run() 无参无返回) 的实现 |
获取Optional容器中的对象
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| T get() | 获取对象,空的话报异常(throw new NoSuchElementException(“No value present”);) |
| T orElse(T other) | 如果有值将其返回,没有值返回other,但是不管有没有值都会执行other |
| T orElseGet(Supplier<? extends T> supplier(无参返回T)) | 如果有值将其返回,没有值返回other,只有在为空时才会执行supplier |
| T orElseThrow() | 如果有值将其返回,没有值抛出默认异常(throw new NoSuchElementException(“No value present”);) |
| T orElseThrow(Supplier<? extends X> exceptionSupplier (无参返回X)) | 如果有值将其返回,没有值抛出由Supplier中方法抛出的异常 |





















 1886
1886











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








